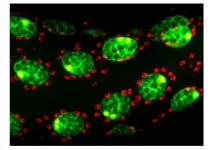
(Press-News.org) Even a well-characterized genome, such as that of the Drosophila the so-called fruit fly, still holds surprises. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, in collaboration with Cornell University (USA) and the University of Groningen (Netherlands), has discovered an RNA coding for a micro-peptide - a very small protein - that plays a crucial role in the competition between spermatozoa from different males with which the female mates. In addition to shedding new light on this biological mechanism, this work, to be read in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), highlights the importance of small peptides, a class of proteins that is now emerging as a key player in complex biological processes.
In many species, including insects, mating induces physiological changes in the female aimed at the reproductive success of the couple. This response is induced by substances in the male's seminal fluid that interact with the female's reproductive system. These post-coital changes include increased ovulation and egg laying, semen storage and release, dietary changes and gut growth. A mated female also becomes less receptive to other males and can use the semen stored in her spermatheca from her first intercourse for many days. However, this behavior is counterbalanced by the "last male preference" phenomenon. Indeed, despite the decrease in libido normally induced by a first mating, females sometimes decide to mate with a new, healthier or stronger male, probably in order to have more robust offspring. In this case, the semen of the first male is expelled and only that of the last male is kept.
A small peptide with a big role in sperm selection
The authors of this study have studied this phenomenon in Drosophila, the small fly that lingers around overripe or rotting fruit. This model organism, very popular with researchers for genetic and developmental studies, allows for easy observation and study of reproductive behavior. The biologists analyzed the proteins produced by the accessory functional gland, homolog of the human prostate. "Among the proteins we identified as essential for a normal response after mating is a micro-peptide, a very small protein that had never been studied before, as the RNA that codes for it was considered 'non-coding'", says Clément Immarigeon, first author of this study conducted in the Department of Genetics and Evolution of the Faculty of Science at UNIGE.
In order to verify if this peptide finally played a determining role, the researchers created mutants that no longer possess it. In females first mated by a mutant male, the phenomenon of "last male preference" is no longer observed. Indeed, if they are then mated by another male, they lay eggs fertilized by the sperm of both males, and not exclusively by the last progenitor, which could reduce the robustness of their offspring. "To our surprise, we found that this micro-peptide - encoded by a putative non-coding transcript - performs important reproductive functions. Such micro-peptides were not previously recognized but are emerging as important players in complex biological processes", summarizes Robert Maeda, researcher in the Department of Genetics and Evolution at UNIGE and last author of the study.
Towards the sterile insect
The study of these mating-induced phenomena is of particular interest in certain insect species responsible for sanitary, economic or environmental problems. A biological alternative to non-selective insecticides is the "sterile insect" method, which limits harmful populations by releasing millions of sterilized males into the wild to prevent females from mating with fertile wild males. A better understanding of the post-mating response will allow the development of even more effective biological control methods.
INFORMATION:
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University have synthetized high-entropy carbide consisting of five various metals using a vacuum-free electric arc method. The research findings are published in the Journal of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics.
High-entropy carbides are a new class of materials simultaneously consisting of four or more various metals and carbon. Their main feature lies in the capability to endure high temperatures and energy flux densities. Combining various elements in the composition, it is possible to obtain the required mix of features ...
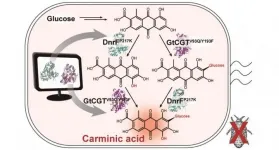
A research group at KAIST has engineered a bacterium capable of producing a natural red colorant, carminic acid, which is widely used for food and cosmetics. The research team reported the complete biosynthesis of carminic acid from glucose in engineered Escherichia coli. The strategies will be useful for the design and construction of biosynthetic pathways involving unknown enzymes and consequently the production of diverse industrially important natural products for the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Carminic acid is a natural red colorant widely being used for products such as strawberry milk and lipstick. However, carminic acid has been produced ...
