TPU scientists first obtain high-entropy carbide in electric arc plasma
2021-04-06
(Press-News.org) Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University have synthetized high-entropy carbide consisting of five various metals using a vacuum-free electric arc method. The research findings are published in the Journal of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics.
High-entropy carbides are a new class of materials simultaneously consisting of four or more various metals and carbon. Their main feature lies in the capability to endure high temperatures and energy flux densities. Combining various elements in the composition, it is possible to obtain the required mix of features (melting point, oxidation temperature, specific weight and others).
"High-entropy materials are called in such a way due to a relatively high degree of disorder in the crystalline lattice, as an atom of every chemical element possesses a certain size in the crystalline lattices.
It causes structural distortions and can positively affect material properties," Alexander Pak, Research Fellow of the TPU Research Center - Ecoenergy 4.0, explains.
The TPU scientists managed to synthetize high-entropy carbide consisting of Ti, Zr, Nb, Hf, Ta and C. Carbide was obtained using a vacuum-free electric arc synthesis. High temperatures are required for a reaction, in order, every primary component interacting with C connects to the face-centered cubic lattice and forms ultra-refractory carbide. The scientists use electric arc plasma to obtain it.
"We became the first who could obtain high-entropy carbide using a vacuum-free electric arc method. It is a great rarity and success for us to synthetize a material that has recently been discovered and to use our method at electric arc reactors created by our research team.
We are planning to improve a synthesis process to obtain a clearer and uncontaminated material, to reduce energy intensity, as well as to research material properties and synthetize high-entropy carbides of the other chemical composition," Alexander Pak adds.
INFORMATION:
The research work is being conducted jointly with scientists of the A.V. Luikov Heat and Mass Transfer Institute of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus. The scientists applied for a patent (method of producing TiZrNbHfTaC5 high-entropy carbide).
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-06
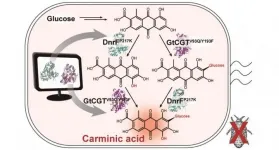
A research group at KAIST has engineered a bacterium capable of producing a natural red colorant, carminic acid, which is widely used for food and cosmetics. The research team reported the complete biosynthesis of carminic acid from glucose in engineered Escherichia coli. The strategies will be useful for the design and construction of biosynthetic pathways involving unknown enzymes and consequently the production of diverse industrially important natural products for the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Carminic acid is a natural red colorant widely being used for products such as strawberry milk and lipstick. However, carminic acid has been produced ...
2021-04-06
El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is one of the most prominent ocean-atmosphere interactions that varies year-to-year. This process exerts significant impacts on global weather and climate. El Niño is the warm phase of ENSO, which can be strong, moderate, or even weak. Within the past four decades, climatologists observed three super El Niño events (1982/83, 1997/98 and 2015/16). These extreme phases impacted global climate far more than moderate or weak events.
El Niño has a profound effect on the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO), which ...
2021-04-06
Metamaterials that can control the refractive direction of light or absorb it to enable invisible cloaks are gaining attention. Recently, a research team at POSTECH has designed a metasurface that can control the acoustic or elastic waves. It is gaining attention as it can be used to escape from threatening earthquakes or build submarines untraceable to SONAR.
Professor Junsuk Rho of POSTECH's departments of mechanical engineering and chemical engineering and Ph.D. candidate Dongwoo Lee of the Department of Mechanical Engineering in collaboration with Professor Jensen Li of HKUST have designed an artificial structure that can control not only the domain of underwater sound but also of vibration. The research team has presented an ...
2021-04-06
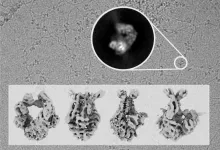
Scientists from the Genomic Integrity and Structural Biology Group led by Rafael Fernández-Leiro at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) have discovered how certain proteins ensure the repair of errors introduced into the DNA during its replication. Using cryo-electron microscopy, they made the MutS protein, also known as the guardian of our genome, visible. That enabled them to describe how this single protein is able to coordinate the essential DNA repair process from beginning to end.
The study was carried out in collaboration with Meindert Lamers of the Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC, The Netherlands) and Titia Sixma of the Netherlands Cancer Institute and the Oncode Institute. Their results are published ...
2021-04-06
Eating together as a family, maintaining the Mediterranean diet's traditional customs of conviviality, influences the eating habits of adolescents and prevents eating behaviour disorders, according to a new study prepared by scientists from the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) and the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) and published in the open access International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
"At a time when lockdown due to the pandemic has revived family meals, this study indicates one of the possible positive aspects of the situation that we have had to confront", explains the study's researcher Anna Bach-Faig from the Foodlab group, and a member of the Faculty of Health Sciences.
The research establishes ...
2021-04-06
The period with the strictest lockdown conditions and quarantining posed additional problems for young people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and their families, given that their routines were suddenly disrupted. Routines form an essential aspect of their everyday life and life structure. However, their response and adaptation to this new situation was better than expected in aspects like communication and interaction with their families.
A study conducted by researchers from the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya, the University of Perugia and the ABAULA Occupational ...
2021-04-06
Lakes act as an important part of the earth system. They have special functions in regulating regional climate and maintaining regional ecological balance. More than 39.2% of the lakes in China are distributed in the plateau. The topography around the plateau lake area is complex and diverse. It leads to a complex and unique local circulation characterized by the superposition of lake-land breeze circulation and mountain-valley breeze circulation, which has a significant impact on the local energy and material circulation, according to Prof. Huizhi Liu, researcher at the Institute of Atmospheric ...
2021-04-06
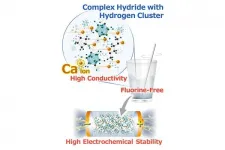
Scientists from Tohoku University have developed a new fluorine-free calcium (Ca) electrolyte based on a hydrogen (monocarborane) cluster that could potentially realize rechargeable Ca batteries.
The researchers say the new material, achieved by designing the coordination structure of Ca cation with a weakly coordinating anion and mixed solvents, shows markedly improved electrochemical performances such as high conductivity and high electrochemical stabilities.
Current lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries have some drawbacks. They are approaching their demand limits of theoretical energy ...
2021-04-06
Making the Case for Adjusting Quality Measures for Social Risk Factors
Henry Ford Health System-led report says adjustments would enhance quality.
DETROIT (April 5, 2021) - A new analysis by a team of researchers led by Dr. David Nerenz of Henry Ford Health System suggests that accounting for social risk factors like poverty, housing instability and transportation insecurity can have meaningful impact on healthcare quality measures without compromising quality of care.
In a report published today in Health Affairs, researchers make the case for using social risk factors in specific circumstances to "level the playing field" for adjusting quality measures used in quality reporting and value-based purchasing programs. Social risk adjustment ...
2021-04-06
CORVALLIS, Ore. - At a time when lumber prices are skyrocketing, an Oregon State University researcher has developed a new way to predict the future price of logs that uses readily accessible economic information.
"Log prices are really variable," said Jeff Reimer, a professor of applied economics at Oregon State. "That makes this a difficult business, whether you are land manager, mill owner, timberland investor or, as we are seeing now, a home builder."
The timber industry is critical to the economy of many regions of the world, including the Pacific Northwest. The health of the timber industry can be measured in various ways, including harvest levels, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] TPU scientists first obtain high-entropy carbide in electric arc plasma