Scientists observe role of cavitation in glass fracturing
2021-04-02
(Press-News.org) Glassy materials play an integral role in the modern world, but inherent brittleness has long been the Achilles' heel that severely limits their usefulness. Due to the disordered amorphous structure of glassy materials, many mysteries remain. These include the fracture mechanisms of traditional glasses, such as silicate glasses, as well as the origin of the intriguing patterned fracture morphologies of metallic glasses.
Cavitation has been widely assumed to be the underlying mechanism governing the fracture of metallic glasses, as well as other glassy systems. Up until now, however, scientists have been unable to directly observe the cavitation behavior of fractures, despite their intensive efforts.
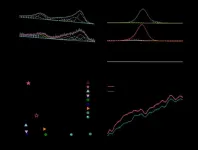
This situation changed with recent work by Dr. SHEN Laiquan, Prof. BAI Haiyang, Prof. SUN Baoan, and others from Prof. WANG Weihua's group at the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), who have successfully observed the effect of cavitation on fracture behavior in glasses. They revealed that crack propagation is dominated by the self-organized nucleation, growth, and coalescence of nanocavities in metallic glasses.
They showed the evolutionary process of crack morphologies from separated nanocavities to wave-like nanocorrugations, and confirmed that cavitation is the origin of periodic fracture surface patterns.
In addition, they found that cavitation-induced nanopatterns are also prevalent in typical polymer glass (polycarbonate) and silicate glass (silica), indicating that the cavitation mechanism is common in the fracture of glasses. Plastic flow exhibited by the cavitation process thus proves that nanoscale ductility is involved in the breakage of nominally brittle glasses.
The discovery of cavitation behavior in the fracture of glasses challenges the traditional concept of how glasses break. The researchers' findings have significant implications for the understanding of the fundamental process of failure in disordered systems, and provides incentives for engineering better glasses.
INFORMATION:
This study, entitled "Observation of cavitation governing fracture in glasses," was published in Science Advances.
The work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program, and the National Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-02
A new study indicates holes the solution to operational speed/coherence trade-off, potential scaling up of qubits to a mini-quantum computer.
Quantum computers are predicted to be much more powerful and functional than today's 'classical' computers.
One way to make a quantum bit is to use the 'spin' of an electron, which can point either up or down. To make quantum computers as fast and power-efficient as possible we would like to operate them using only electric fields, which are applied using ordinary electrodes.
Although spin does not ordinarily 'talk' to electric fields, in some materials spins can interact with electric fields indirectly, and these are some of the hottest materials currently studied ...
2021-04-02
In May 2020, a team led by thoracic surgeon Konrad Hoetzenecker of the Department of Surgery of MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital performed a lung transplant on a 44-year-old patient who had been seriously ill with Covid-19, making her the first patient in Europe to receive a lung transplant for this indication. The Vienna lung transplantation programme now plays a leading role in an international consortium comprising experts from the USA, Europe and Asia. Based on the expertise from Vienna, approximately 40 transplants have now been carried out on Covid-19 patients throughout the world. In a study published in the leading journal ...
2021-04-02
Russian researchers have developed an inexpensive, safe, and reliable packed eggs surface disinfection technology. This technology helps to kill bacteria, including salmonella, on eggshells. Also, it allows growing broiler chickens with strong immunity to viral diseases. Packed eggs are disinfected with 50 nanoseconds (one billionth of a second) electron beam. Disinfection takes place in plastic containers. The description of the technology was published in Food and Bioproducts Processing.
"Disinfection of the packed eggs protects eggs from subsequent contamination during storage", said Sergey Sokovnin, a professor at Ural Federal University and Ural Branch of Russian Academy of Science. "We found out that 5 kGy is enough for disinfection. Such dose allows to ...