El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is one of the most prominent ocean-atmosphere interactions that varies year-to-year. This process exerts significant impacts on global weather and climate. El Niño is the warm phase of ENSO, which can be strong, moderate, or even weak. Within the past four decades, climatologists observed three super El Niño events (1982/83, 1997/98 and 2015/16). These extreme phases impacted global climate far more than moderate or weak events.
El Niño has a profound effect on the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO), which ...
Metamaterials that can control the refractive direction of light or absorb it to enable invisible cloaks are gaining attention. Recently, a research team at POSTECH has designed a metasurface that can control the acoustic or elastic waves. It is gaining attention as it can be used to escape from threatening earthquakes or build submarines untraceable to SONAR.
Professor Junsuk Rho of POSTECH's departments of mechanical engineering and chemical engineering and Ph.D. candidate Dongwoo Lee of the Department of Mechanical Engineering in collaboration with Professor Jensen Li of HKUST have designed an artificial structure that can control not only the domain of underwater sound but also of vibration. The research team has presented an ...
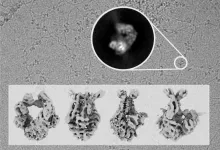
Scientists from the Genomic Integrity and Structural Biology Group led by Rafael Fernández-Leiro at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) have discovered how certain proteins ensure the repair of errors introduced into the DNA during its replication. Using cryo-electron microscopy, they made the MutS protein, also known as the guardian of our genome, visible. That enabled them to describe how this single protein is able to coordinate the essential DNA repair process from beginning to end.
The study was carried out in collaboration with Meindert Lamers of the Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC, The Netherlands) and Titia Sixma of the Netherlands Cancer Institute and the Oncode Institute. Their results are published ...
Eating together as a family, maintaining the Mediterranean diet's traditional customs of conviviality, influences the eating habits of adolescents and prevents eating behaviour disorders, according to a new study prepared by scientists from the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) and the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) and published in the open access International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
"At a time when lockdown due to the pandemic has revived family meals, this study indicates one of the possible positive aspects of the situation that we have had to confront", explains the study's researcher Anna Bach-Faig from the Foodlab group, and a member of the Faculty of Health Sciences.
The research establishes ...
The period with the strictest lockdown conditions and quarantining posed additional problems for young people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and their families, given that their routines were suddenly disrupted. Routines form an essential aspect of their everyday life and life structure. However, their response and adaptation to this new situation was better than expected in aspects like communication and interaction with their families.
A study conducted by researchers from the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya, the University of Perugia and the ABAULA Occupational ...
Lakes act as an important part of the earth system. They have special functions in regulating regional climate and maintaining regional ecological balance. More than 39.2% of the lakes in China are distributed in the plateau. The topography around the plateau lake area is complex and diverse. It leads to a complex and unique local circulation characterized by the superposition of lake-land breeze circulation and mountain-valley breeze circulation, which has a significant impact on the local energy and material circulation, according to Prof. Huizhi Liu, researcher at the Institute of Atmospheric ...
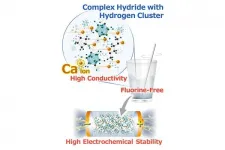
Scientists from Tohoku University have developed a new fluorine-free calcium (Ca) electrolyte based on a hydrogen (monocarborane) cluster that could potentially realize rechargeable Ca batteries.
The researchers say the new material, achieved by designing the coordination structure of Ca cation with a weakly coordinating anion and mixed solvents, shows markedly improved electrochemical performances such as high conductivity and high electrochemical stabilities.
Current lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries have some drawbacks. They are approaching their demand limits of theoretical energy ...
Making the Case for Adjusting Quality Measures for Social Risk Factors
Henry Ford Health System-led report says adjustments would enhance quality.
DETROIT (April 5, 2021) - A new analysis by a team of researchers led by Dr. David Nerenz of Henry Ford Health System suggests that accounting for social risk factors like poverty, housing instability and transportation insecurity can have meaningful impact on healthcare quality measures without compromising quality of care.
In a report published today in Health Affairs, researchers make the case for using social risk factors in specific circumstances to "level the playing field" for adjusting quality measures used in quality reporting and value-based purchasing programs. Social risk adjustment ...