(Press-News.org) UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Like moths to a flame, spotted lanternflies are visually drawn toward and seemingly captivated by vertical objects such as utility poles, a behavior that could be valuable in predicting where the pests might be heading, according to entomologists in Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences.
Research from the laboratory of Tom Baker, recently published in the Journal of Insect Behavior, is laying the foundation for future strategies to monitor and possibly trap the invasive insect from Asia, which first was found in North America in Berks County, Pennsylvania, in 2014. The planthopper now is confirmed in 34 Pennsylvania counties and several surrounding states.
These findings show that telephone poles attract flight-dispersing spotted lanternflies, which are visually drawn to turn and land on the poles when they are less than about 10 feet away. They remain on the pole for many minutes, even hours, while crawling up toward the top to try to take flight again.
However, a large proportion of those launching themselves from the pole are drawn back to the pole, which serves as a sort of "visual magnet" from which the insects cannot escape for a while. The pole thus attracts and retains a large proportion of the lanternflies that are drawn to it.
"The spotted lanternfly feeds on more than 70 plant species, making it a great concern to U.S. tree-fruit and grape growers, as well as to the forest products industry," said Baker, distinguished professor of entomology and chemical ecology.
"Understanding the how and why of its flight capabilities and its attraction to stimuli from the environment can help us better exploit these behaviors to assess, and possibly thwart, future threats from this pest."
This latest study is an offshoot of experiments on the insect's flight behaviors and dispersal patterns led by Baker and his colleagues Andrew Myrick, assistant research professor of entomology, and Michael Wolfin, postdoctoral research associate.
Their flight-dispersal research efforts began during late summer and early fall in September and October of 2017 and 2018 at a fruit farm near Oley and at Dorney Park in Allentown. Both locations had been severely affected by spotted lanternfly infestations.
Baker's team had found that, in the lanternflies' apparent quest to find new sources of food to complete their development and then mate, they will fly onto and crawl to the top of the nearest vertical surfaces -- including inanimate objects such as buildings and telephone poles and host and nonhost plants -- and launch themselves into the wind.
Because lanternflies cannot generate much lift, only thrust, their normal flight paths conform to gradually descending, straight-line trajectories in which they are able to traverse usually only 30 to 150 feet over the ground before landing.
Baker reported that their landing sites are indiscriminate with respect to species of trees, bushes and inanimate objects. "The lanternflies' forced landings on the ground due to insufficient lift are indiscriminate, too," he said.
An exception to the typical low-to-the-ground flights occurs on days with high temperatures and rising air currents, allowing the low-flying lanternflies to be lifted to higher altitudes, with the now high-flying adults being transported downwind for perhaps thousands of yards.
It is on such occasional late-summer days during the past few years when huge swarms have been deposited by the tens of thousands -- much to the alarm of the human population -- in shopping center parking lots, gas stations, and industrial and residential areas within heavily infested regions, Baker pointed out.
However, he said that the pest's typical, low-to-ground flight coupled with its visual attraction to tall vertical objects may provide an effective and inexpensive way to monitor and even trap the insect.
"Telephone poles, which are plentiful and visible from the roadway, could be used by field scouts to document the presence or absence of spotted lanternfly by driving along and examining the poles at designated intervals," said Baker, who also suggested the possible use of poles as "attract-and-kill stations" to protect designated areas.
Despite the importance of these natural flight-dispersal abilities, a method of travel for the lanternflies that citizens should be very concerned about is human transport of adults and egg masses via trains, trucks and recreational vehicles, noted Baker.
"People who are traveling through, or residing in, an area affected by spotted lanternfly should check their vehicles and items they are transporting before leaving to ensure they are not carrying these unwanted hitchhikers to new locations," he said.
INFORMATION:
Yanchen Wang, former visiting doctoral student from Northeast Forestry University in Harbin, China, also contributed to the study, which received funding from the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service.
Acomprehensive review published in the journal Psychological Science re-examines previous work that claimed to show a direct link between early screen time and attention problems in children. Although other studies do not reflect these findings, the earlier research continues to be widely reported by the media.
"The findings from the original study, upon further scrutiny, are not borne out. We found that there is still no evidence that TV, by itself, causes ADHD or any kind of attention problems in young children," said Wallace E. Dixon, Jr., a professor of psychology ...
Long-term, regular use of baby aspirin--at least 15 times per month--prior to a diagnosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) may reduce the risk of death from the disease by limiting the spread of cancerous tumors pre-diagnosis, according to a study led by Cedars-Sinai Cancer researchers.
While previous research has offered consistent evidence that low-dose aspirin use reduces colorectal cancer risk, key findings from the study, published in the peer-reviewed Journal of the National Cancer Institute, revealed that the use of baby aspirin prior to the diagnosis of non-metastatic CRC was associated with a lower rate of metastasis, or tumor spread. Starting ...
