INFORMATION:
These findings appear online in the journal Stem Cell Reports.
Funding for this research was provided by Evergrande MassCPR, Fast Grants, and NIH NCATS grant UL1TR001430 awards to EM. AM is supported by the Kilachand Multicellular Design Program at Boston University. GM is supported by NIH Grants N0175N92020C00005 and 1R01DA05188901
Study provides novel platform to study how SaRS-CoV-2 affects the gut
May help design better diagnostic and therapeutic tools to fight the virus
2021-04-13
(Press-News.org) (Boston)--How could studying gastrointestinal cells help the fight against COVD-19, which is a respiratory disease? According to a team led by Gustavo Mostoslavsky, MD, PhD, at the BU/BMC Center for Regenerative Medicine (CReM) and Elke Mühlberger, PhD, from the National Emerging Infectious Diseases Laboratories (NEIDL) at Boston University, testing how SARS-CoV-2 affects the gut can potentially serve to test novel therapeutics for COVID-19.
In order to study SARS-CoV-2, models are needed that can duplicate disease development in humans, identify potential targets and enable drug testing. BU researchers have created human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC)-derived intestinal organoids or 3-D models that can be infected and replicated with SARS-CoV-2.
iPSC are stem cells derived from the donated skin or blood cells that are reprogrammed back to an embryonic stem cell-like state and then can be developed into any cell type in the body.
"Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived intestinal organoids represent an inexhaustible cellular resource that could serve as a valuable tool to study SARS-CoV-2, as well as other intestinal viruses that infect the intestinal epithelium," explained corresponding author Mostoslavsky, associate professor of microbiology at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) and co-director of the CReM.
Using human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) the researchers differentiated the iPSC cells into colonic and small intestine 3D organoids. The organoids were then passed along to the Mühlberger lab at the NEIDL where they were infected with SARS-CoV-2 to analyze the effect of infection on the cells by staining against markers, by electron microscopy and by RNA-sequencing.
"Our findings suggests that different epithelial tissues (such as the lung and the gut) react in similar manner to SARS-CoV-2 infection and therefore can help identify common mechanisms of disease that can be targeted by drugs," added Mühlberger, director of Integrated Science Services at the NEIDL and professor of microbiology at BUSM.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
DNA structure itself is involved in genome regulation
2021-04-13
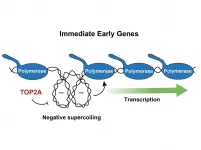
The (when stretched) two-metre-long DNA molecule in each human cell is continuously being unpacked and packed again to enable the expression of genetic information. When genes must be accessed for transcription, the DNA double helix unwinds and the strands separate from each other so that all the elements needed for gene expression can access the relevant DNA region. This process results in the accumulation of DNA supercoiling that needs to be resolved. A study recently published by Felipe Cortés, Head of the Topology and DNA Breaks Group at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), and the members of his team, in cooperation with Silvia Jimeno González, Professor ...
Scaling up genome editing big in tiny worms
2021-04-13
Understanding the effects of specific mutations in gene regulatory regions - the sections of DNA and RNA that turn genes on and off - is important to unraveling how the genome works, as well as normal development and disease. But studying a large variety of mutations in these regulatory regions in a systematic way is a monumental task. While progress has been made in cell lines and yeast, few studies in live animals have been done, especially in large populations.
Experimental and computational biologists at the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC) have teamed up to establish an approach to induce thousands of different mutations in up to 1 million ...
The role of hydrophobic molecules in catalytic reactions
2021-04-13
Electrochemical processes could be used to convert CO2 into useful starting materials for industry. To optimise the processes, chemists are attempting to calculate in detail the energy costs caused by the various reaction partners and steps. Researchers from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) and Sorbonne Université in Paris have discovered how small hydrophobic molecules, such as CO2, contribute to the energy costs of such reactions by analysing how the molecules interact in water at the interface. The team describes the results in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, PNAS for short, published online on 13 April 2021.
To conduct the ...
