Kirigami-style fabrication may enable new 3D nanostructures
2021-04-02
(Press-News.org) A new technique that mimics the ancient Japanese art of kirigami may offer an easier way to fabricate complex 3D nanostructures for use in electronics, manufacturing and health care.
Kirigami enhances the Japanese artform of origami, which involves folding paper to create 3D structural designs, by strategically incorporating cuts to the paper prior to folding. The method enables artists to create sophisticated three-dimensional structures more easily.
"We used kirigami at the nanoscale to create complex 3D nanostructures," said Daniel Lopez, Penn State Liang Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, and leader of the team that published this research in Advanced Materials. "These 3D structures are difficult to fabricate because current nanofabrication processes are based on the technology used to fabricate microelectronics which only use planar, or flat, films. Without kirigami techniques, complex three-dimensional structures would be much more complicated to fabricate or simply impossible to make."
Lopez said that if force is applied to a uniform structural film, nothing really happens other than stretching it a bit, like what happens when a piece of paper is stretched. But when cuts are introduced to the film, and forces are applied in a certain direction, a structure pops up, similar to when a kirigami artist applies force to a cut paper. The geometry of the planar pattern of cuts determines the shape of the 3D architecture.
"We demonstrated that it is possible to use conventional planar fabrication methods to create different 3D nanostructures from the same 2D cut geometry," Lopez said. "By introducing minimum changes to the dimensions of the cuts in the film, we can drastically change the three-dimensional shape of the pop-up architectures. We demonstrated nanoscale devices that can tilt or change their curvature just by changing the width of the cuts a few nanometers."
This new field of kirigami-style nanoengineering enables the development of machines and structures that can change from one shape to another, or morph, in response to changes in the environment. One example is an electronic component that changes shape in elevated temperatures to enable more air flow within a device to keep it from overheating.
"This kirigami technique will allow the development of adaptive flexible electronics that can be incorporated onto surfaces with complicated topography, such as a sensor resting on the human brain," Lopez said. "We could use these concepts to design sensors and actuators that can change shape and configuration to perform a task more efficiently. Imagine the potential of structures that can change shape with minuscule changes in temperature, illumination or chemical conditions."
Lopez will focus his future research on applying these kirigami techniques to materials that are one atom thick, and thin actuators made of piezoelectrics. These 2D materials open new possibilities for applications of kirigami-induced structures. Lopez said his goal is to work with other researchers at Penn State's Materials Research Institute (MRI) to develop a new generation of miniature machines that are atomically flat and are more responsive to changes in the environment.
"MRI is a world leader in the synthesis and characterization of 2D materials, which are the ultimate thin-films that can be used for kirigami engineering," Lopez said. "Moreover, by incorporating ultra-thin piezo and ferroelectric materials onto kirigami structures, we will develop agile and shape-morphing structures. These shape-morphing micro-machines would be very useful for applications in harsh environments and for drug delivery and health monitoring. I am working at making Penn State and MRI the place where we develop these super-small machines for a specific variety of applications."
INFORMATION:
Other authors on the study include Xu Zhang from Carnegie Mellon University and Haogang Cai from New York University, both former postdoctoral fellows with Lopez. Lior Medina and H. Espinosa from Northwestern University and Vladimir Askyuk from the National Institute of Standards and Technology also are part of the team. The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-02
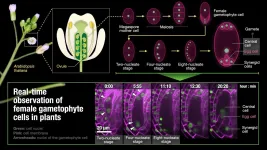
Scientists from Nagoya University, Yokohama City University and Chubu University have developed a system which enables the live imaging of the formation of the female gamete in plants.
In flowering plants, the sperm cell and egg cell meet and fertilization takes place in the flower. While sperm cells are made in the pollen, egg cells are made in the ovule, the structure that becomes the seed. However, as the ovule is buried deep within the pistil, it has thus far been impossible to observe the formation of the egg cell in living plants.
The team, led by Dr Daisuke Kurihara and Dr Tetsuya Higashiyama of Nagoya University Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM), Dr Daichi Susaki of Yokohama City University Kihara Institute for Biological Research ...
2021-04-02
Washington, DC, April 1, 2021 - A study in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (JAACAP), published by Elsevier, reports that middle schoolers from a predominantly Latinx community, with elevated levels of mental health problems, showed a reduction in symptoms during the early stages of the pandemic.
"While the negative impact of the COVID pandemic on mental health is widespread, our study found that COVID-19 stay-at-home measures may have offered some protective effects for youth mental health early in the pandemic," said study coordinator Francesca Penner, MA, University ...
