(Press-News.org) A new study analyzing bean production and food security across 11 countries in sub-Saharan Africa, found COVID-19 pandemic-related restrictions to significantly impact bean production. Border controls and high transport costs have led to drops in production of the key food security crop, threatening to reverse gains made in achieving Sustainable Development Goals 1 and 2, towards no poverty and zero hunger, respectively.
Even before the pandemic, 55% of the world's hungry people and 70% of the world's poorest people lived in Africa, the researchers said. In addition, food systems across Africa were already affected by the adverse impacts of climate change, disease and pests, such as the worst desert locust outbreak in 70 years impacting food security in Kenya, Somalia, Ethiopia and other countries in eastern Africa.
Other impacts of COVID-19 restrictions, both direct and indirect, can be found in the study: "Regional impact of COVID-19 on the production and food security of common bean smallholder farmers in Sub-Saharan Africa: Implication for SDG's," published in the Global Food Security edition of peer-reviewed platform Science Direct. Direct impacts include farms and food businesses closing down; while indirect impacts are linked to lockdown, border closures, social distancing, and restricted transportation and trade.
"The food system is already highly inefficient. What we've seen is that measures taken to control the virus led to wider food security restrictions and disruptions, exacerbating those already-existing insecurities," said author Eileen Nchanji, a gender researcher at The Alliance of Bioversity International and the International Center for Tropical Agriculture (The Alliance). "Pay cuts, job losses, and high food prices due to reduced food imports and closure of informal markets all disrupted food supplies, with poorer communities especially affected."
From border closures to national lockdowns, delayed cargo further exacerbated food shortages, the researchers said. For instance, 15% of imported food in Kenya before the pandemic was sourced from countries that imposed export restrictions, affecting the availability and flow of crops and food. Restrictions also led to limited access to seed, farm inputs, hired labor, and agricultural finance for smallholder farmers, especially those in Uganda, where planting was beginning.
The data, collected between March and April 2020, shows that most households in Eastern Africa ate only twice during the pandemic. Uganda was most affected, with all surveyed farmers eating only once per day during the pandemic. The research also found a 34% decrease in access to labor attributed to the fear of getting the disease, the high cost of public transportation, and social distancing measures. Farmers also noted difficulties in accessing finance, farm inputs, seed and extension information.
The research highlights that 36%, 20%, and 3% of farmers in Burundi, Uganda, and Kenya respectively lost income during the pandemic, with knock-on impacts on food security. The low number in Kenya is due to the fact that crops were already planted, and farmers were relying on maize and other crops stored from the previous harvest for food and to generate income, while in Uganda and Burundi, planting was ongoing, and so more money was spent on inputs, seed and food, as prices and costs of transport increased.
In West Africa, challenges included insecurity, political instability, social conflicts, and climate change, the report said, citing Food and Agriculture projections that 17 million people in the region will face severe food insecurity following measures to contain the virus.
Although governments across the continent have responded by offering economic stimulus packages, much needs to be done to enable the sub-sector to recover from ruins caused by the pandemic, authors said.
Cosmas Lutomia, at the Kenya Agriculture and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO), said: "The pandemic has necessitated a much needed discussion around the complexity of our food systems. We can only achieve sustainable and resilient food systems through strengthening public-private partnerships. We implore governments across the region to strengthen the food systems' resilience to present and future shocks."
The authors called for an immediate transformation of food systems in all the sub-regions. Governments should invest directly in input supply systems and short food supply chains through digital access, mobile-based payments, credit and food delivery, they added.
INFORMATION:
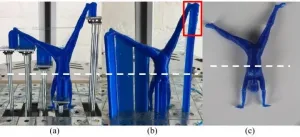
3-D printing has the potential to revolutionize product design and manufacturing in a vast range of fields--from custom components for consumer products, to 3-D printed dental products and bone and medical implants that could save lives. However, the process also creates a large amount of expensive and unsustainable waste and takes a long time, making it difficult for 3-D printing to be implemented on a wide scale.
Each time a 3-D printer produces custom objects, especially unusually-shaped products, it also needs to print supports-printed stands that balance the object as the printer creates layer by layer, ...
Likely the first extinction event of the 2000s in Europe, the sad history of the Pyrenean Ibex (Capra pyrenaica pyrenaica) is a powerful example of the ever-increasing species loss worldwide due to causes related to human activity. It can, however, give us valuable information on what should be done (or avoided) to halt this extinction vortex.
