(Press-News.org) Patients with a high number of genes most associated with pathways that lead to cell death in lung cancer are at increased risk of dying early from their disease, researchers report.
Also seemingly paradoxically, patients with high expression of this "21-gene cell death signature" the researchers have identified, have indicators that their immune system is attacking the cancer, like higher levels of cytotoxic T cells, which typically kill cancer.
But they also have high levels of molecules that can suppress those T cells, helping transform them into dysfunctional, "exhausted" T cells, they report in the journal Cancers.
This novel genomic signature can be used both to better predict how a patient with lung cancer will do and, more importantly, to better tailor treatments to improve patient survival, says Dr. Ravindra Kolhe, director of the Georgia Esoteric and Molecular (GEM) Laboratory, and vice chair for translational research in the Medical College of Georgia Department of Pathology.
"Immunotherapy is a great approach to treatment but it's not going to be effective in everyone, and we think this will help identify at the point of diagnosis which immunotherapy will benefit a patient the most," says Kolhe, the study's corresponding author.
For example, cancer cells use immune checkpoints, like the protein PD-L1, which normally protects our own cells from being attacked by the immune system, to shield themselves from T cells. The study found a compromised immune function in the tumor microenvironment of patients with the highest cell death index. That means those patients should benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors like PD-L1 inhibitors, to better enable the immune system to attack their cancer, Kolhe says.
To find a way to improve patient survival, they started by looking at how cells die in this cancer.
Millions of cells die daily and the ways they die include so-called programmed cell death, including apoptosis, in which cells commit suicide because, for example, they have a mutation that cannot be repaired that might cause cancer; and autophagy, where cells basically consume themselves, because of a problem like a malfunctioning component. The more passive, unplanned death is necrosis, where cells might die because of injury. The immune system naturally works through these genes and pathways to kill off invaders and so do cancer treatments like chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
They looked at retrospective data on 510 patients with lung cancer from the national Cancer Genome Atlas, a joint effort of the National Cancer Institute and National Human Genome Research Institute. Genes involved in the different modes of cell death in these patients were assessed, and the researchers found 21 genes occurred most often. They identified 59 individuals with the highest expression and 49 with the lowest expression of these most prominent cell death genes. They also looked at key indicators of immune system activity and compared overall survival, disease-free survival and disease-specific survival in those two groups.
While a prospective study is still needed, Kolhe hopes the cell death index that emerged, will soon give patients with lung cancer, at the time of their diagnosis, the same benefits that good prognostic markers today provide patients with breast cancer.
Lung cancer is the third most common cancer in the United States and the leading cause of cancer death among men and women, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The Food and Drug Administration approved the first lung cancer specific immunotherapy in 2015 and more are currently in clinical trials. Standard lung cancer treatment has included surgery, chemotherapy and radiation with immunotherapy a more recent adjunct, that has helped patients with advanced lung cancer live longer, according to the Cancer Research Institute.
In their early assessment of patients, molecular and genetic pathologists like Kolhe also routinely run a panel for a handful of genes known to drive lung cancer, like EGFR, a protein on the cell surface that normally helps cells grow and divide. In the most common lung cancer type, non-small cell lung cancer, which Kolhe looked at in this study, there can be mutations in EGFR which result, for example, in a lot more of the protein which enables rapid cancer cell growth, and there are inhibitors that block some of these mutations at least for a time.
INFORMATION:
Read the full study.
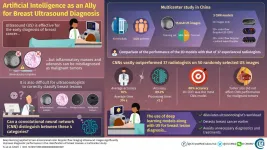
In 2020, the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization stated that breast cancer accounts for most cancer morbidities and mortalities in women worldwide. This alarming statistic not only necessitates newer methods for the early diagnosis of breast cancer, but also brings to light the importance of risk prediction of the occurrence and development of this disease. Ultrasound is an effective and noninvasive diagnostic procedure that truly saves lives; however, it is sometimes difficult for ultrasonologists to distinguish between malignant tumors and other ...
X-Ray Experiments, Machine Learning Could Trim Years Off Battery R&D
By Glenn Roberts Jr.
An X-ray instrument at Berkeley Lab contributed to a battery study that used an innovative approach to machine learning to speed up the learning curve about a process that shortens the life of fast-charging lithium batteries.
Researchers used Berkeley Lab's Advanced Light Source, a synchrotron that produces light ranging from the infrared to X-rays for dozens of simultaneous experiments, to perform a chemical imaging technique known as scanning transmission ...
