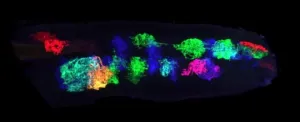
Scientists at IRB Barcelona identify a potential target to treat lung cancer
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) In cancer, personalised medicine takes advantage of the unique genetic changes in an individual tumour to find its vulnerabilities and fight it. Many tumours have a higher number of mutations due to a antiviral defence mechanism, the APOBEC system, which can accidentally damage DNA and cause mutations.
Researchers at IRB Barcelona led by Dr. Travis Stracker and Dr. Fran Supek have found the HMCES enzyme to be the Achilles heel of some lung tumours, specifically those with a higher number of mutations caused by the APOBEC system.
"We have discovered that blocking HMCES is very damaging to cells with an activated APOBEC system (which are many lung cancer cells), but much less so for those in which it is not activated (as is often the case in healthy cells)," explains Dr. Supek, ICREA researcher and head of the Genome Data Science lab at IRB Barcelona.
"Besides showing specificity to cancer cells, HMCES is potentially targetable by drugs, which makes it a great candidate for future lung cancer treatments," adds Dr. Stracker, former group leader at IRB Barcelona, now working at the National Cancer Institute (NIH/NCI) in the USA.
A multidisciplinary approach to double-check the best strategy
Involving collaboration between two research groups working on different disciplines, the study comprised both a computational and experimental approach. Genetic screening experiments were performed using CRISPR/Cas9 on several types of human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. "These experiments can interrogate the effects of removing each gene individually from the cancer cells and they allow us to see whether the cancer can tolerate this change," say Josep Biayna and Isabel Garcia, IRB Barcelona researchers and first and second authors of the article. Previous data from CRISPR genetic screens performed by other labs were also statistically analysed and confirmed the experimental results.
A mutation fog caused by a defence system
When cells sense a mismatch in their DNA, they undergo a DNA repair reaction to preserve genetic information. Remarkably, this reaction can become coupled to the APOBEC enzymes, typically used by human cells to defend against viruses and having an important role in fighting hepatitis and HIV. This mechanism was previously described by the Genome Data Science lab and indicates that, in some cases, when the APOBEC enzymes and the DNA repair process are simultaneously active, APOBEC hijacks DNA repair, thus generating the mutation fog.
Outsmarting cancer evolution
Late-stage cancers can accumulate a high number of mutations in their DNA, which can cause the cancer to become more aggressive or to resist drugs better. Many of these mutations may be caused by APOBEC which accelerates tumor evolution. Therefore, killing cancer cells that activate APOBEC should slow down tumor evolution and prevent it from gaining new dangerous mutations.
INFORMATION:
This work was funded by the ERC Starting Grant "HYPER-INSIGHT", awarded to Dr. Fran Supek, ICREA researcher and EMBO Young Investigator, the Severo Ochoa grant awarded to IRB Barcelona by the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities, and the NIH/NCI.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-08
Hispanic immigrants of working age -- 20 to 54 years old -- are over 11 times more likely to die of COVID-19 than U.S.-born men and women who are not Hispanic, according to a USC study of California death certificate data from 2020.
The study, published Monday in the END ...
2021-04-08
QUT researchers have used carbon dots, created from human hair waste sourced from a Brisbane barbershop, to create a kind of "armour" to improve the performance of cutting-edge solar technology.
In a study published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A, the researchers led by Professor Hongxia Wang in collaboration with Associate Professor Prashant Sonar of QUT's Centre for Materials Science showed the carbon nanodots could be used to improve the performance of perovskites solar cells.
Perovskites solar cells, a relatively new photovoltaic technology, are seen as the best PV candidate to deliver low-cost, highly efficient solar electricity in coming years. ...
2021-04-08
EUGENE, Ore. -- April 8, 2021 -- Researchers exploring the developing central nervous system of fruit flies have identified nonelectrical cells that transition the brain from highly plastic into a less moldable, mature state.
The cells, known as astrocytes for their star-like shapes, and associated genes eventually could become therapeutic targets, said University of Oregon postdoctoral researcher Sarah Ackerman, who led the research.
