(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Toronto have found that a calorie labelled is not the same as a calorie digested and absorbed, when the food source is almonds.
The findings should help alleviate concerns that almonds contribute to weight gain, which persist despite the widely recognized benefits of nuts as a plant-based source of protein, vitamins and minerals.
"Nuts have generally been thought of as healthy the last two decades, but the messaging around nuts has often come with a disclaimer that they are high in fat and energy," said John Sievenpiper, principal investigator on the study and an associate professor in the departments of nutritional sciences and medicine at the Temerty Faculty of Medicine.
"We still see that caveat in the media and on the internet today, and it has been part of many clinical guidelines, although that is changing," said Sievenpiper, who is also a staff physician and scientist at St. Michael's Hospital, Unity Health Toronto.
"Other researchers have shown that there is a bioaccessibility issue with nuts, that a calorie labelled may not be a calorie absorbed. This study quantifies that effect with almonds in a relevant population," Sievenpiper said.
The journal Mayo Clinic Proceedings published the findings today.
The researchers found that after digestion, about 20 per cent of calories derived largely from fat in almonds remained unabsorbed, which they observed in stool samples. That translated to about two per cent less energy absorbed from the diet overall among study participants.
A person eating the same amount of almonds in a daily diet of 2,000 to 3,000 calories would absorb 40 to 60 calories less than would be predicted by Atwater factors, on which many food labels are based. That could result in weight loss up to 2.9 kilograms or 6.3 pounds over a year, assuming no compensation in the form of increased intake or decreased energy expenditure.
Participants in the study did not gain weight, which is consistent with the majority of high-quality trials that measure nut consumption and weight gain, some of which show an association with weight loss, Sievenpiper said.
The researchers used a randomized crossover trial to study 22 women and men with high cholesterol, who underwent a series of three, month-long dietary interventions separated by a week-long washout period.
All study participants consumed an NCEP Step-2 diet (low in saturated fat and cholesterol, part of the U.S. National Cholesterol Education Program). The three dietary interventions were full-dose almonds (75 grams per day or three quarters of a cup); half-dose almonds plus half-dose muffins; and full-dose muffins as a study control.
Nutritional makeup of the muffins matched the almonds in amount of protein, fibre and fats.
"One unique aspect of this study is that it assessed people with high cholesterol, who are at greater risk for cardiovascular disease," said Stephanie Nishi, a doctoral student in nutritional sciences at the time of the study who is now a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Rovira i Virgili in Spain.
"That has not been done in this population before, and it's important because this group typically gets many messages to eat more nuts, owing to the evidence for nut consumption and heart health," Nishi said.
Nishi and Sievenpiper both said there is a big gap between the number of nuts people are recommended to consume and how many they actually eat, generally and in populations at risk for cardiovascular and other disease.
Further barriers stemming from concerns about weight gain are counter-productive, they said.
Diabetes Canada recently adjusted their guidelines based in part on the study's findings, and to avoid the stigma around nuts and weight gain, said Sievenpiper, who has contributed to guidelines for patients with diabetes and other metabolic disorders, and for cardiovascular disease.
INFORMATION:
Inland waters are an important component of the global carbon cycle and function as active reactors, transporting and transforming large quantities of naturally- and anthropogenically-derived carbon. Previous studies suggest that inland waters are major sources for greenhouse gas emissions to the atmosphere, yet these emissions are poorly constrained (Note 1).
As a primary greenhouse gas that drives global climate change, carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from inland waters play a key role in assessing global carbon cycle. While most efforts over the last decade have focused on refining the emission flux estimates at the regional and global scales, scientists do not fully understand the responsiveness of regional ...
A recent study finds U.S. companies that have a substantial number of employees in foreign jurisdictions with lower tax rates are more likely than their peers to "artificially" locate earnings in those jurisdictions - and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is less likely to challenge these complex tax-planning activities.
"Many politicians seek to encourage domestic employment and discourage sending jobs overseas," says Nathan Goldman, co-author of the study and an assistant professor of accounting in North Carolina State University's Poole College of Management. "To do that, they'll need to address elements of corporate tax policy that effectively encourage ...