The distribution of this subspecies of Iberian Ibex was limited to the French and Spanish Pyrenees. Its first mention in an official written document, dating back to 1767, already refers to it as extremely rare. Like many other mountain goats, it was almost hunted to extinction before its killing became prohibited in 1913. Neither the institution ...
Insomnia is a common problem in patients with schizophrenia, and a new study reinforces a close association between insomnia, more suicidal thoughts and actions and increased problems like anxiety and depression in these patients.
It also provides more evidence that keeping tabs on how patients are sleeping -- and intervening when needed -- is important to their overall care.
"We are now aware that significant insomnia is putting our patients at even higher risk for suicide, so if they are having changes in sleep patterns, if they are having significant insomnia, then we really need to hone in on those questions even more related to suicidal thinking and do what we can to help," says Dr. ...
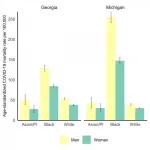
A new paper in the Journal of General Internal Medicine published by the GenderSci Lab at Harvard University shows that Black women are dying at significantly higher rates than white men, and that disparities in mortality rates among women of all races are greater than those between white women and white men.
The study is the first to quantify the inequities in COVID-19 mortality looking at both race and sex group.
"This analysis complicates the simple narrative that men are dying at greater rates of COVID-19 than women," said lead author Tamara Rushovich, Harvard Ph.D. candidate in population health sciences and lab member ...
The adult human body produces hundreds of billions of blood cells every day. This essential process unavoidably leads to the appearance of mutations in the DNA of the progenitor cells. These are known as somatic mutations because they are acquired, not inherited. While most of these mutations are innocuous, occasionally a mutation gives affected cells a competitive advantage that allows them to expand progressively, generating clonal populations of blood cells. This phenomenon is known as clonal hematopoiesis.
Now, a team of scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) and the Hospital Universitario Virgen de Arrixaca in Murcia has discovered that the presence of these acquired mutations in blood cells increases ...
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. ACP Best Practice Advice: Shorter course of antibiotics may be appropriate for some common infections
HD video soundbites of ACP's president discussing the paper are available to download at http://www.dssimon.com/MM/ACP-antibiotics-paper.
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-7355
Free ...
Researchers at the Human Genome and Stem Cell Research Center (HUG-CELL), hosted by the University of São Paulo's Institute of Biosciences (IB-USP) in Brazil, have developed a technique to reconstruct and produce livers in the laboratory.
The proof-of-concept study was conducted with rat livers. In the next stage of their research, the scientists will adapt the technique for the production of human livers in order in future to increase the supply of these organs for transplantation.
The study was supported by FAPESP and is reported in an article published in Materials Science and Engineering: ...
PITTSBURGH, April 5, 2021 - "Near-poor" Americans--people just above the federal poverty level but still well below the average U.S. income--who rely on Medicare for health insurance face high medical bills and may forgo essential health care, according to new research led by health policy scientists at the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health. This is due to a coverage "cliff" in Medicaid, which supplements Medicare for people with incomes below poverty but excludes individuals above the federal poverty threshold, including the near-poor.
In a report published today in the April issue of the journal Health Affairs, the authors describe the effects of this cliff and propose solutions to fix it, with the aim of lessening barriers to care among near-poor people ...
PHILADELPHIA-- Approximately 6.5 million people are under correctional supervision in the United States on any given day. Justice-involved individuals (people currently or recently in prison or jail, on probation or parole, or arrested) experience higher rates of substance use disorders than the general population. In fact, among people with opioid use disorder (OUD), more than half have reported contact with the criminal justice system.
Numerous clinical studies have shown that medications for OUD -- specifically, methadone or buprenorphine -- lead to superior outcomes for retention in treatment, reduced illicit opioid use, and decreased opioid-related overdose rates and serious acute care compared with treatments that ...
PHILADELPHIA-- While the emergency department (ED) functions as an integral part of the United States healthcare safety net by handling all medical complaints regardless of insurance status, ED visits are expensive, and many are for lower-acuity conditions that may be amenable to care in other settings. Previous research has suggested that greater availability of urgent care centers - freestanding facilities with extended hours that staff emergency physicians, primary care physicians, or nurse practitioners, and focus on a broad range of lower acuity complaints, like rash, muscle strain, bronchitis, and urinary tract infection - helps decrease ED visits, but whether the centers reduce or increase net spending for patients ...