Giant electronic conductivity change driven by artificial switch of crystal dimensionality
2021-04-13
(Press-News.org) The electronic properties of solid materials are highly dependent on crystal structures and their dimensionalities (i.e., whether the crystals have predominantly 2D or 3D structures). As Professor Takayoshi Katase of Tokyo Institute of Technology notes, this fact has an important corollary: "If the crystal structure dimensionality can be switched reversibly in the same material, a drastic property change may be controllable." This insight led Prof. Katase and his research team at Tokyo Institute of Technology, in partnership with collaborators at Osaka University and National Institute for Materials Science, to embark on research into the possibility of switching the crystal structure dimensionality of a lead-tin-selenide alloy semiconductor. Their results appear in a paper published in a recent issue of the peer-reviewed journal Science Advances.
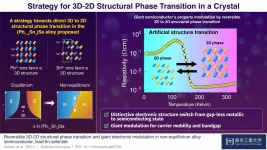
The lead-tin-selenide alloy, (Pb1?xSnx)Se is an appropriate focus for such research because the lead ions (Pb2+) and tin ions (Sn2+) favor distinct crystal dimensionalities. Specifically, pure lead selenide (PbSe) has a 3D crystal structure, whereas pure tin selenide (SnSe) has a 2D crystal structure. SnSe has bandgap of 1.1 eV, similar to the conventional semiconductor Si. Meanwhile, PbSe has narrow bandgap of 0.3 eV and shows 1 order of magnitude higher carrier mobility than SnSe. In particular, the 3D (Pb1-xSnx)Se has gathered much attention as a topological insulator. That is, the substitution for Pb with Sn in the 3D PbSe reduces the band gap and finally produces a gap-less Dirac-like state. Therefore, if these crystal structure dimensionality can be switched by external stresses such as temperature, it would lead to a giant functional phase transition, such as large electronic conductivity change and topological state transition, enhanced by the distinct electronic structure changes.
The alloying PbSe and SnSe would manipulate the drastic transition in structure, and such (Pb1-xSnx)Se alloy should induce strong frustration around phase boundaries. However, there is no direct phase boundary between the 3D PbSe and the 2D SnSe phases under thermal equilibrium. Through their experiments, Prof. Katase and his research team successfully developed a method for growing the nonequilibrium lead-tin-selenide alloy crystals with equal amounts of Pb2+ and Sn2+ ions (i.e., (Pb0.5Sn0.5)Se) that underwent direct structural phase transitions between 2D and 3D forms based on temperature. At lower temperatures, the 2D crystal structure predominated, whereas at higher temperatures, the 3D structure predominated. The low-temperature 2D crystal structure was more resistant to electrical current than the high-temperature 3D crystal was, and as the alloy was heated, its resistivity levels took a sharp dive around the temperatures at which the dimensionality phase transition occurred. The present strategy facilitates different structure dimensionality switching and further functional property switching in semiconductors using artificial phase boundary.
In sum, the research team developed a form of the semiconductor alloy (Pb1?xSnx)Se that undergoes temperature-dependent crystal dimensionality phase transitions, and these transitions have major implications for the alloy's electronic properties. When asked about the importance of his team's work, Prof. Katase notes that this form of the (Pb1?xSnx)Se alloy can "serve as a platform for fundamental scientific studies as well as the development of novel function in semiconductor technologies." This specialized alloy may, therefore, lead to exciting new semiconductor technologies with myriad benefits for humanity.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-13
A study carried out by the University of Granada indicates that smoking cannabis significantly alters key visual functions, such as visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, three-dimensional vision (stereopsis), the ability to focus, and glare sensitivity
Yet, more than 90% of users believe that using cannabis has no effect on their vision, or only a slight effect
A group of researchers from the Department of Optics of the University of Granada (UGR) has studied the effects of smoking cannabis on various visual parameters compared to the effect that the users themselves perceive the drug to have on their vision.
