Criteria for selecting COVID-19 patients for lung lung transplantation
International consortium has already performed more than 40 procedures
2021-04-02
(Press-News.org) In May 2020, a team led by thoracic surgeon Konrad Hoetzenecker of the Department of Surgery of MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital performed a lung transplant on a 44-year-old patient who had been seriously ill with Covid-19, making her the first patient in Europe to receive a lung transplant for this indication. The Vienna lung transplantation programme now plays a leading role in an international consortium comprising experts from the USA, Europe and Asia. Based on the expertise from Vienna, approximately 40 transplants have now been carried out on Covid-19 patients throughout the world. In a study published in the leading journal "The Lancet Respiratory Medicine", the consortium has now proposed the first general selection criteria for lung transplantation in Covid-19 patients.
"We have collated the first experiences in the world of performing lung transplants on Covid-19 patients. It is clear that such a complex intervention should only be considered for patients who, by virtue of their age and good general health, have a good chance of recovery with new lungs," explains Konrad Hoetzenecker, Head of the lung transplantation programme at MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital. The Vienna team performs around 100 lung transplants a year, making it one of the largest programmes in the world, alongside Toronto, Cleveland and Hanover.
Medical guidelines for the world
The following factors were established as criteria for potential transplantation: exhaustion of all conservative treatment options, no recovery of the Covid-19-damaged lungs despite at least four weeks of ventilation/ECMO, evidence of advanced and irreversible lung damage in several consecutive CT scans, age below 65 and no relevant comorbidities. In addition to this, candidates for a lung transplant must be in good physical condition and have a good chance of complete physical rehabilitation following the transplant. "These guidelines can be applied worldwide for making a sound selection of patients who are suitable for a lung transplant following a Covid-19 infection."
The surgical team at MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital has meanwhile carried out twelve lung transplantations on Covid-19 patients, demonstrating that even the most seriously ill patients, who would otherwise die, can survive with a lung transplant.
Patient No. 1
In March 2020, patient number one suffered total pulmonary failure as a result of Covid-19, so that artificial ventilation was no longer possible. She could only be kept alive by the circulation pump. At the time of the transplant, the PCR test showed that virus particles were still present but were no longer infectious. The MedUni Vienna/Vienna General Hospital thoracic surgeons and surgical team managed to replace the patient's completely destroyed lungs with new donor lungs.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-02
Russian researchers have developed an inexpensive, safe, and reliable packed eggs surface disinfection technology. This technology helps to kill bacteria, including salmonella, on eggshells. Also, it allows growing broiler chickens with strong immunity to viral diseases. Packed eggs are disinfected with 50 nanoseconds (one billionth of a second) electron beam. Disinfection takes place in plastic containers. The description of the technology was published in Food and Bioproducts Processing.
"Disinfection of the packed eggs protects eggs from subsequent contamination during storage", said Sergey Sokovnin, a professor at Ural Federal University and Ural Branch of Russian Academy of Science. "We found out that 5 kGy is enough for disinfection. Such dose allows to ...
2021-04-02
Niigata, Japan - Cancer is the world's second deadliest disease which contributes towards the fatality of over 10 million people per year. Oncologists adopt a variety of treatment procedures to treat cancer cells. Among the different methods used to fight cancer, chemotherapeutic treatment is a prominent and well-adopted technique. It is a drug based method, wherein powerful chemical compounds are injected into the body to annihilate the malignant cells. Although these chemicals support the destruction of the cancerous cells, optimizing their dosage has always been a challenge to the medical ...
2021-04-02
In United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, Number 6, addresses the need for access to clean water and sanitation for all. In the worldwide situation, one in three people do not have access to safe drinking water, and two out of five do not have basic hand-washing facilities with soap and water.
Water quality also address to elements dissolved. In the case of fluoride, controlled amount are recommended for protect tooth, e.g. included in toothpaste. Higher levels can cause fluorosis, interfere in tooth enamel formation, correct growth of the bones, and cause crippling deformities of the spine and joints. The incidence of higher concentrations of fluoride in water is higher in rural areas without ...
