As lumber prices skyrocket, professor develops method to predict future price changes
2021-04-06
(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. - At a time when lumber prices are skyrocketing, an Oregon State University researcher has developed a new way to predict the future price of logs that uses readily accessible economic information.
"Log prices are really variable," said Jeff Reimer, a professor of applied economics at Oregon State. "That makes this a difficult business, whether you are land manager, mill owner, timberland investor or, as we are seeing now, a home builder."
The timber industry is critical to the economy of many regions of the world, including the Pacific Northwest. The health of the timber industry can be measured in various ways, including harvest levels, employment in timber harvesting and at mills, and lumber demand. Yet the prices of cut and delivered logs may be the most direct way to monitor the condition of timber markets, Reimer said.
Reimer's study, recently published in the journal Forest Policy and Economics, focused on Douglas-fir, the most commercially important timber species in the Pacific Northwest.
He found that simply knowing the number of housing permits issued in a month can explain about 46.8% of the variation in log prices over time. Adding additional information - including the monthly inventory of homes, mortgage rates, the exchange rate with Canada (also a big timber supplier) and the Case-Shiller home price index - explains about 74.3% of the price variation.
"These variables are readily observable and thus can be used by industry decision-makers to make better predictions about future values of logs and timberland," said Reimer, a professor in Oregon State's College of Agricultural Sciences.
In the paper, Reimer cites data that shows the average price of Douglas-fir logs between 2005 and 2020 was $631 per MBF (a forestry term for 1,000 board feet of lumber) of mill logs in southern Oregon. One board foot of lumber is 1 square foot and 1-inch thick.
Yet this average disguises a great deal of variation in price. From 2005 to 2020, the price ranged from $346 per MBF to $924 per MBF. The difference between the minimum and maximum was $578, nearly as large as the 15-year average price itself.
Since the paper was written, lumber prices have increased more, reaching the $1,000 per MBF range. The National Association of Home Builders recently released a report that said lumber prices have added an average of $24,000 to the cost of a new home.
"Right now log prices are phenomenally high," Reimer said. "It can feel like feast or famine in this industry but there is a logic that underlies the changes. The benefit of this paper is that we have identified a few pieces of readily observable information that allow people in the timber industry to make solid predictions about what will be happening in the next six months or so."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-06
TUCSON, Ariz., April 6, 2021 - Dry periods between rainstorms have become longer and annual rainfall has become more erratic across most of the western United States during the past 50 years, according to a new study published by the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Agricultural Research Service and the University of Arizona
Against the backdrop of steadily warming temperatures and decreasing total yearly rainfall, rain has been falling in fewer and sometimes larger storms, with longer dry intervals between. Total yearly rainfall has decreased by an average of four inches over the last half century, while the longest dry period in each year increased from 20 to 32 days across the West, explained ...
2021-04-06
DNA sequencing has become so common, few realize how hard it is to even extract a single molecule of DNA from a biological sample.
Research led by UC Riverside is making it easier to detect and capture DNA from fluid samples such as blood using a tiny glass tube and electric current. The technique, described in the journal, Nanoscale, can also improve cancer diagnosis in the future.
DNA, a double-stranded, electrically charged molecule that contains all the information an organism needs to create and organize the building blocks of life, is tightly folded within the cell nucleus. Extracting the DNA from a single cell is time consuming and impractical for many medical and scientific purposes. Fortunately, as cells die naturally, their membranes burst, releasing the contents, including ...
2021-04-06
Bans on menthol cigarettes across Canada from 2016 to 2017 led to a significant increase in the number of smokers who attempted to quit, smokers who quit successfully, and lower rates of relapse among former smokers, according to a new research study from the International Tobacco Control Policy Evaluation Project (the ITC Project) at the University of Waterloo.
Menthol is the most common flavoring for cigarettes in many countries. Menthol creates a cooling sensation, which reduces the harshness of cigarette smoke. Because of this, menthol leads to increased experimentation and progression ...
2021-04-06
New research from UVA Cancer Center could rescue once-promising immunotherapies for treating solid cancer tumors, such as ovarian, colon and triple-negative breast cancer, that ultimately failed in human clinical trials.