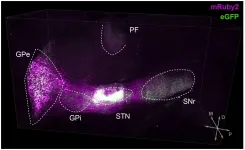
Parkinson's disease (PD) is well known as a debilitating disease that gradually worsens over time. Although the disease's progression has been largely tied to the loss of motor functions, non-motor symptoms, including the loss of cognitive abilities, often emerge early in the disease.
Much less understood is the role that specific neural circuits play in these distinct motor and non-motor functions.
A new study led by neurobiologists at the University of California San Diego and their colleagues found that specific, identifiable neural pathways are charged with particular functions during stages of the disease. ...
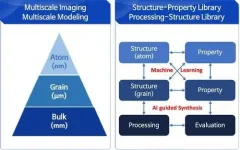
Developing new materials and novel processes has continued to change the world. The M3I3 Initiative at KAIST has led to new insights into advancing materials development by implementing breakthroughs in materials imaging that have created a paradigm shift in the discovery of materials. The Initiative features the multiscale modeling and imaging of structure and property relationships and materials hierarchies combined with the latest material-processing data.
The research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong analyzed the materials research projects reported by leading global ...
Researchers at the Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center have developed DeepTCR, a software package that employs deep-learning algorithms to analyze T-cell receptor (TCR) sequencing data. T-cell receptors are found on the surface of immune T cells. These receptors bind to certain antigens, or proteins, found on abnormal cells, such as cancer cells and cells infected with a virus or bacteria, to guide the T cells to attack and destroy the affected cells.
"DeepTCR is an open-source software that ...
A research team led by Professor PAN Jianwei and Professor XU Feihu from University of Science and Technology of China achieved single-photon 3D imaging over 200 km using high-efficiency optical devices and a new noise-suppression technique, which is commented by the reviewer as an almost "heroic" attempt at single photon lidar imaging at very long distances.
Lidar imaging technology has enabled high precision 3D imaging of target scene in recent year. Single photon imaging lidar is an ideal technology for remote optical imaging with single-photon level sensitivity and picosecond resolution, yet its imaging range is strictly limited by the quadratically decreasing count of photons that echo back.
Researchers first optimized transceiver optics. The lidar system setup adopted ...
A new automated process prints a peptide-based hydrogel scaffold containing uniformly distributed cells. The scaffolds hold their shapes well and successfully facilitate cell growth that lasts for weeks.
"Bioprinting" -- 3D printing that incorporates living cells -- has the potential to revolutionize tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Scientists have experimented with natural and synthetic "bioinks" to print out scaffolds that hold cells in place as they grow and form a tissue with a specific shape. But there are challenges with cell survival. Natural bioinks, such as gelatin and collagen, need to be treated with chemicals or ultraviolet light to hold their shape, which affects ...
A new analysis of the entire genetic makeup of more than 53,000 people offers a bonanza of valuable insights into heart, lung, blood and sleep disorders, paving the way for new and better ways to treat and prevent some of the most common causes of disability and death.
The analysis from the Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine (TOPMed) program examines the complete genomes of 53,831 people of diverse backgrounds on different continents. Most are from minority groups, which have been historically underrepresented in genetic studies. The increased representation should translate into better understanding of how heart, lung, blood and sleep disorders affect minorities and should help reduce longstanding health disparities.
"The Human Genome Project has generated ...
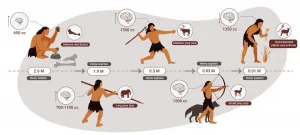
Researchers at Tel Aviv University were able to reconstruct the nutrition of stone age humans. In a paper published in the Yearbook of the American Physical Anthropology Association, Dr. Miki Ben-Dor and Prof. Ran Barkai of the Jacob M. Alkov Department of Archaeology at Tel Aviv University, together with Raphael Sirtoli of Portugal, show that humans were an apex predator for about two million years. Only the extinction of larger animals (megafauna) in various parts of the world, and the decline of animal food sources toward the end of the stone age, led humans to gradually increase the vegetable element in their nutrition, until finally they had no choice but to domesticate both plants and animals - and became farmers.
"So far, attempts to reconstruct the diet of stone-age humans ...
WASHINGTON, April 5, 2021 -- Forever chemicals are known for being water-, heat- and oil-resistant, which makes them useful in everything from rain jackets to firefighting foams. But the chemistry that makes them so useful also makes them stick around in the environment and in us -- and that could be a bad thing: https://youtu.be/tqKEG5LxPiY.
INFORMATION:
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions and follow us on Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS' mission is to advance the broader ...