2021-04-02
EUGENE, Ore. -- April 2, 2021 -- Across California's Central Valley, under stress from large-scale agriculture and climate change, native bee species that are flexible in their pollination behavior when around other wild bee populations appear best suited for survival in shrinking habitats.
That's the primary finding of a study published online April 1 in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution.
A research team led by University of Oregon biologist Lauren C. Ponisio
identified 1,150 network interactions involving 157 wild bee species and 152 plant species at 63 sites spread across three counties. The findings emerged from observations of adult bees from 31 species whose pollination activities with at ...
2021-04-02
FINDINGS
A UCLA research team has shown that using a truncated form of the CD4 molecule as part of a gene therapy to combat HIV yielded superior and longer-lasting results in mouse models than previous similar therapies using the CD4 molecule.
This new approach to CAR T gene therapy -- a type of immunotherapy that involves genetically engineering the body's own blood-forming stem cells to create HIV-fighting T cells -- has the potential to not only destroy HIV-infected cells but to create "memory cells" that could provide lifelong protection from infection with the virus that causes AIDS.
BACKGROUND
CAR therapies have emerged as a powerful immunotherapy for various forms of cancer and show promise ...
2021-04-02
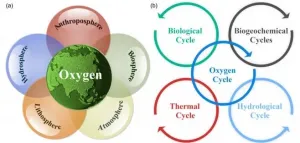
As an essential material for the survival and reproduction of almost all aerobic organisms, oxygen is closely related to the formation and development of complex organisms. A recent review provides a systematic overview of the latest advances in the oxygen cycle at different spatial and temporal scales and the important role that oxygen plays in shaping our current habitable Earth.
Professor Jianping Huang from Lanzhou University is the corresponding author of the review entitled "The oxygen cycle and a habitable Earth", which is the cover article of the 64(4) of SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences in 2021.
Based ...
2021-04-02
BOSTON - In the first study to use whole genome sequencing (WGS) to discover rare genomic variants associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD), researchers have identified 13 such variants (or mutations). In another novel finding, this study establishes new genetic links between AD and the function of synapses, which are the junctions that transmit information between neurons, and neuroplasticity, or the ability of neurons to reorganize the brain's neural network. These discoveries could help guide development of new therapies for this devastating neurological condition. Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center report these findings in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
Over ...
2021-04-02
Bottom Line: Among patients at high risk of melanoma, those who received routine skin cancer screening and education about skin self-exams were significantly more likely to be diagnosed with thinner and earlier stage melanomas.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Michael Sargen, MD, a dermatologist and clinical fellow in the Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics at the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH)
Background: "Whole-body screening for melanoma is currently routine for individuals at high ...
2021-04-02
The Tibet ASγ experiment, a China-Japan joint research project on cosmic-ray observation, has discovered ultra-high-energy diffuse gamma rays from the Milky Way galaxy. The highest energy detected is estimated to be unprecedentedly high, nearly 1 Peta electronvolts (PeV, or one million billion eV).
Surprisingly, these gamma rays do not point back to known high-energy gamma-ray sources, but are spread out across the Milky Way (see Fig.1).
Scientists believe these gamma rays are produced by the nuclear interaction between cosmic rays escaping from the most powerful galactic sources ...
2021-04-02
A dangerous toxin has been witnessed - for the first time - releasing into the air from pond scum, research published in the peer-reviewed journal Lake and Reservoir Management today shows.
Not only is pond scum - otherwise known as algal bloom - an unsightly formation which can occur on still water across the world, it can also prove dangerous to wildlife and humans.
For the first time, scientists have now detected the presence of the algal toxin anatoxin-a (ATX)which is also known as 'Very Fast Death Factor', in the air near a Massachusetts pond with large algal blooms.
ATX can cause a range of symptoms at acute doses, including loss of coordination, muscular twitching and respiratory paralysis, and has been linked to the deaths of livestock, waterfowl and dogs from ...
2021-04-02
Researchers from University of Queensland, University of Melbourne, and Universidad Finis Terrae published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that studies consumer resistance to a nationwide plastic bag ban implemented in Chile in 2019.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "How Do I Carry All This Now?': Understanding Consumer Resistance to Sustainability Interventions" and is authored by Claudia Gonzalez-Arcos, Alison M. Joubert, Daiane Scaraboto, and Jörgen Sandberg.
As environmental crisis challenges accelerate, governments are searching for solutions to reduce the negative impacts of economic activity. One popular measure has been to ban disposable plastic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Kirigami-style fabrication may enable new 3D nanostructures