(Press-News.org) Thirty years ago, clinical psychiatrist Jonathan Shay drew attention to similarities between the trauma experienced by the Greek warriors, as documented in the epic poem "The Iliad," and Vietnam veterans in America. Could the experience of war impact people in similar ways in vastly different cultural milieus?
Research published this week by ASU researcher Sarah Mathew and former ASU postdoctoral researcher Matthew Zefferman in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences shows that Turkana pastoralist warriors from Kenya also experience PTSD (post-traumatic stress disorder) symptoms, even though their lifestyles and combat experiences are markedly different from that of Western soldiers. However, these pastoralists experience less of the PTSD symptoms associated with depression relative to American service members. This difference may be due to aspects of Turkana military organization and practice.
Combat stress is considered to be a major part of the human cost of industrialized warfare. It is estimated that 10 to 20% of American combat veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars suffer from PTSD.
The roots of PTSD are controversial. Some think that PTSD is largely a syndrome of military service members of industrialized societies who do not have social support systems typical in small-scale societies. Others expect it to be a universal phenomenon caused by adaptive responses to acute life-threatening events.
"Distinguishing between these theories has been challenging because PTSD in combatants has been studied almost exclusively in large-scale industrialized societies," said Zefferman, who is a US Air Force veteran and an assistant professor at the Naval Postgraduate School in Monterey. Zefferman was a postdoctoral researcher with the Institute of Human Origins at Arizona State University at the time he began this project.
Zefferman spent six months interviewing warriors in a remote part of Kenya near the border of South Sudan, where Mathew has been running a field research site since 2007. Mathew is an associate professor at ASU in the School of Human Evolution and Social Change and a research affiliate of the Institute of Human Origins. She was awarded an Andrew Carnegie Fellowship in 2015 that allowed her to undertake this study.
Lethal interethnic cattle raiding, once common in several pastoralist societies, continues unabated in this part of Kenya, with semi-automatic rifles replacing spears starting in the late 1970s.
"The Turkana communities in this area see cattle raiding as integral to their livelihood - without going on raids, they cannot recover livestock they lost when they were attacked, and they would get pushed out of critical dry season pastures and water wells," said Mathew.
Turkana in this area have a high degree of combat exposure with about half of adult male mortality due to combat. Twenty-eight percent of the 218 warriors interviewed for the study reported PTSD symptom severity scores that would qualify for a provisional PTSD diagnosis.
To delve further, they compared Turkana symptoms with those of treatment-seeking American combat veterans. They found that the Turkana, compared to American service members, have similarly high levels of symptoms that Zefferman and Mathew hypothesized facilitate learning from and reacting to future combat-related dangers. However, they have lower rates of depressive PTSD symptoms. The researchers suggest that depressive symptoms have different evolutionary origins than other PTSD symptoms and may be related to moral injury -- trauma from witnessing or participating in acts that violate one's moral beliefs.
The researchers also believe that the lack of hierarchical coercive leadership in the Turkana helps them avoid morally questionable actions relative to members of militaries in industrial societies. Because combat is so pervasive in the Turkana, there is not as strong a separation between military and civilian life. The Turkana employ numerous rituals after killing in combat that may help relieve these symptoms.
To see if PTSD symptomology among the Turkana supported their proposition, they statistically modeled which aspects of Turkana combat experiences are associated with depressive (negative beliefs/feelings, low concentration, and irritability/agreesion) versus "learning-and-reacting" (hypervigilance, nightmares, flashbacks) PTSD symptoms. They found that predictors measuring exposure to the dangers of combat like being ambushed, shooting at or being shot by the enemy, hand-to-hand combat, and suffering bullet wounds were more strongly associated with learning-and-reacting than depressive symptoms of PTSD. Conversely, predictors measuring exposure to combat-related moral violations like failing to save the life of another Turkana, seeing people get shot or die, killing an enemy, or being socially sanctioned for combat-related actions were more strongly associated with depressive than learning-and-reacting symptoms.
"The findings provide an evolutionarily and cross-culturally informed framework to further probe the origins and causes of moral injury and its connection to combat-related PTSD," said Zefferman.
In 2018, sponsored by the ASU Center for Evolution and Medicine, the researchers co-organized a workshop with the center's founding director Randy Nesse, M.D. The workshop brought together anthropologists, clinical psychiatrists and evolutionary psychologists to ASU to discuss avenues for future interdisciplinary research.
"Establishing which aspects of PTSD are dependent on social and moral forces, and which will tend to be universal, can help focus clinical research on ways to prevent or treat combat stress," added Mathew.
INFORMATION:
This research was published as "Combat stress in a small-scale society suggest divergent evolutionary roots for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) symptons," Matthew R. Zerrerman and Sarah Mathew, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Direct human alterations to natural aquatic ecosystems can increase methane emissions, a new study has found.