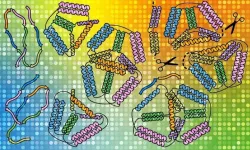
Origami may sound more like art than science, but a complex folding pathway that proteins use to determine their shape has been harnessed by molecular biologists, enabling them to build some of the most complex synthetic protein nanostructures to date.
Using EMBL Hamburg's world-class beamline P12 at DESY's PETRA III synchrotron, a team of Slovenian researchers, in collaboration with EMBL's Svergun group, directed powerful X-ray beams at artificial proteins called coiled-coil origami. The proteins were designed to fold into a particular shape based on short modules that interact ...
Smoking cannabis when you're young may increase your risk of developing heart disease later, according to a recent University of Guelph study.
In the first study to look at specific risk indicators for cardiovascular disease (CVD) in young, healthy cannabis users, researchers found subtle but potentially important changes in heart and artery function.
Cigarette smoking is known to affect cardiovascular health, causing changes to blood vessels and the heart. Less is known about the impact of smoking cannabis on long-term CVD risk, even as use of the substance grows in Canada and abroad. Cannabis is the most commonly used recreational substance worldwide after ...
High blood pressure, the most important cause of disease worldwide, accelerates atherosclerosis but the mechanism is unknown. Using gene modified minipigs, researchers from the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) and Aarhus University (Denmark), demonstrate that high blood pressure alters the structure of arteries leading to more accumulation of LDL cholesterol and faster development of atherosclerosis. The study has been published in The Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
Blood pressure-lowering drugs are routinely used to prevent the development of atherosclerosis and heart disease, but the mechanism of this effect is still ...
The detrimental impact of pesticides on non-target organisms is one of the most urgent concerns in current agriculture. Double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) represent the most species-specific class of pesticides to date, potentially allowing control of a target pest without effecting other species. The unprecedented target-specificity of dsRNA is due to its nucleotide sequence-specific mode of action that results in post-transcriptional gene silencing, or RNA interference (RNAi), in the target species. The development and field use of dsRNAs, via both the insertion of transgenes into the plant genome and the application ...
The plasticisers contained in many everyday objects can impair important brain functions in humans. Biologists from the University of Bayreuth warn of this danger in an article in Communications Biology. Their study shows that even small amounts of the plasticisers bisphenol A and bisphenol S disrupt the transmission of signals between nerve cells in the brains of fish. The researchers consider it very likely that similar interference can also occur in the brains of adult humans. They therefore call for the rapid development of alternative plasticisers that do ...
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (04/12/2021) -- A new probe into the lingering impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic revealed correlations to six unhealthy eating behaviors, according to a study by the University of Minnesota Medical School and School of Public Health. Researchers say the most concerning finding indicates a slight increase or the re-emergence of eating disorders, which kill roughly 10,200 people every year -- about one person every 52 minutes.
U of M Medical School's Melissa Simone, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, collaborated with School of Public Health ...
BOSTON - (April 12, 2021) - A new source of energy expending brown fat cells has been uncovered by researchers at the Joslin Diabetes Center, which they say points towards potential new therapeutic options for obesity. According to the new report, published today by Nature Metabolism, the key lies in the expression of a receptor called Trpv1 (temperature-sensitive ion channel transient receptor potential cation subfamily V member 1) -- a protein known to sense noxious stimuli, including pain and temperature.
Specifically, the authors point to smooth muscle cells expressing the Trpv1 receptor and identify them as a novel source of energy-burning brown fat cells (adipocytes). This should translate into increased overall energy ...
Histones are tiny proteins that bind to DNA and hold information that can help turn on or off individual genes. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet have developed a technique that makes it possible to examine how different versions of histones bind to the genome in tens of thousands of individual cells at the same time. The technique was applied to the mouse brain and can be used to study epigenetics at a single-cell level in other complex tissues. The study is published in the journal Nature Biotechnology.
"This technique will be an important tool for examining what makes cells different from each other at the epigenetic level," says Marek ...