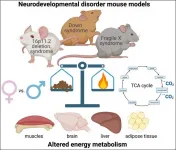
Mouse models of neurodevelopmental disorders display metabolic dysfunction
Three different mouse models have unique, sex-specific metabolic signatures
2021-04-05
(Press-News.org) Mouse models of neurodevelopmental disorders possess unique, sex-specific metabolic dysfunctions, according to a new study in eNeuro. Understanding the unique metabolic effects of each disorder in both animal models and humans may lead to more personalized treatments and diagnostic methods.
Any disorder affecting the brain also impacts the body. People with neurodevelopmental disorders -- including Down syndrome and autism spectrum disorders -- are at increased risk for developing diabetes, obesity, and hypertension. Yet the impact of these three disorders on metabolism has not been studied.
Menzies et al. measured the resting energy metabolism of three neurodevelopmental disorder mouse models: Down syndrome, 16p11.2 deletion syndrome, and Fragile X syndrome. The mice spent 48 hours in a special cage that tracked gas exchange, activity, food consumption, and heat production. The research team also measured metabolites in the blood. Despite similar food consumption and physical activity levels, each mouse model exhibited a unique, sex-specific metabolic signature. The signatures varied in terms of energy expenditure, fat and carbohydrate utilization, body composition, and metabolite levels. The results suggested all three mouse models may be showing signs of mitochondrial dysfunction, meaning their cells have issues using and producing energy.
INFORMATION:
Paper title: Distinct Basal Metabolism in Three Mouse Models of Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Please contact media@sfn.org for full-text PDF and to join SfN's journals media list.
About eNeuro
eNeuro is an online, open-access journal published by the Society for Neuroscience. Established in 2014, eNeuro publishes a wide variety of content, including research articles, short reports, reviews, commentaries and opinions.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world's largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 37,000 members in more than 90 countries and over 130 chapters worldwide.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-05
A new report by AARP Pennsylvania and Drexel University's College of Nursing and Health Professions highlights how geographic, racial/ethnic and economic factors are combining to restrict access to health care services for many Pennsylvanians, creating disparities that have become more pronounced during the COVID-19 pandemic.
"Disrupting Disparities in Pennsylvania: Retooling for Geographic, Racial and Ethnic Growth" shows that health inequities are most acute among those living in rural and low resourced areas of the state, and among underrepresented populations (particularly Black/African American and Latino), who lack access to health care, experience digital divide and face persistent ...
2021-04-05
In an effort to save her beloved animals, Kathy Janson, a Maine Coon cat enthusiast reached out to a University of Cincinnati researcher to find a way to help her pets who were developing heart troubles.
Maine Coon cats are known as great mousers, popular farm cats and, of course, for their enormous size. The New England breed is a really big cat and can weigh up to 19 pounds and grow up to 40 inches in length. Janson fell in love with these animals more than 25 years ago bringing them into her Cincinnati suburban home to become part of her family.
"Maine ...
2021-04-05
Researchers from the University of Minnesota Twin Cities College of Science and Engineering and Medical School have developed a unique head-mounted mini-microscope device that allows them to image complex brain functions of freely moving mice in real time over a period of more than 300 days.
The device, known as the mini-MScope, offers an important new tool for studying how neural activity from multiple regions of the outer part of the brain, called the cortex, contribute to behavior, cognition and perception. The groundbreaking study provides new insight into fundamental research that could improve human brain conditions such as concussions, autism, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's disease, as well as better understanding ...
2021-04-05
A study at the University of Chicago Medicine found U.S. women experienced increased incidence of health-related socioeconomic risks (HRSRs), such as food insecurity and interpersonal violence, early in the COVID-19 pandemic. This was associated with "alarmingly high rates" of mental health problems, including depression and anxiety. The research was published April 5 in the Journal of Women's Health.
Other studies have found evidence for higher rates of anxiety and depression and related issues, such as alcohol overuse, connected to the pandemic -- but this study is the first to link early pandemic-related changes in HRSRs to mental health effects ...
2021-04-05
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and collaborators have demonstrated an atom-based sensor that can determine the direction of an incoming radio signal, another key part for a potential atomic communications system that could be smaller and work better in noisy environments than conventional technology.
NIST researchers previously demonstrated that the same atom-based sensors can receive commonly used communications signals. The capability to measure a signal's "angle of arrival" helps ensure the accuracy of radar and wireless communications, ...
2021-04-05
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- A team led by a biomedical scientist at the University of California, Riverside, has developed a new RNA-sequencing method-- "Panoramic RNA Display by Overcoming RNA Modification Aborted Sequencing," or PANDORA-seq -- that can help discover numerous modified small RNAs that were previously undetectable.
RNA plays a central role in decoding the genetic information in DNA to sustain an organism's life. It is generally known as the intermediate molecule used to synthesize proteins from DNA. Cells are full of RNA molecules in complex and diverse forms, two main types ...
2021-04-05
Although stratospheric ozone protects us by filtering out the sun's ultraviolet radiation, tropospheric ozone is a harmful pollutant. A new study has shown that ozone in the lower layers of the atmosphere decreases crop yields in maize and changes the types of chemicals that are found inside the leaves.
Ozone is formed when nitrous oxide, released from industries and tail pipes of cars, is broken down by sunlight and chemically reacts to form ozone. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have been studying the effects of ozone pollution on crops for over 20 years at a unique facility where crops can be grown under real-world farm ...
2021-04-05
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - April 5, 2021 - According to the American Cancer Society, a noninvasive breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) accounts for approximately one of every four new breast cancer cases in the United States. If left untreated, DCIS has the potential to evolve into invasive cancer, so many patients choose to have breast-conserving surgery or mastectomy after a diagnosis.
However, obtaining clear or negative margins -- no cancer cells in the outer edge of removed tissue -- is critical to mastectomy success as positive margins are associated with higher rates of recurrence.
A new study from Wake Forest School of Medicine suggests removing ...
2021-04-05
A new study published in Indoor Air provides design-based solutions on how to best use ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UVGI) to disinfect occupied rooms without harming individuals. This research was conducted by Dorit Aviv, assistant professor of architecture and director of the Thermal Architecture Lab at the University of Pennsylvania Stuart Weitzman School of Design, Penn visiting scholar Miaomiao Hou, and Jovan Pantelic, an air quality expert at Katholieke Universiteit Leuven.
Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UVGI) devices use short-wavelength ultraviolet ...
2021-04-05
Palmer Amaranth is a high-impact agronomic weed species that has cost the United States agriculture industry billions of dollars since its discovery outside of its native range in the southwestern U.S. and northwestern Mexico. Over the last 20 years, it has moved further north, and now poses a major threat to corn, soybean, and cotton growers across the south and Midwest regions of the United States.
It is not legal to sell any kind of seed in Minnesota if the seed lot contains Palmer Amaranth. The problem is this particular invasive species--which has shown potential to wipe out up to 91% of corn yields, 68% of soybean yields, and 54% of cotton yields-- is difficult to visibly distinguish from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Mouse models of neurodevelopmental disorders display metabolic dysfunction
Three different mouse models have unique, sex-specific metabolic signatures




