Competing for high status speeds up aging in male baboons
Study suggests that high social status contributes to accelerated aging in baboons, despite its other advantages
2021-04-06
(Press-News.org) Battling other male baboons to achieve high social status comes with physiological costs that accelerate aging, according to study published today in eLife.
The findings suggest that current life circumstances may be more important contributors to premature aging than early life hardship, at least in baboons.
Chemical changes to DNA, also called epigenetic changes, can be used as a kind of 'clock' to measure aging. While these epigenetic changes usually correspond with age, they can also be used to detect signs of premature aging.
"Environmental stressors can make the clock tick faster, so that some individuals appear biologically older than their actual age and experience a higher risk of age-related disease," explains co-first author Jordan Anderson, a PhD student in Evolutionary Anthropology at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, US. "We sought to answer what social or early life experiences contribute to accelerated aging in baboons."
The team measured aging in 245 wild baboons from a well-studied population in Kenya using the epigenetic clock and other methods. They found that the epigenetic clock was a good predictor of chronological age overall. But contrary to what they expected, early life adversity was not a good predictor of accelerated aging in the animals.
Instead, they found that the highest-ranking males showed signs of accelerated aging. Higher body mass index, which is associated with having more lean muscle mass in baboons, was also associated with accelerated aging, likely because of the physical demands of maintaining high status. The team was also able to show that the epigenetic clock sped up as the animals climbed the social ladder and slowed down as they moved down it.
"Our results argue that achieving high rank for male baboons - the best predictor of reproductive success in these animals - imposes costs that are consistent with a 'live fast, die young,' life history strategy," says co-first author Rachel Johnston, Postdoctoral Associate in Evolutionary Anthropology at Duke University.
"While the findings reveal how social pressures can influence aging for males, we don't see the same effect of rank in female baboons, who are born into their social rank rather than having to fight for it," adds senior author Jenny Tung, Associate Professor in the Departments of Evolutionary Anthropology and Biology at Duke University, and a Faculty Associate of the Duke University Population Research Institute.
"Our results have important implications for research on the social determinants of health in humans and other animals because they show that 'high status' can mean very different things in different contexts. They also highlight the importance of examining the effects of both early life and current life environments on biological aging," Tung concludes.
INFORMATION:
This study will be published as part of 'Evolutionary Medicine: A Special Issue' from eLife. For more information, visit https://elifesciences.org/inside-elife/bb34a238/special-issue-call-for-papers-in-evolutionary-medicine.
Media contact
Emily Packer, Media Relations Manager
eLife
e.packer@elifesciences.org
+44 (0)1223 855373
About eLife
eLife is a non-profit organisation created by funders and led by researchers. Our mission is to accelerate discovery by operating a platform for research communication that encourages and recognises the most responsible behaviours. We aim to publish work of the highest standards and importance in all areas of biology and medicine, including Evolutionary Biology, and Genetics and Genomics, while exploring creative new ways to improve how research is assessed and published. eLife receives financial support and strategic guidance from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Max Planck Society and Wellcome. Learn more at https://elifesciences.org/about.
To read the latest Evolutionary Biology research published in eLife, visit https://elifesciences.org/subjects/evolutionary-biology.
And for the latest in Genetics and Genomics, see https://elifesciences.org/subjects/genetics-genomics.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-06
OAK BROOK, Ill. - Screening with digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) reduces the rate of interval breast cancers compared to screening with digital mammography, according to a study published in Radiology. The study adds to a growing body of evidence supporting DBT as a breast cancer screening tool with important advantages over mammography.
DBT works by capturing a series of X-ray images of the breast from different angles. Previous research has shown that it has a higher sensitivity for breast cancer detection than digital mammography.
The impact of these additional DBT-detected cancers is not fully understood. ...
2021-04-06
OAK BROOK, Ill. - Body composition information derived from routine chest CTs can provide important information on the overall health of people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including their risk of all-cause mortality, according to a study published in Radiology.
COPD is a group of chronic, progressive lung diseases like emphysema and chronic bronchitis that affect about 30 million people in the United States alone. It is frequently associated with obesity and sarcopenia, a loss of muscle mass and strength. Obesity is associated with lower mortality in patients with COPD. The longer survival rates of obese patients compared to leaner counterparts, a phenomenon ...
