INFORMATION:
See the article: Zhai LM, Zhang B*, Liang HJ, Wu HB, Yang XC, LuoG, Zhao SC, Qin Y. The selective deposition of Fe species inside ZSM-5 for the oxidation of cyclohexane to cyclohexanone. Sci. China Chem., 2021, DOI:10.1007/s11426-020-9968-x.
http://engine.scichina.com/doi/10.1007/s11426-020-9968-x.
Depositing Fe species inside ZSM-5 to oxidize cyclohexane to cyclohexanone
2021-04-02
(Press-News.org) The directly catalytic oxidation of alkanes has high atomic economy and application value to form corresponding chemical organic products such as alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acid. It is challenging to achieve efficient and selective oxidation of alkane under mild conditions due to the inert C-H bonds of alkanes.
Many researchers have developed a series of supported iron based catalysts to simulate the alkane biological monooxygenase with iron center atoms. However, traditional methods, such as impregnation method, ion exchange method, etc., are difficult to control the dispersion and the deposition position of iron species on the catalyst support.
Generally, iron species can easily replace the H+ of Brønsted acid sites to reduce the number of Brønsted acid sites, and many types of iron species will be formed on other different potential sites of ZSM-5 (Lewis acid sites and defect sites, etc.). The coexistence of multiple active centers on the catalyst is one of the main reasons for the low selectivity.
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is an advanced thin film technology by single-layer chemisorption and reaction of vapor precursors on the surface of substrates with atomic and molecular control precision.
Recently, Dr. Bin Zhang and colleagues in the Institute of Coal Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, report a general strategy to selectively deposit high-dispersed Fe species into the micropores of ZSM-5 to prepare FeOx/ZSM-5 catalysts.
The obtained FeOx/ZSM-5 catalysts perform high selectivity of cyclohexanone (92%-97%), and the catalyst activity is significantly higher than those of the iron-based catalysts reported in the literature. Ferrocene (Fe(Cp)2) is used as a precursor for the deposition since its kinetic diameter is smaller than the pore size of ZSM-5. The framework of ZSM-5 and the Brønsted acid sites are intact during ALD, and the Fe species are selectively deposited onto the defect and Lewis acid sites of ZSM-5. The loading, size and surface electronic state of FeOx species can be precisely controlled by merely changing ALD cycles. The Fe content in the FeOx/ZSM-5 catalyst increases linearly with the increase of ALD cycles. Fe-O-Si bonds are dominantly formed over FeOx/ZSM-5 with a low loading of Fe, while FeOx nanoparticles are generated at a high Fe loading. Compared with the FeOx nanoparticles, the Fe-O-Si species performs higher turnover frequency and stability in the oxidation reaction.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists turn to deep learning to improve air quality forecasts
2021-04-02
Air pollution from the burning of fossil fuels impacts human health but predicting pollution levels at a given time and place remains challenging, according to a team of scientists who are turning to deep learning to improve air quality estimates. Results of the team's study could be helpful for modelers examining how economic factors like industrial productivity and health factors like hospitalizations change with pollution levels.
"Air quality is one of the major issues within an urban area that affects people's lives," said Manzhu Yu, assistant professor of geography at Penn State. "Yet existing observations are not adequate to provide comprehensive information that may help vulnerable populations ...
Kirigami-style fabrication may enable new 3D nanostructures
2021-04-02
A new technique that mimics the ancient Japanese art of kirigami may offer an easier way to fabricate complex 3D nanostructures for use in electronics, manufacturing and health care.
Kirigami enhances the Japanese artform of origami, which involves folding paper to create 3D structural designs, by strategically incorporating cuts to the paper prior to folding. The method enables artists to create sophisticated three-dimensional structures more easily.
"We used kirigami at the nanoscale to create complex 3D nanostructures," said Daniel Lopez, Penn State ...
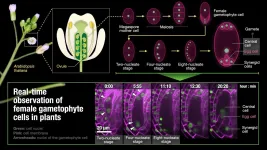
Realtime imaging of female gamete formation in plants
2021-04-02
Scientists from Nagoya University, Yokohama City University and Chubu University have developed a system which enables the live imaging of the formation of the female gamete in plants.
In flowering plants, the sperm cell and egg cell meet and fertilization takes place in the flower. While sperm cells are made in the pollen, egg cells are made in the ovule, the structure that becomes the seed. However, as the ovule is buried deep within the pistil, it has thus far been impossible to observe the formation of the egg cell in living plants.