The research from Jogender Tushir-Singh, PhD, explains why the antibody approaches effectively killed cancer tumors in lab tests but proved ineffective in people. He found that the approaches had an unintended effect on the human immune system that potentially disabled the immune response they sought to enhance.
The new findings allowed Tushir-Singh to increase the approaches' effectiveness significantly in lab models, reducing tumor size and improving overall survival. The promising results suggest the renewed potential for the strategies in human patients, he and his ...
2021-04-06
Seafood is a pillar of global food security--long recognized for its protein content. But research is highlighting a critical new link between the biodiversity of aquatic ecosystems and the micronutrient-rich seafood diets that help combat micronutrient deficiencies, or 'hidden hunger', in vulnerable populations.
"Getting the most nutritional value per gram of seafood is crucial in fighting hidden hunger and meeting United Nations Sustainable Development Goals," says Dr. Joey Bernhardt, an ecologist from the University of British Columbia (UBC) who led the study, published this week in the Proceedings of the National ...
2021-04-06
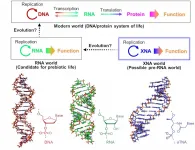
Nagoya University scientists in Japan have demonstrated how DNA-like molecules could have come together as a precursor to the origins of life. The findings, published in the journal Nature Communications, not only suggest how life might have begun, but also have implications for the development of artificial life and biotechnology applications.
"The RNA world is widely thought to be a stage in the origin of life," says Nagoya University biomolecular engineer Keiji Murayama. "Before this stage, the pre-RNA world may have been based on molecules called xeno nucleic acids ...
2021-04-06
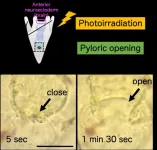
Tsukuba, Japan - Many life forms use light as an important biological signal, including animals with visual and non-visual systems. But now, researchers from Japan have found that neuronal cells may have initially evolved to regulate digestion according to light information.
In a study published this month in BMC Biology, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that sea urchins use light to regulate the opening and closing of the pylorus, which is an important component of the digestive tract.
Light-dependent systems often rely on the activity of proteins in the Opsin family, and these are found across the animal kingdom, including in organisms with visual and non-visual systems. Understanding ...
2021-04-06
LOS ANGELES (April 5, 2021) -- New research from the Smidt Heart Institute shows that more patients--specifically those with medical risk factors or from underserved communities--opted into telehealth appointments for their cardiovascular care during the COVID-19 pandemic. The data also suggests these telehealth patients underwent fewer diagnostic tests and received fewer medications than patients who saw their doctors in person.
The findings, published in JAMA (Journal of the American Medical Association) Network Open, point to "digital shifts" in cardiovascular care amid the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
"We were encouraged to learn that access to cardiovascular ...
2021-04-06
DURHAM, N.C. -- Emily Ury remembers the first time she saw them. She was heading east from Columbia, North Carolina, on the flat, low-lying stretch of U.S. Highway 64 toward the Outer Banks. Sticking out of the marsh on one side of the road were not one but hundreds dead trees and stumps, the relic of a once-healthy forest that had been overrun by the inland creep of seawater.
"I was like, 'Whoa.' No leaves; no branches. The trees were literally just trunks. As far as the eye could see," said Ury, who recently earned a biology Ph.D. at Duke University working with professors Emily Bernhardt and Justin Wright.
In bottomlands throughout the U.S. East ...
2021-04-06
Tsukuba, Japan - With a prevalence of about one in 10 people worldwide, chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a global health problem. It also often goes undetected, leading to a range of negative health outcomes, including death. Catching it at an early stage and adjusting nutrition and lifestyle can improve and extend life, but only if there are economically feasible systems in place to promote and educate on this.
Amid finite health-care resources, any CKD intervention must be both practical and cost-effective. A team of researchers centered at the University of Tsukuba now believe they have found a CKD behavioral intervention that can be delivered at a reasonable cost. They published their findings in the Journal of Renal Nutrition.
Changing eating and lifestyle habits, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] As lumber prices skyrocket, professor develops method to predict future price changes