Reclamation releases technical reports supporting the 2021 SECURE Water Act Report
Climate change impacts assessed on water supplies in 17 western states
2021-04-05
(Press-News.org) The Bureau of Reclamation today released final technical reports supporting the Water Reliability in the West - 2021 SECURE Water Act Report. Reclamation's 2021 West-Wide Climate and Hydrology Assessment and seven individual basin reports provide detailed information on climate change impacts and adaptation strategies to increase water supply reliability in the West. A new 2021 SECURE Report Web Portal is also available to provide a user-friendly, web-based format for delivery of information in the reports.
"Western water supply and delivery systems are affected by changing hydrologic conditions and competing demands," Deputy Commissioner Camille Calimlim Touton said. "These reports highlight Reclamation's effort to use the best-available science to meet its mission while also collaborating with its water and power customers, states and local agencies, and tribes to address critical western water management issues."
The 2021 West-Wide Assessment provides estimates of changes in temperature, precipitation, snowpack, and streamflow across the West using consistent methodology, similar to previous SECURE Water Act Reports. For this report, additional drought analyses based on paleohydrology (using tree rings) was performed. These results will enable water managers to compare the frequency and severity of droughts that occurred several hundred years ago to projections of future droughts and develop water management strategies in time to take action.
The West-Wide Assessment finds that temperatures are expected to increase across the West while precipitation changes are variable. With warmer temperatures, more precipitation will fall as rain and snow will melt sooner, reducing snowpack in the future that can impact streamflow timing. These key findings on future climate and hydrology are consistent with the conclusions of the 2016 SECURE Water Act Report.
The seven basin reports analyze climate change impacts to water resources within each basin. Each report also identifies Reclamation's collaborative actions to increase water and power delivery reliability since the last SECURE Water Act Report in 2016, including science and research, planning, infrastructure sustainability, efficient hydropower production and on-the-ground activities to meet irrigation needs and water needed for municipalities, power, Tribes and the environment. These basin reports also describe some of the innovative approaches underway locally to address vulnerabilities.
Reclamation is collaborating with its customers, stakeholders, and other partners to develop appropriate mitigation strategies to increased risks of drought and changes to precipitation, runoff, and increased temperatures. These strategies include:
Supporting reliable water deliveries through construction activities and water management improvements, as well as diversifying supplies through water reuse and ground and surface water conjunctive use.
Improving hydropower generation capability, flexibility, and reliability through new advanced decision support tools to maximize the amount of power produced with available water supplies and new technologies to keep hydropower plants operating.
Maintaining healthy ecosystems and protecting federally listed fish, wildlife, plants, and designated critical habitat affected by Reclamation facilities through a range of programs and activities.
Addressing drought risks by proactively building resilience as the severity, duration, and frequency of drought increases.
INFORMATION:
The SECURE Water Act Report released today is available at http://www.usbr.gov/climate.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-05
Humans have long explored three big scientific questions: evolution of the universe, evolution of Earth, and evolution of life. Geoscientists have embraced the mission of elucidating the evolution of Earth and life, which are preserved in the information-rich but incomplete geological record that spans more than 4.5 billion years of Earth history. Delving into Earth's deep-time history helps geoscientists decipher mechanisms and rates of Earth's evolution, unravel the rates and mechanisms of climate change, locate natural resources, and envision the future of Earth.
Two common approaches, deductive reasoning ...
2021-04-05
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed an exosome-coated stent with a "smart-release" trigger that could both prevent reopened blood vessels from narrowing and deliver regenerative stem cell-derived therapy to blood-starved, or ischemic, tissue.
Angioplasty - a procedure that opens blocked arteries - often involves placing a metal stent to reinforce arterial walls and prevent them from collapsing once the blockage is removed. However, the stent's placement usually causes some injury to the blood vessel wall, which stimulates smooth muscle cells to proliferate and migrate to the site in an attempt to repair the injury. The result is restenosis: a re-narrowing of the blood vessel previously opened by angioplasty.
"The ...
2021-04-05
ITHACA, N.Y. - The cost of harvesting solar energy has dropped so much in recent years that it's giving traditional energy sources a run for their money. However, the challenges of energy storage - which require the capacity to bank an intermittent and seasonally variable supply of solar energy - have kept the technology from being economically competitive.
