Association of race/ethnicity, sex, income with well-being during COVID-19
2021-04-07
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did:
This observational study identifies and quantifies the association of race/ethnicity, sex and income, as well as state-specific lockdown measures, with six well-being dimensions in the United States.
Authors:
Leigh C. Hamlet, B.S., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study:
Visit our For The Media website at this link
https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.7373)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory:
The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article
This link will be live at the embargo time
http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.7373?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=040721
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is the new online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-07
A new estimation of the strength of the magnetic field around the muon--a sub-atomic particle similar to, but heavier than, an electron--closes the gap between theory and experimental measurements, bringing it in line with the standard model that has guided particle physics for decades.
A paper describing the research by an international team of scientists appears April 8, 2021 in the journal Nature.
Twenty years ago, in an experiment at Brookhaven National Laboratory, physicists detected what seemed to be a discrepancy between measurements of the muon's "magnetic ...
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: Researchers report on the observation of a newly associated mucocutaneous eruption in a pediatric patient with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection
Authors: Zachary E. Holcomb, M.D., of Boston Children's Hospital, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0385)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers ...
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: In this observational study of 3.4 million live births in 2018, criminalizing immigrant policies were associated with higher rates of preterm birth for Black women born outside the U.S., while inclusive immigrant policies were associated with lower preterm birth for all women born outside the U.S.,particularly White women born outside the U.S.
Authors: May Sudhinaraset, Ph.D., of the Jonathan and Karin Fielding School of Public Health at the University of California, Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: Researchers projected to the year 2040 what will become the most common and deadly cancers in the United States.
Authors: Lola Rahib, Ph.D., of Cancer Commons in Mountain View, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4708)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and ...
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: Questionnaire responses were compared to examine whether transgender children and teens experience significantly higher levels of anxiety and depression than their cisgender peers.
Authors: Dominic J. Gibson, Ph.D., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4739)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
2021-04-07
Ancient DNA from Neandertals and early modern humans has recently shown that the groups likely interbred somewhere in the Near East after modern humans left Africa some 50,000 years ago. As a result, all people outside Africa carry around 2% to 3% Neandertal DNA. In modern human genomes, those Neandertal DNA segments became increasingly shorter over time and their length can be used to estimate when an individual lived. Archaeological data published last year furthermore suggests that modern humans were already present in southeastern Europe 47-43,000 years ago, but due to a scarcity of fairly complete human fossils and the lack of genomic DNA, there is little understanding of who these early human colonists were - or of their relationships to ancient and present-day ...
2021-04-07
Analysis by international team including University of Warwick of the first transiting exoplanet that was discovered has revealed six different chemicals in its atmosphere.
It is the first time that so many molecules have been measured, and points to an atmosphere with more carbon present than oxygen
This chemical fingerprint is typical of a planet that formed much further away from its sun than the current location, a mere 7 million km from the star
Study tests techniques that will be useful for detecting signs of potentially habitable planets when more powerful telescopes come online
Artist's impression available - see Notes to Editors
Astronomers have found ...
2021-04-07
A new clinical trial from King's College London's Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology, & Neuroscience, in collaboration with Oxford University, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust, Sussex University, and Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust has established an innovative therapy as an effective means of treating paranoid thoughts in people experiencing psychosis.
In research published in JAMA Psychiatry today, participants of the SlowMo therapy trial had eight face-to-face therapy sessions with support from an interactive web platform and app. The app, designed in collaboration with people experiencing psychosis and the Royal College of Art, is used outside the clinic to help individuals feel safer in daily life.
Paranoia is fuelled ...
2021-04-07
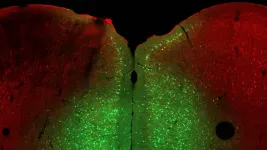
Everyone faces stress occasionally, whether in school, at work, or during a global pandemic. However, some cannot cope as well as others. In a few cases, the cause is genetic. In humans, mutations in the OPHN1 gene cause a rare X-linked disease that includes poor stress tolerance. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Linda Van Aelst seeks to understand factors that cause specific individuals to respond poorly to stress. She and her lab studied the mouse gene Ophn1, an analog of the human gene, which plays a critical role in developing brain cell connections, memories, and stress tolerance. When Ophn1 was removed in a specific part of the ...
2021-04-07
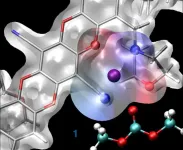
Membranes that allow certain molecules to quickly pass through while blocking others are key enablers for energy technologies from batteries and fuel cells to resource refinement and water purification. For example, membranes in a battery separating the two terminals help to prevent short circuits, while also allowing the transport of charged particles, or ions, needed to maintain the flow of electricity.
The most selective membranes - those with very specific criteria for what may pass through - suffer from low permeability for the working ion in the battery, which limits the battery's power and energy efficiency. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Association of race/ethnicity, sex, income with well-being during COVID-19