(Press-News.org) Why is sugar not transparent? Because light that penetrates a piece of sugar is scattered, altered and deflected in a highly complicated way. However, as a research team from TU Wien (Vienna) and Utrecht University (Netherlands) has now been able to show, there is a class of very special light waves for which this does not apply: for any specific disordered medium--such as the sugar cube you may just have put in your coffee--tailor-made light beams can be constructed that are practically not changed by this medium, but only attenuated. The light beam penetrates the medium, and a light pattern arrives on the other side that has the same shape as if the medium were not there at all.
This idea of "scattering-invariant modes of light" can also be used to specifically examine the interior of objects. The results have now been published in the journal Nature Photonics.
Astronomically many possible wave forms
The waves on a turbulent water surface can take on an infinite number of different shapes--and in a similar way, light waves can also be made in countless different forms. "Each of these light wave patterns is changed and deflected in a very specific way when you send it through a disordered medium," explains Prof. Stefan Rotter from the Institute of Theoretical Physics at TU Wien.
Together with his team, Stefan Rotter is developing mathematical methods to describe such light scattering effects. The expertise to produce and characterise such complex light fields was contributed by the team around Prof. Allard Mosk at Utrecht University. "As a light-scattering medium, we used a layer of zinc oxide--an opaque, white powder of completely randomly arranged nanoparticles," explains Allard Mosk, the head of the experimental research group.
First, you have to characterise this layer precisely. You shine very specific light signals through the zinc oxide powder and measure how they arrive at the detector behind it. From this, you can then conclude how any other wave is changed by this medium--in particular, you can calculate specifically which wave pattern is changed by this zinc oxide layer exactly as if wave scattering was entirely absent in this layer.
"As we were able to show, there is a very special class of light waves--the so-called scattering-invariant light modes, which produce exactly the same wave pattern at the detector, regardless of whether the light wave was only sent through air or whether it had to penetrate the complicated zinc oxide layer," says Stefan Rotter. "In the experiment, we see that the zinc oxide actually does not change the shape of these light waves at all--they just get a little weaker overall," explains Allard Mosk.
A stellar constellation at the light detector
As special and rare as these scattering-invariant light modes may be, with the theoretically unlimited number of possible light waves, one can still find many of them. And if you combine several of these scattering-invariant light modes in the right way, you get a scattering-invariant waveform again.
"In this way, at least within certain limits, you are quite free to choose which image you want to send through the object without interference," says Jeroen Bosch, who worked on the experiment as a Ph.D. student. "For the experiment we chose a constellation as an example: The Big Dipper. And indeed, it was possible to determine a scattering-invariant wave that sends an image of the Big Dipper to the detector, regardless of whether the light wave is scattered by the zinc oxide layer or not. To the detector, the light beam looks almost the same in both cases."
A look inside the cell
This method of finding light patterns that penetrate an object largely undisturbed could also be used for imaging procedures. "In hospitals, X-rays are used to look inside the body--they have a shorter wavelength and can therefore penetrate our skin. But the way a light wave penetrates an object depends not only on the wavelength, but also on the waveform," says Matthias Kühmayer, who works as a Ph.D. student on computer simulations of wave propagation. "If you want to focus light inside an object at certain points, then our method opens up completely new possibilities. We were able to show that using our approach the light distribution inside the zinc oxide layer can also be specifically controlled." This could be interesting for biological experiments, for example, where you want to introduce light at very specific points in order to look deep inside cells.
What the joint publication of the scientists from the Netherlands and Austria shows already is how important international cooperation between theory and experiment is for achieving progress in this area of research.
INFORMATION:
Original publication
P. Pai, J. Bosch, M. Kühmayer, S. Rotter, A.P. Mosk; Scattering invariant modes of light in complex media, Nature Photonics (2021). https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00789-9 or https://rdcu.be/cikbl
Contact
Prof. Stefan Rotter
Institute for Theoretical Physics
TU Wien
Wiedner Hauptstraße 8-10, 1040 Vienna, Austria
+43 1 58801 13618
stefan.rotter@tuwien.ac.at
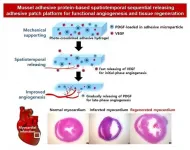
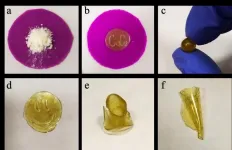
Blood vessels deliver nutrients and oxygen to each organ in our body. They are difficult to completely restore to their original conditions once damaged by myocardial infarction or severe ischemic diseases. This is because various angiogenic growth factors must be applied sequentially in order to restore the vascular structure. Recently, a research team at POSTECH has bioengineered a novel adhesive patch platform that can efficiently deliver blood vessel-forming growth factors spatiotemporally using mussel adhesive protein (MAP), a bio-adhesive material that is made from mussels harmless to humans.
A POSTECH research team led by Professor Hyung Joon ...