2021-04-02
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis (AD), is sometimes called "the itch that rashes." Often, the itch begins before the rash appears, and, in many cases, the itchiness of the skin condition never really goes away. Approximately 9.6 million children and 16.5 million adults in the U.S. have AD, which can have a serious effect on quality of life for patients. Although much has been learned about the uncomfortable sensation that triggers the desire to scratch, many mysteries remain about chronic itch, making it a challenge to treat. A paper by authors from Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School published in The Proceedings ...
2021-04-02
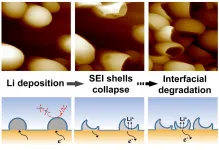
The interfacial decomposition products forming the so-called solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) during the first charging/discharging significantly determine the electrochemical performances of lithium (Li) batteries. To date, the dynamic evolutions, chemical compositions, stabilities and the influencing factors of the SEI films have been captured tremendous attentions.
It's noted that, in contrast to the SEI film formation at the surface of electrodes, a kind of SEI shells usually conformally forms at the outmost layer of the on-site deposited Li once the freshly deposited Li contacts with the electrolyte, which could directly influence Li nucleation, growth behaviors ...
2021-04-02
Purely organic room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) materials have been a hot research topic. Currently, the pure RTP materials have been realized by the introduction of heavy halogen atoms, carbonyls groups or some heteroatoms, hydrogen bonding, H-aggregation, strong intermolecular electronic coupling, molecular packing, host-guest interaction, etc. However, the complicated synthesis and high expenditure are still inevitable in these systems. In addition, their performances in air are not satisfactory and the introduction of halogen atoms is generally necessary. Therefore, a new facile and robust host-guest strategy utilizing only electron-rich materials is a promising alternative for constructing RTP systems.
Very ...
2021-04-02
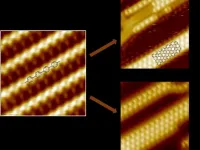
On-surface synthesis has received great attention as a method to create atomically-precise one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) polymers with intriguing properties. In particular, graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), a category of quasi-1D nanomaterials derived from graphene, have been widely studied due to their tunable electronic properties and potential applications in semiconductor devices, such as field-effect transistors and spintronics. A series of top-down approaches have been pursued to produce GNRs, but a lack of control over the ribbon width and edge structure has hindered their further development.
In 2010, Cai et al. firstly reported the fabrication of an atomically-precise armchair GNR (AGNR) on the Au(111) surface using a bottom-up ...
2021-04-02
The directly catalytic oxidation of alkanes has high atomic economy and application value to form corresponding chemical organic products such as alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acid. It is challenging to achieve efficient and selective oxidation of alkane under mild conditions due to the inert C-H bonds of alkanes.
Many researchers have developed a series of supported iron based catalysts to simulate the alkane biological monooxygenase with iron center atoms. However, traditional methods, such as impregnation method, ion exchange method, etc., are ...
2021-04-02
Air pollution from the burning of fossil fuels impacts human health but predicting pollution levels at a given time and place remains challenging, according to a team of scientists who are turning to deep learning to improve air quality estimates. Results of the team's study could be helpful for modelers examining how economic factors like industrial productivity and health factors like hospitalizations change with pollution levels.
"Air quality is one of the major issues within an urban area that affects people's lives," said Manzhu Yu, assistant professor of geography at Penn State. "Yet existing observations are not adequate to provide comprehensive information that may help vulnerable populations ...
2021-04-02
A new technique that mimics the ancient Japanese art of kirigami may offer an easier way to fabricate complex 3D nanostructures for use in electronics, manufacturing and health care.
Kirigami enhances the Japanese artform of origami, which involves folding paper to create 3D structural designs, by strategically incorporating cuts to the paper prior to folding. The method enables artists to create sophisticated three-dimensional structures more easily.
"We used kirigami at the nanoscale to create complex 3D nanostructures," said Daniel Lopez, Penn State ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Criteria for selecting COVID-19 patients for lung lung transplantation
International consortium has already performed more than 40 procedures