"All of the cell types and signaling pathways I looked at are present in humans," Ackerman said. "Two of the genes that I ...
2021-04-08
More than a third of the Antarctic's ice shelf area could be at risk of collapsing into the sea if global temperatures reach 4°C above pre-industrial levels, new research has shown.
The University of Reading led the most detailed ever study forecasting how vulnerable the vast floating platforms of ice surrounding Antarctica will become to dramatic collapse events caused by melting and runoff, as climate change forces temperatures to rise.
It found that 34% of the area of all Antarctic ice shelves - around half a million square kilometres - including 67% of ice shelf area on the Antarctic Peninsula, would be at risk of destabilisation under 4°C of warming. Limiting temperature ...
2021-04-08
INDIANAPOLIS--Worldwide, 1 in 4 people will suffer from a depressive episode in their lifetime.
While current diagnosis and treatment approaches are largely trial and error, a breakthrough study by Indiana University School of Medicine researchers sheds new light on the biological basis of mood disorders, and offers a promising blood test aimed at a precision medicine approach to treatment.
Led by Alexander B. Niculescu, MD, PhD, Professor of Psychiatry at IU School of Medicine, the study was published today in the high impact journal Molecular Psychiatry . The work builds on previous research conducted by Niculescu and his colleagues into blood biomarkers that track suicidality as well as pain, post-traumatic stress ...
2021-04-08
The almost 15-million-year-old Nördlinger Ries is an asteroid impact crater filled with lake sediments. Its structure is comparable to the craters currently being explored on Mars. In addition to various other deposits on the rim of the basin, the crater fill is mainly formed by stratified clay deposits. Unexpectedly, a research team led by the University of Göttingen has now discovered a volcanic ash layer in the asteroid crater. In addition, the team was able to show that the ground under the crater is sinking in the long term, which provides important ...
2021-04-08
LOUISVILLE, Ky. - When a new drug is being developed, the first question is, "Does it work?" The second question is, "Does it do harm?" No matter how effective a therapy is, if it harms the patient in the process, it has little value.
Doctoral student Robert Skolik and Associate Professor Michael Menze, Ph.D., in the Department of Biology at the University of Louisville, have found a way to make cell cultures respond more closely to normal cells, allowing drugs to be screened for toxicity earlier in the research timeline.
The vast majority of cells used for biomedical research are derived from cancer tissues stored in biorepositories. They are cheap to maintain, easy to grow and multiply quickly. Specifically, ...
2021-04-08
PISCATAWAY, NJ - Adolescents who frequently see billboard or storefront advertisements for recreational cannabis are more likely to use the drug weekly and to have symptoms of a cannabis use disorder, according to a new study in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
Despite use being illegal for those below age 21 even in states that have approved recreational marijuana, "legalization may alter the ways that youth use cannabis," write the study authors, led by Pamela J. Trangenstein, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
An increasing number of states have legalized or are considering legalizing recreational marijuana, and public concern over the risks of cannabis use has declined in recent ...
2021-04-08
A horse's gut microbiome communicates with its host by sending chemical signals to its cells, which has the effect of helping the horse to extend its energy output, finds a new study published in Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences. This exciting discovery paves the way for dietary supplements that could enhance equine athletic performance.
"We are one of the first to demonstrate that certain types of equine gut bacteria produce chemical signals that communicate with the mitochondria in the horse's cells that regulate and generate energy," says Eric Barrey, author of this study and the Integrative Biology and Equine Genetics team leader at the National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food and Environment, France. "We believe that metabolites - small molecules created ...
2021-04-08
Eliminating racist and anti-LGBTQ policies is essential to improving the health of Black gay, bisexual and other sexual minority men, according to a Rutgers-led research team.
The study, published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, examined the impact that U.S. state-level structural racism and anti-LGBTQ policies have on the psychological and behavioral health of Black and white sexual minority men.
"Our results illuminate the compounding effects of racist and anti-LGBTQ policies and their implementation for Black gay, bisexual, and queer men. To improve mental and physical health and support their human rights, these oppressive policies must be changed," said lead author Devin English, an assistant professor at Rutgers School of Public Health.
The researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists at IRB Barcelona identify a potential target to treat lung cancer