Atmospheric methane has tripled since pre-industrial times. It traps heat far more effectively than carbon dioxide and accounts for 25% of atmospheric warming to date. And much of that methane is coming from aquatic ecosystems, with human activities contributing to the emissions levels, a new paper published in Nature Geoscience has found.
The global contribution and importance of aquatic ecosystems as methane emitters has been underestimated, ...
Anyone who has visited the Australian outback would be familiar with spinifex grasses, which cover almost a fifth of our continent.
Like many scientists, they may have also wondered why this iconic arid grass grows in striking ring shapes.
Previous studies have tested whether spinifex rings could be caused by termites, water availability or nutrient depletion, but none has provided a convincing explanation.
Now scientists from UNSW Sydney have found that pathogenic soil microbes play a role in how the spinifex got its hole.
Their study, the first of its kind in an arid ecosystem, has been published in the Australian Journal of Botany.
Professor Angela Moles and Neil Ross from ...
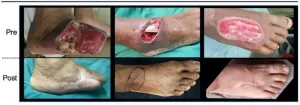
Durham, NC - According to the results of a phase 1 clinical trial just published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine, a new stem cell therapy shows promise of making diabetes-related amputations a thing of the past. The trial involved injecting diabetes patients suffering from non-healing diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) with a cell preparation containing adult stem cells harvested from their own fat. The results showed that the treatment induced regeneration of the blood vessels surrounding the DFUs, accelerated healing - all with no serious side effects.
"Non-healing diabetic foot ulcers usually ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Eucalyptus, a pest-resistant evergreen valued for its hardy lumber and wellness-promoting oil, can be genetically modified not to reproduce sexually, a key step toward preventing the global tree plantation staple from invading native ecosystems.
Oregon State University's Steve Strauss led an international collaboration that showed the CRISPR Cas9 gene editing technique could be used with nearly 100% efficiency to knock out LEAFY, the master gene behind flower formation.
"The flowers never developed to the point where ovules, pollen or ...
Two thirds of New Zealanders believed there were 'silver linings' to the country's Alert Level 4 COVID-19 lockdown imposed in March last year, a University of Otago survey has found.
The researchers were able to question New Zealanders while they were at home, giving a unique insight into their lives during the nationwide lockdown between 25 March and 23 April, widely regarded as one of the strictest imposed anywhere in the world.
One year on from lockdown, the results of their study have been published in the international scientific journal, PLOS ONE.
Participants were asked 'Have you experienced any silver linings, or positive aspects during the COVID-19 Level 4 lockdown' and were able to answer 'yes, for me personally', ...
Can a mirror turn an orange into a doughnut? The answer is definitely no in the real (macro) world. But at the nanoscale, a mirror can turn an "orange" shaped pattern into a "doughnut" shaped pattern by overlapping the "orange" with its reflected mirror image.
A team of researchers from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) has shown for the first time that fluorescent nanoparticles placed near a mirror generate unique patterns that can be used to pinpoint their location.
The researchers attribute this effect to the light emitting nanoparticle's interference with its own mirror image. Using this method they can also detect the size of particles to a resolution of one nanometre - or around 1/80,000th of the diameter of a human ...
Areas with a relatively greater amount of misogynistic tweets have higher incidences of domestic and family violence, a UNSW study has found.
The study, published in Psychological Science, not only found this connection with domestic and family violence carried over from one year to the next, but also occurred despite the 'usual suspects' of domestic violence, such as alcohol and inequality.
Examples of misogynistic tweets identified by the researchers included, "Women are all bitches," "Whore had it coming," and, "Make me a sandwich, slut."
"We found that misogynistic ...
Ever since the early humans learned to walk upright, they have suffered, as an unfortunate consequence of their erect posture, from low back pain. Modern understanding on this matter dictates that low back pain, in particular, is caused due to a postural instability resulting from poor "proprioception", which is a term for the perception of part of our body's own position in space. In fact, our trunk and lower legs are key to maintaining postural stability due to the presence of "proprioceptors"--sensory receptors responding to position and movement--in those areas.
Elderly people suffering from low back pain tend to have poorly performing proprioceptors, ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Researchers have found a way to use chaos to help develop digital fingerprints for electronic devices that may be unique enough to foil even the most sophisticated hackers.
Just how unique are these fingerprints? The researchers believe it would take longer than the lifetime of the universe to test for every possible combination available.
"In our system, chaos is very, very good," said Daniel Gauthier, senior author of the study and professor of physics at The Ohio State University.
The study was recently published online in the journal IEEE Access.
The researchers created a new version ...
(Boston)--Diagnosing Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) during life is crucial for developing therapies and for determining how common the disease is among individuals exposed to repetitive head impacts from contact sports, military service and physical violence.
While the ability to diagnose CTE prior to death has remained elusive, researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) for the first time have shown that progressive memory loss and issues with executive function, the ability to focus, follow directions, and problem-solve, are more useful for predicting CTE pathology than mood and behavior symptoms.
CTE is a progressive brain disease. Clinically, impulsivity, explosivity, depression, memory impairment and executive dysfunction have been reported to ...