The team, led by Dr Daisuke Kurihara and Dr Tetsuya Higashiyama of Nagoya University Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM), Dr Daichi Susaki of Yokohama City University Kihara Institute for Biological Research ...
Middle schoolers with elevated levels of mental health problems pre-pandemic showed reduction in symptoms during the early stages of the pandemic
2021-04-02
Washington, DC, April 1, 2021 - A study in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (JAACAP), published by Elsevier, reports that middle schoolers from a predominantly Latinx community, with elevated levels of mental health problems, showed a reduction in symptoms during the early stages of the pandemic.
"While the negative impact of the COVID pandemic on mental health is widespread, our study found that COVID-19 stay-at-home measures may have offered some protective effects for youth mental health early in the pandemic," said study coordinator Francesca Penner, MA, University ...
Adjusting interactions help some California's wild bee populations survive
2021-04-02
EUGENE, Ore. -- April 2, 2021 -- Across California's Central Valley, under stress from large-scale agriculture and climate change, native bee species that are flexible in their pollination behavior when around other wild bee populations appear best suited for survival in shrinking habitats.
That's the primary finding of a study published online April 1 in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution.
A research team led by University of Oregon biologist Lauren C. Ponisio
identified 1,150 network interactions involving 157 wild bee species and 152 plant species at 63 sites spread across three counties. The findings emerged from observations of adult bees from 31 species whose pollination activities with at ...
Researchers devise more efficient, enduring CAR gene therapy to combat HIV
2021-04-02
FINDINGS
A UCLA research team has shown that using a truncated form of the CD4 molecule as part of a gene therapy to combat HIV yielded superior and longer-lasting results in mouse models than previous similar therapies using the CD4 molecule.
This new approach to CAR T gene therapy -- a type of immunotherapy that involves genetically engineering the body's own blood-forming stem cells to create HIV-fighting T cells -- has the potential to not only destroy HIV-infected cells but to create "memory cells" that could provide lifelong protection from infection with the virus that causes AIDS.
BACKGROUND
CAR therapies have emerged as a powerful immunotherapy for various forms of cancer and show promise ...
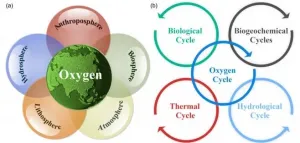
Exploring the evolution of Earth's habitability regulated by oxygen cycle
2021-04-02
As an essential material for the survival and reproduction of almost all aerobic organisms, oxygen is closely related to the formation and development of complex organisms. A recent review provides a systematic overview of the latest advances in the oxygen cycle at different spatial and temporal scales and the important role that oxygen plays in shaping our current habitable Earth.
Professor Jianping Huang from Lanzhou University is the corresponding author of the review entitled "The oxygen cycle and a habitable Earth", which is the cover article of the 64(4) of SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences in 2021.
Based ...
Thirteen new Alzheimer's genes identified in first-of-its-kind human genome study
2021-04-02
BOSTON - In the first study to use whole genome sequencing (WGS) to discover rare genomic variants associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD), researchers have identified 13 such variants (or mutations). In another novel finding, this study establishes new genetic links between AD and the function of synapses, which are the junctions that transmit information between neurons, and neuroplasticity, or the ability of neurons to reorganize the brain's neural network. These discoveries could help guide development of new therapies for this devastating neurological condition. Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center report these findings in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
Over ...
Whole-body screening and ed. in melanoma-prone families may improve early detection rates
2021-04-02
Bottom Line: Among patients at high risk of melanoma, those who received routine skin cancer screening and education about skin self-exams were significantly more likely to be diagnosed with thinner and earlier stage melanomas.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Michael Sargen, MD, a dermatologist and clinical fellow in the Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics at the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH)
Background: "Whole-body screening for melanoma is currently routine for individuals at high ...
Evidence for PeVatrons, the Milky Way's most powerful particle accelerators
2021-04-02
The Tibet ASγ experiment, a China-Japan joint research project on cosmic-ray observation, has discovered ultra-high-energy diffuse gamma rays from the Milky Way galaxy. The highest energy detected is estimated to be unprecedentedly high, nearly 1 Peta electronvolts (PeV, or one million billion eV).
Surprisingly, these gamma rays do not point back to known high-energy gamma-ray sources, but are spread out across the Milky Way (see Fig.1).
Scientists believe these gamma rays are produced by the nuclear interaction between cosmic rays escaping from the most powerful galactic sources ...