(Press-News.org) Study: "The Infrastructure of Social Control: A Multi-Level Counterfactual Analysis of Surveillance, Punishment, Achievement, and Persistence"
Authors: Odis Johnson (Johns Hopkins University), Jason F. Jabbari (Washington University in St. Louis)
This study will be presented today at the AERA 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting.
Session: The School-to-Prison and Prison-to-School Pipelines: Studies of the Nexus of Schooling and the Justice System
Date/Time: Sunday, April 11, 10:40 a.m. - 12:10 p.m. ET
Main Findings:
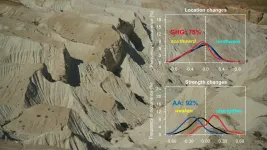
After controlling for levels of school social disorder and student misbehavior, students attending high-surveillance high schools are more likely to be subjected to in-school suspension than those at low-surveillance schools, have lower math achievement, and are less likely to attend college.
Black students are four times more likely to attend a high versus low-surveillance school.
Details:
In response to decades of mass shootings, policymakers have increased surveillance measures in schools in an effort to ensure more safe learning environments. These can include detection mechanisms (e.g., metal detectors and drug sniffing dogs), security personnel (e.g., school resource officers), visual monitors (e.g., security cameras), and restrictions on cultural expressions (e.g., strict dress codes)
Recent research has suggested that these measures have not necessarily made schools safer. Rather, instead of being used to thwart the uncommon school shooting, these surveillance measures may increase the capacity for schools to identify and punish students for more common and less-serious offenses.
This study examined the relationship between high-surveillance schools and in-school suspensions for minor offenses, math achievement, and college attendance. In-school suspensions keep students in school but isolate them from the rest of the student population.
The authors used data from the U.S. Department of Education's Educational Longitudinal Study of 2002 to examine outcomes on approximately 6,000 students across the country.
The authors found that students who attend high-surveillance schools are more likely to be poor, Black, come from a single parent home, and to have previously repeated a grade. These students are also more likely to attend schools in an urban area with higher perceptions of crime and lower perceptions of safety.
After controlling for levels of school social disorder and student misbehavior, students attending high-surveillance schools were more likely to be subjected to in-school suspension than those at low-surveillance schools.
The authors found that attending a high-surveillance school also significantly decreases 12th grade math test scores and decreases college attendance, with higher rates of suspensions partially explaining the relationships.
"High-surveillance schools create the capacity for high-suspension schools to exist," said Odis Johnson, a professor at Johns Hopkins University and executive director of the Johns Hopkins Center for Safe and Healthy Schools. "Greater detection leads to greater punishment, regardless of the students who attend these schools, which ultimately decreases academic achievement and college enrollment."
"When considering the costs of these apparatuses of surveillance, efforts should be made to make schools feel less like prisons," Johnson said. "Not only are these measures not the reasons why schools are safer today than they were in the past, but they may be placing more students on the discipline track and fewer students on the STEM track, and reducing the college enrollment of minoritized students. In schools that are unable to remove surveillance mechanisms, efforts should be made to both reduce suspensions and improve math achievement."
"We argue that if we were able reform schools to lessen the influence of social control through surveillance, disproportionate suspensions, and their impacts on math test scores, young Black adolescents of both genders, would be more likely to enter college," said Johnson.
To request a copy of the working paper, or to talk to study authors, please contact AERA Communications: Tony Pals, Director of Communications, tpals@aera.net, cell: (202) 288-9333; Tong Wu, Communications Associate, twu@aera.net, cell: (202) 957-3802
INFORMATION:
About AERA
The American Educational Research Association (AERA) is the largest national interdisciplinary research association devoted to the scientific study of education and learning. Founded in 1916, AERA advances knowledge about education, encourages scholarly inquiry related to education, and promotes the use of research to improve education and serve the public good. Find AERA on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
New research by Yale Cancer Center shows insights into modeling resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors, a form of cancer immunotherapy. The study was presented today at the American Association of Cancer Research (AACR) virtual annual meeting.
"Acquired resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors is a growing clinical challenge. About 50% of lung cancer patients who initially respond to immune checkpoint inhibitors eventually develop acquired resistance to these therapies," said Camila Robles-Oteiza, lead author of the study from Yale Cancer Center. ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Coastal communities face increasing danger from rising water and storms, but the level of risk will be more closely tied to policy decisions regarding development than the varying conditions associated with climate change, new research by Oregon State University suggests.
The findings, published in the journal Water, provide an important framework for managing the interactions between human-made and natural systems in cities and towns along shorelines as the Earth continues to warm, the researchers said.