2021-04-06
A statistically rigorous survey of Japanese consumers has found that they have more negative opinions about the use of new gene-editing techniques on livestock than they do about use of the same technologies on vegetables.
The survey findings were reported in the journal BMC CABI Agriculture and Bioscience on March 31st, 2021.
Because humans tend to feel closer to animals than plants, and commonly express feelings regarding animal welfare but not plant welfare, the researchers, led by Naoko Kato-Nitta, a research scientist at Tokyo's Joint Support Center for Data Science Research and Institute of Statistical ...
2021-04-06
Even a well-characterized genome, such as that of the Drosophila the so-called fruit fly, still holds surprises. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, in collaboration with Cornell University (USA) and the University of Groningen (Netherlands), has discovered an RNA coding for a micro-peptide - a very small protein - that plays a crucial role in the competition between spermatozoa from different males with which the female mates. In addition to shedding new light on this biological mechanism, this work, to be read in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), highlights the importance of small peptides, a class of proteins that ...
2021-04-06
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University have synthetized high-entropy carbide consisting of five various metals using a vacuum-free electric arc method. The research findings are published in the Journal of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics.
High-entropy carbides are a new class of materials simultaneously consisting of four or more various metals and carbon. Their main feature lies in the capability to endure high temperatures and energy flux densities. Combining various elements in the composition, it is possible to obtain the required mix of features ...
2021-04-06
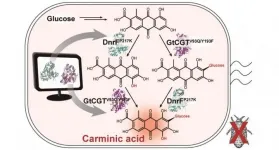
A research group at KAIST has engineered a bacterium capable of producing a natural red colorant, carminic acid, which is widely used for food and cosmetics. The research team reported the complete biosynthesis of carminic acid from glucose in engineered Escherichia coli. The strategies will be useful for the design and construction of biosynthetic pathways involving unknown enzymes and consequently the production of diverse industrially important natural products for the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Carminic acid is a natural red colorant widely being used for products such as strawberry milk and lipstick. However, carminic acid has been produced ...
2021-04-06
El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is one of the most prominent ocean-atmosphere interactions that varies year-to-year. This process exerts significant impacts on global weather and climate. El Niño is the warm phase of ENSO, which can be strong, moderate, or even weak. Within the past four decades, climatologists observed three super El Niño events (1982/83, 1997/98 and 2015/16). These extreme phases impacted global climate far more than moderate or weak events.
El Niño has a profound effect on the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO), which ...
2021-04-06
Metamaterials that can control the refractive direction of light or absorb it to enable invisible cloaks are gaining attention. Recently, a research team at POSTECH has designed a metasurface that can control the acoustic or elastic waves. It is gaining attention as it can be used to escape from threatening earthquakes or build submarines untraceable to SONAR.
Professor Junsuk Rho of POSTECH's departments of mechanical engineering and chemical engineering and Ph.D. candidate Dongwoo Lee of the Department of Mechanical Engineering in collaboration with Professor Jensen Li of HKUST have designed an artificial structure that can control not only the domain of underwater sound but also of vibration. The research team has presented an ...
2021-04-06
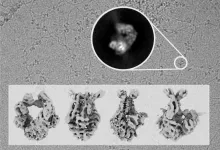
Scientists from the Genomic Integrity and Structural Biology Group led by Rafael Fernández-Leiro at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) have discovered how certain proteins ensure the repair of errors introduced into the DNA during its replication. Using cryo-electron microscopy, they made the MutS protein, also known as the guardian of our genome, visible. That enabled them to describe how this single protein is able to coordinate the essential DNA repair process from beginning to end.
The study was carried out in collaboration with Meindert Lamers of the Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC, The Netherlands) and Titia Sixma of the Netherlands Cancer Institute and the Oncode Institute. Their results are published ...
2021-04-06
Eating together as a family, maintaining the Mediterranean diet's traditional customs of conviviality, influences the eating habits of adolescents and prevents eating behaviour disorders, according to a new study prepared by scientists from the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) and the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) and published in the open access International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
"At a time when lockdown due to the pandemic has revived family meals, this study indicates one of the possible positive aspects of the situation that we have had to confront", explains the study's researcher Anna Bach-Faig from the Foodlab group, and a member of the Faculty of Health Sciences.
The research establishes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Competing for high status speeds up aging in male baboons
Study suggests that high social status contributes to accelerated aging in baboons, despite its other advantages