The amount of time children spend watching screens influences their eating habits
2021-04-13
The time children and adolescents spend on screen time entertainment -computers, mobile phones, television and video games- adversely affects their eating habits. This is the main conclusion drawn from a research carried out by EpiPHAAN (Epidemiology, Physical Activity, Accelerometry and Nutrition) research group of the University of Malaga, which further establishes that parents' education level is also associated with the adherence to the Mediterranean diet.
This research was conducted within the PASOS Study -Physical Activity, Sedentarism, lifestyles and Obesity in Spanish youth- of Gasol Foundation, which analyzed more than ...
UK cancer patients more likely to die following COVID-19 than European cancer patients
2021-04-13
Cancer patients from the UK were 1.5 times more likely to die following a diagnosis with COVID-19 than cancer patients from European countries.
This is the finding of a study of over 1000 patients - 924 from European countries and 468 from the UK - during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. The research team, led by Imperial College London, say the study highlights the need for UK cancer patients to be prioritised for vaccination.
The study tracked data between 27 February to 10 September 2020, across 27 centres in six countries: Italy, Spain, France, Belgium, Germany and the UK.
The results, published in the European Journal of Cancer, showed that 30 days after a COVID-19 diagnosis, 40.38 per cent of UK cancer patients had died, versus 26.5 per cent of ...
Machine learning can help slow down future pandemics
2021-04-13
Artificial intelligence could be one of the keys for limiting the spread of infection in future pandemics. In a new study, researchers at the University of Gothenburg have investigated how machine learning can be used to find effective testing methods during epidemic outbreaks, thereby helping to better control the outbreaks.
In the study, the researchers developed a method to improve testing strategies during epidemic outbreaks and with relatively limited information be able to predict which individuals offer the best potential for testing.
"This can be a first step towards society ...
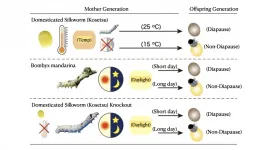
Silk moth's diapause reverts back to ancestors' through gene editing!?
2021-04-13
Diapause is a phenomenon in which animals and insects foresee changes in the environment and actively reduce metabolism, or halt regular differentiation and development. It is an adaptation strategy for adverse environments such as surviving winters, but also to encourage uniform growth of the generational group. By knocking out genes that allow the silkworm to detect temperature, researchers at Shinshu University et al. found that the silk moth diapause changes from temperature to photoperiod, or day length. This is not only valuable as an elucidation of the molecular mechanism in the environmental response mechanism of organisms such as insects, but also a very important finding in exploring the process of domestication of silk ...
Skoltech studies collective behavior of nanosatellites
2021-04-13
Scientists from the Skoltech Space Center (SSC) have developed nanosatellite interaction algorithms for scientific measurements using a tetrahedral orbital formation of CubeSats that exchange data and apply interpolation algorithms to create local maps of physical measurements in real time. The study presents an example of geomagnetic field measurement, which shows that these data can be used by other satellites for attitude control and, therefore, provided on a data-as-a-service basis. The research was published in the journal Advances in Space Research.
SSC is the research ...
People may trust computers more than humans
2021-04-13
Despite increasing concern over the intrusion of algorithms in daily life, people may be more willing to trust a computer program than their fellow humans, especially if a task becomes too challenging, according to new research from data scientists at the University of Georgia.
From choosing the next song on your playlist to choosing the right size pants, people are relying more on the advice of algorithms to help make everyday decisions and streamline their lives.
"Algorithms are able to do a huge number of tasks, and the number of tasks that they are able to do is expanding practically every day," said Eric Bogert, a Ph.D. student in the Terry College of ...
Study shows powered prosthetic ankles can restore a wide range of functions for amputees
2021-04-13
A recent case study from North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill demonstrates that, with training, neural control of a powered prosthetic ankle can restore a wide range of abilities, including standing on very challenging surfaces and squatting. The researchers are currently working with a larger group of study participants to see how broadly applicable the findings may be.
"This case study shows that it is possible to use these neural control technologies, in which devices respond to electrical signals from a patient's muscles, to help patients using robotic prosthetic ankles move more naturally and intuitively," says Helen Huang, corresponding author of the study. Huang ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Study provides novel platform to study how SaRS-CoV-2 affects the gutMay help design better diagnostic and therapeutic tools to fight the virus