Professor Peter Ruggiero of OSU's College of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric Sciences and John Bolte, chair of OSU's Biological and Ecological Engineering program, led the study, which employed a modeling platform known as ...
Groundbreaking research from Tel Aviv University may lead to a significant breakthrough in the battle against deadly brain cancer. To begin with, the researchers identified a failure in the brain's immune system, leading to the amplification of cell division and spread of Glioblastoma cancer cells. The failure results partially from the secretion of a protein called P-Selectin (SELP), which, when bound to its receptor on the brain immune cells, alters their function so that instead of inhibiting the spread of cancer cells, they do the opposite, enabling them to proliferate and penetrate brain tissues.
At the next stage of the study, the researchers were able to inhibit the secretion of the SELP protein, thereby neutralizing the failure in the immune system, restoring its normal activity, ...
A comprehensive analysis of 80 scientific studies has identified a 'window of impairment' of between three and 10 hours caused by moderate to high doses of the intoxicating component of cannabis, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The findings have implications for the application of drug-driving laws globally, researchers say.
The study found the exact duration of impairment depends on the dose of THC, whether the THC is inhaled or taken orally, whether the cannabis user is regular or occasional and the demands of the task being undertaken while intoxicated.
The study represents the first ...
The search for life on other planets has received a major boost after scientists revealed the spectral signatures of almost 1000 atmospheric molecules that may be involved in the production or consumption of phosphine, a study led by UNSW Sydney revealed.
Scientists have long conjectured that phosphine - a chemical compound made of one phosphorous atom surrounded by three hydrogen atoms (PH3) - may indicate evidence of life if found in the atmospheres of small rocky planets like our own, where it is produced by the biological activity of bacteria.
So when an international team of scientists last year claimed to ...
The economies of northern Central Asia rely heavily on agriculture and are particularly affected by changes in the local hydrological cycle. However, this region is one of the largest dryland regions in the Northern Hemisphere and is facing a crisis of water resources shortage in recent decades. One example is the rapid desiccation and salinization of the Aral Sea. While the construction of dams, diversion of waterways and wasting of water have been blamed for the shortage, how climate change has influenced regional water resources remains unknown.
In a recently published research article in Geophysical Research Letters (drying trend over northern Central Asia), Jie Jiang and Tianjun Zhou from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese ...
Clouds play a key role in balancing incoming and outgoing solar and thermal radiation. This is a critical process in the earth-atmosphere system. Monitoring cloud height, particle size, particle concentration, etc. are integral to understanding climate dynamics and global climate change. These physical attributes determine the radiative forcing effect of a cloud, or how much incoming radiation that a cloud reflects back to space. Satellites and ground-based radar can measure the cloud top height (CTH). However, inconsistencies exist between various satellites and radar data due to different detection methods and algorithms used to process raw information.
To quantify these conflicts, Bo Liu, jointly supervised by Dr. Juan Huo and Prof. Daren Lyu from Institute of Atmospheric ...
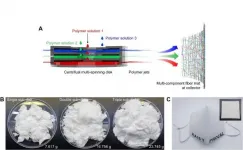
KAIST researchers have developed a novel nanofiber production technique called 'centrifugal multispinning' that will open the door for the safe and cost-effective mass production of high-performance polymer nanofibers. This new technique, which has shown up to a 300 times higher nanofiber production rate per hour than that of the conventional electrospinning method, has many potential applications including the development of face mask filters for coronavirus protection.
Nanofibers make good face mask filters because their mechanical interactions with aerosol particles give them a greater ability ...
Family history of early cardiac events in first degree relatives such as a parent or sibling is a major risk factor, especially for premature events. Currently, data on risks in close relatives of patients with a family history of premature heart attacks, chronic stable angina or peripheral vascular disease are sparse.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University's Schmidt College of Medicine in collaboration with an international team of leading scientists in Italy, the United Kingdom and Poland, assembled a consecutive series of 230 patients with premature onset of heart attacks, strokes, angina or peripheral artery disease and a comparison group of apparently healthy men and women during a 24-month period. The comparison group had no family or ...
Breast cancer survivors who are overweight have a statistically significant increased risk of developing second primary cancers, according to results from a study conducted by Kaiser Permanente researchers and published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
There are approximately 3.9 million breast cancer survivors in the United States today and studies have found women diagnosed with breast cancer have an 18% increased risk for developing a second cancer compared to the general population. This increased risk is likely due to shared risk factors between the first and second cancers, genetic susceptibility, and long-term effects of breast ...