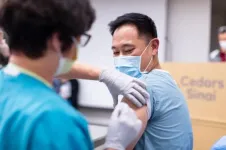
LOS ANGELES (April 1, 2021) -- A single dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine for individuals who previously had COVID-19 generates an immunologic response similar to that of individuals receiving the two-dose recommended sequence, according to a Cedars-Sinai study published today by the journal Nature Medicine.
"Our findings extend those from smaller studies reported elsewhere and support a potential strategy of providing a single dose of vaccine to persons with a confirmed prior history of coronavirus infection, along with two doses for people not previously infected," said Susan Cheng, MD, MPH, MMSc, associate professor of Cardiology and director of Public Health Research at ...
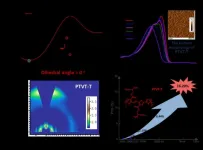
Organic solar cell (OSC) is one of the most important green energy technologies. The photovoltaic efficiencies of OSCs are closely related to the photoactive layers, which are prepared by blending electron donor and acceptor materials. With the emergence of a large number of new organic photovoltaic materials and effective molecular modification methods, the photovoltaic efficiency of OSCs has been greatly improved. Accordingly, the molecular structure of the materials is becoming much more complex with high costs, which is difficult to meet the requirements of the industrialization of OSCs. Thus, it is of great importance to develop novel photovoltaic ...
Scientists in Japan have developed and tested a novel probiotic formulation to control severe diarrhea in calves, ensuring their health and reducing mortality, and in turn reducing economic loss.
The health of calves is a crucial component in animal husbandry; diseases that affect calves cause economic losses to livestock farms either directly, due to death of the calves, or indirectly, due to weight loss that reduces productivity over the animals' lifespans. In Japan, bovine rotavirus (BRV) and bovine cryptosporidiosis infections are major diseases that cause severe diarrhea in calves.
A team of scientists from Hokkaido, including Associate Professor Satoru Konnai of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine at Hokkaido University, have ...
Researchers in Italy have identified a pair of microRNA molecules that help maintain a population of cancerous stem cells that drive the growth of breast cancers and initiate tumor relapse after treatment. The study, which will be published April 2 in the Journal of Cell Biology (JCB), reveals that targeting these microRNAs makes cancer stem cells more susceptible to some chemotherapies and could potentially improve the prognosis of patients with aggressive forms of breast cancer.
Many tumors contain a small population of cancer stem cells that initiate tumor growth and give rise to the various cell types found in tumors. Moreover, because cancer stem cells are often resistant to radio- and chemotherapies, they can survive and promote tumor ...
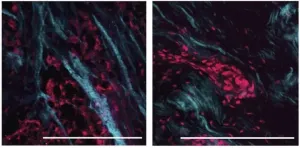
Researchers at the University of California, San Francisco, have discovered that aggressive, triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) can evade treatment by reorganizing and softening the collagen matrix that surrounds the cancer cells. The study, which will be published April 2 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), shows that the softer matrix activates a signaling pathway that promotes the cancer cells' survival, and suggests that targeting this pathway could enhance the effectiveness of chemo- and radiotherapy in TNBC patients.
TNBC is an aggressive type of breast cancer with worse survival rates than other forms of the disease. Because TNBC cells lack the HER2 signaling ...
A team of researchers has identified several candidates for drugs against the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 at DESY´s high-brilliance X-ray lightsource PETRA III. They bind to an important protein of the virus and could thus be the basis for a drug against Covid-19. In a so-called X-ray screening, the researchers, under the leadership of DESY, tested almost 6000 known active substances that already exist for the treatment of other diseases in a short amount of time. After measuring about 7000 samples, the team was able to identify a total of 37 substances that bind to the main protease (Mpro) of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, as the scientists report online today in the journal ...
Glassy materials play an integral role in the modern world, but inherent brittleness has long been the Achilles' heel that severely limits their usefulness. Due to the disordered amorphous structure of glassy materials, many mysteries remain. These include the fracture mechanisms of traditional glasses, such as silicate glasses, as well as the origin of the intriguing patterned fracture morphologies of metallic glasses.
Cavitation has been widely assumed to be the underlying mechanism governing the fracture of metallic glasses, as well as other glassy systems. Up until now, however, scientists ...
A new study indicates holes the solution to operational speed/coherence trade-off, potential scaling up of qubits to a mini-quantum computer.
Quantum computers are predicted to be much more powerful and functional than today's 'classical' computers.
One way to make a quantum bit is to use the 'spin' of an electron, which can point either up or down. To make quantum computers as fast and power-efficient as possible we would like to operate them using only electric fields, which are applied using ordinary electrodes.
Although spin does not ordinarily 'talk' to electric fields, in some materials spins can interact with electric fields indirectly, and these are some of the hottest materials currently studied ...