Cornell University researchers led by Lynden Archer, Dean and Professor of Engineering, have been exploring the use of low-cost materials to create rechargeable batteries that will make energy storage more ...
2021-04-05
AMHERST, Mass. - A team of polymer science and engineering researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has demonstrated for the first time that the positions of tiny, flat, solid objects integrated in nanometrically thin membranes - resembling those of biological cells - can be controlled by mechanically varying the elastic forces in the membrane itself. This research milestone is a significant step toward the goal of creating ultrathin flexible materials that self-organize and respond immediately to mechanical force.
The team has discovered that rigid solid plates in biomimetic fluid membranes experience interactions ...
2021-04-05
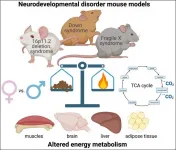
Mouse models of neurodevelopmental disorders possess unique, sex-specific metabolic dysfunctions, according to a new study in eNeuro. Understanding the unique metabolic effects of each disorder in both animal models and humans may lead to more personalized treatments and diagnostic methods.
Any disorder affecting the brain also impacts the body. People with neurodevelopmental disorders -- including Down syndrome and autism spectrum disorders -- are at increased risk for developing diabetes, obesity, and hypertension. Yet the impact of these three disorders on metabolism has not been studied.
Menzies et al. measured the resting energy metabolism of three neurodevelopmental disorder mouse models: Down syndrome, ...
2021-04-05
A new report by AARP Pennsylvania and Drexel University's College of Nursing and Health Professions highlights how geographic, racial/ethnic and economic factors are combining to restrict access to health care services for many Pennsylvanians, creating disparities that have become more pronounced during the COVID-19 pandemic.
"Disrupting Disparities in Pennsylvania: Retooling for Geographic, Racial and Ethnic Growth" shows that health inequities are most acute among those living in rural and low resourced areas of the state, and among underrepresented populations (particularly Black/African American and Latino), who lack access to health care, experience digital divide and face persistent ...
2021-04-05
In an effort to save her beloved animals, Kathy Janson, a Maine Coon cat enthusiast reached out to a University of Cincinnati researcher to find a way to help her pets who were developing heart troubles.
Maine Coon cats are known as great mousers, popular farm cats and, of course, for their enormous size. The New England breed is a really big cat and can weigh up to 19 pounds and grow up to 40 inches in length. Janson fell in love with these animals more than 25 years ago bringing them into her Cincinnati suburban home to become part of her family.
"Maine ...
2021-04-05
Researchers from the University of Minnesota Twin Cities College of Science and Engineering and Medical School have developed a unique head-mounted mini-microscope device that allows them to image complex brain functions of freely moving mice in real time over a period of more than 300 days.
The device, known as the mini-MScope, offers an important new tool for studying how neural activity from multiple regions of the outer part of the brain, called the cortex, contribute to behavior, cognition and perception. The groundbreaking study provides new insight into fundamental research that could improve human brain conditions such as concussions, autism, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's disease, as well as better understanding ...
2021-04-05
A study at the University of Chicago Medicine found U.S. women experienced increased incidence of health-related socioeconomic risks (HRSRs), such as food insecurity and interpersonal violence, early in the COVID-19 pandemic. This was associated with "alarmingly high rates" of mental health problems, including depression and anxiety. The research was published April 5 in the Journal of Women's Health.
Other studies have found evidence for higher rates of anxiety and depression and related issues, such as alcohol overuse, connected to the pandemic -- but this study is the first to link early pandemic-related changes in HRSRs to mental health effects ...
2021-04-05
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and collaborators have demonstrated an atom-based sensor that can determine the direction of an incoming radio signal, another key part for a potential atomic communications system that could be smaller and work better in noisy environments than conventional technology.
NIST researchers previously demonstrated that the same atom-based sensors can receive commonly used communications signals. The capability to measure a signal's "angle of arrival" helps ensure the accuracy of radar and wireless communications, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Reclamation releases technical reports supporting the 2021 SECURE Water Act Report
Climate change impacts assessed on water supplies in 17 western states