Squirrels and other tree-dwelling rodents evolved to have bigger brains than their burrowing cousins, a study suggests.
This greater brain power has given them key abilities needed to thrive in woodland habitats, including better vision and motor skills, and improved head and eye movements, researchers say.
Scientists have shed light on how the brains of rodents - a diverse group that accounts for more than 40 per cent of all mammals - have changed since they evolved around 50 million years ago.
Few studies looking into factors affecting brain size in mammals have taken account ...
New Orleans, LA - A study led by Hui-Yi Lin, Ph.D., Professor of Biostatistics, and a team of researchers at LSU Health New Orleans Schools of Public Health and Medicine has found that adequate levels of five antioxidants may reduce infection with the strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) associated with cervical cancer development. Findings are published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
Although previous studies have suggested that the onset of HPV-related cancer development may be activated by oxidative stress, the association had not been clearly understood. This study evaluated associations between 15 antioxidants and vaginal HPV infection status -- no, low-risk, and oncogenic/high-risk HPV (HR-HPV) -- in 11,070 women aged 18-59 who participated ...
In 2018, Pompeu Fabra University launched its Planetary Wellbeing initiative, a long-term institutional strategy spurred by the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) and based on the Planetary Health project promoted by the Rockefeller Foundation and The Lancet.
Fifteen academics and public officials, led by the three directors of the initiative, Josep Maria Antó, scientific director of ISGlobal; Josep Lluís Martí, UPF vice-rector for innovation projects, and Jaume Casals, UPF rector, are the authors of an academic article published in the journal ...
Cancer is one of the top causes of death worldwide. The cancer burden is related not only to genetic predisposition, but also to environmental pollution and socioeconomic factors such as lifestyle. Consequently, the burden of this disease is not uniform across all countries. In fact, the public health of China, a country known for the rapid change in its development status in the last few decades, has undergone a paradigm shift with respect to cancer incidence and mortality.
To better understand the cancer burden of the country, a team of researchers from Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College reviewed the data of GLOBOCAN 2020, an online database of cancer incidence and mortality compiled by the International Agency for Research ...
Researchers at the Laboratory of Cluster Catalysis at St Petersburg University have synthesised polymers from biomass. What makes them different is that they can be easily recycled.
Today, our life is simply unthinkable without polymers. Plastics, fibres, films, paint and lacquer coating - they are all polymers. We use them both in our everyday life and in industry. Yet the goods made from polymers, e.g. bottles, bags, or disposable tableware, are used just once or for a short period of time before they are thrown away. Due to the chemical compounds that they may release during recycling, they pose a real threat to our environment.
There ...
Study: "Students Enrolled in Late-Start-Time Districts Report Higher Academic Achievement and Sleeping More"
Authors: Julio Caesar (Bloomington Public Schools), Rik Lamm (University of Minnesota), Michael C. Rodriguez (University of Minnesota), David J. Heistad (Bloomington Public Schools)
This study will be presented today at the AERA 2021 Annual Meeting.
Session: Organizational Effects Examining Academic Achievement and Student Support
Date/Time: Saturday, April 10, 2:30 p.m. - 4:00 p.m. ET
Main Finding:
Later school start times are linked ...
Study: "Exploring the Association Between Student-College Match and Student Outcomes Over Time"
Author: Amanda M. Cook (Northwestern University)
This study will be presented today at the AERA 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting.
Session: Nuances and Challenges to Traditional Notions of College Success
Date/Time: Saturday, April 10, 10:40 a.m. - 12:10 p.m. ET
Main Findings:
Over the past 20 years, bachelor's degree completion rates for students who overmatch (i.e., attend colleges that may appear too academically selective for them) have improved substantially. Over the same time period, bachelor's degree completion rates for students who undermatch (i.e., attend colleges that appear too academically unselective ...
Study: "Characterizing Remote Instruction Provided by Elementary School Teachers during School Closures due to COVID-19"
Authors: Michael Hebert (University of Nebraska-Lincoln), J. Marc Goodrich (University of Nebraska-Lincoln), Jessica M. Namkung (University of Nebraska-Lincoln)
This study will be presented today at the AERA 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting.
Session: Technology Supports and Experiences During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Date/Time: Saturday, April 10, 10:40 a.m. - 11:40 a.m. ET
Main Findings:
While teachers in spring 2020 felt that 60 percent of their students were prepared for the next grade level, in ...
Study: "Do Students in Gifted Programs Perform Better? Linking Gifted Program Participants to Achievement and Nonachievement Outcomes"
Authors: Christopher Redding (University of Florida), Jason A. Grissom (Vanderbilt University)
This study will be presented today at the AERA 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting.
Session: On the Road to Equity: Studies of the Impact and Influences of Education Policy
Date/Time: Saturday, April 10, 2:30 p.m. - 4:00 p.m. ET
Main Findings:
Participating in elementary school gifted programs is associated with reading and math achievement for the average student, ...