2021-04-02
Niigata, Japan - Cancer is the world's second deadliest disease which contributes towards the fatality of over 10 million people per year. Oncologists adopt a variety of treatment procedures to treat cancer cells. Among the different methods used to fight cancer, chemotherapeutic treatment is a prominent and well-adopted technique. It is a drug based method, wherein powerful chemical compounds are injected into the body to annihilate the malignant cells. Although these chemicals support the destruction of the cancerous cells, optimizing their dosage has always been a challenge to the medical ...
2021-04-02
In United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, Number 6, addresses the need for access to clean water and sanitation for all. In the worldwide situation, one in three people do not have access to safe drinking water, and two out of five do not have basic hand-washing facilities with soap and water.
Water quality also address to elements dissolved. In the case of fluoride, controlled amount are recommended for protect tooth, e.g. included in toothpaste. Higher levels can cause fluorosis, interfere in tooth enamel formation, correct growth of the bones, and cause crippling deformities of the spine and joints. The incidence of higher concentrations of fluoride in water is higher in rural areas without ...
2021-04-02
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis (AD), is sometimes called "the itch that rashes." Often, the itch begins before the rash appears, and, in many cases, the itchiness of the skin condition never really goes away. Approximately 9.6 million children and 16.5 million adults in the U.S. have AD, which can have a serious effect on quality of life for patients. Although much has been learned about the uncomfortable sensation that triggers the desire to scratch, many mysteries remain about chronic itch, making it a challenge to treat. A paper by authors from Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School published in The Proceedings ...
2021-04-02
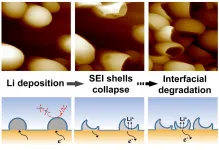
The interfacial decomposition products forming the so-called solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) during the first charging/discharging significantly determine the electrochemical performances of lithium (Li) batteries. To date, the dynamic evolutions, chemical compositions, stabilities and the influencing factors of the SEI films have been captured tremendous attentions.
It's noted that, in contrast to the SEI film formation at the surface of electrodes, a kind of SEI shells usually conformally forms at the outmost layer of the on-site deposited Li once the freshly deposited Li contacts with the electrolyte, which could directly influence Li nucleation, growth behaviors ...
2021-04-02
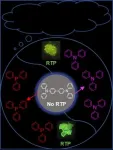
Purely organic room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) materials have been a hot research topic. Currently, the pure RTP materials have been realized by the introduction of heavy halogen atoms, carbonyls groups or some heteroatoms, hydrogen bonding, H-aggregation, strong intermolecular electronic coupling, molecular packing, host-guest interaction, etc. However, the complicated synthesis and high expenditure are still inevitable in these systems. In addition, their performances in air are not satisfactory and the introduction of halogen atoms is generally necessary. Therefore, a new facile and robust host-guest strategy utilizing only electron-rich materials is a promising alternative for constructing RTP systems.
Very ...
2021-04-02
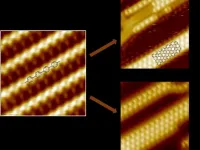
On-surface synthesis has received great attention as a method to create atomically-precise one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) polymers with intriguing properties. In particular, graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), a category of quasi-1D nanomaterials derived from graphene, have been widely studied due to their tunable electronic properties and potential applications in semiconductor devices, such as field-effect transistors and spintronics. A series of top-down approaches have been pursued to produce GNRs, but a lack of control over the ribbon width and edge structure has hindered their further development.
In 2010, Cai et al. firstly reported the fabrication of an atomically-precise armchair GNR (AGNR) on the Au(111) surface using a bottom-up ...
2021-04-02
The directly catalytic oxidation of alkanes has high atomic economy and application value to form corresponding chemical organic products such as alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acid. It is challenging to achieve efficient and selective oxidation of alkane under mild conditions due to the inert C-H bonds of alkanes.
Many researchers have developed a series of supported iron based catalysts to simulate the alkane biological monooxygenase with iron center atoms. However, traditional methods, such as impregnation method, ion exchange method, etc., are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists observe role of cavitation in glass fracturing