This study, led by Carolina Ortiz Herrera and Rosario González Anera, has been published in the journal Scientific Reports. Its main author, Sonia Ortiz Peregrina, explains that ...
2021-04-13
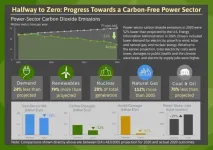
Concerns about climate change are driving a growing number of states, utilities, and corporations to set the goal of zeroing out power-sector carbon emissions. To date 17 states plus Washington, D.C. and Puerto Rico have adopted laws or executive orders to achieve 100% carbon-free electricity in the next couple of decades. Additionally, 46 U.S. utilities have pledged to go carbon free no later than 2050. Altogether, these goals cover about half of the U.S. population and economy.
These are ambitious targets, but a new look at the past 15 years in the electricity sector shows that large reductions in emissions are possible.
New research from the Department of Energy's Lawrence ...
2021-04-13
As the Rhode Island legislature considers designating the Northern Star Coral an official state emblem, researchers are finding that studying this local creature's recovery from a laboratory-induced stressor could help better understand how to protect endangered tropical corals.
A new study published today in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology, investigates antibiotic-induced disturbance of the coral (Astrangia poculata) and shows that antibiotic exposure significantly altered the composition of the coral's mucus bacterial microbiome, but that all the treated corals recovered ...
2021-04-13
A new study published in Elementa by researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz and NOAA examines traditional aspects of seafood sustainability alongside greenhouse gas emissions to better understand the "carbon footprint" of U.S. tuna fisheries.
Fisheries in the United States are among the best managed in the world, thanks to ongoing efforts to fish selectively, end overfishing, and rebuild fish stocks. But climate change could bring dramatic changes in the marine environment that threaten seafood productivity and sustainability. That's one reason why researchers ...
2021-04-13
Physicists from Swansea University are part of an international research collaboration which has identified a new technique for testing the quality of quantum correlations.
Quantum computers run their algorithms on large quantum systems of many parts, called qubits, by creating quantum correlations across all of them. It is important to verify that the actual computation procedures lead to quantum correlations of desired quality.
However, carrying out these checks is resource-intensive as the number of tests required grows exponentially with the number of qubits involved.
Researchers from the College of Science, working with colleagues from Spain ...
2021-04-13
Biomedical scientists are increasingly using deconvolution methods, those used to computationally analyze the composition of complex mixtures of cells. One of their challenges is to select one method that is appropriate for their experimental conditions among nearly 50 available.
To help with method selection, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children's Hospital have extensively evaluated 11 deconvolution methods that are based on RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) data analysis, determining each method's ...
2021-04-13
Almost all bacteria rely on the same emergency valves--protein channels that pop open under pressure, releasing a deluge of cell contents. It is a last-ditch effort, a failsafe that prevents bacteria from exploding and dying when stretched to the limit. If we understood how those protein channels worked, antibiotic drugs could be designed to open them on demand, draining a bacterium of its nutrients by exploiting a floodgate common to many species.
But these channels are tricky to operate in the lab. And how precisely they open and close, passing through a sub-conducting state and ending in a desensitized state under the influence of mechanical forces, remains poorly understood. Now, new research from ...
2021-04-13
A study done in rooms where COVID-19 patients were isolated shows that the virus's RNA - part of the genetic material inside a virus - can persist up to a month in dust.
The study did not evaluate whether dust can transmit the virus to humans. It could, however, offer another option for monitoring COVID-19 outbreaks in specific buildings, including nursing homes, offices or schools.
Karen Dannemiller, senior author of the study, has experience studying dust and its relationship to potential hazards like mold and microbes.
"When the pandemic started, we really wanted to find a way that we could help ...
2021-04-13
WHAT:
Many people who have COVID-19 make a full recovery and return to their baseline state of health; however, some people have symptoms or other sequelae weeks or months after initial SARS-CoV-2 infection. These heterogeneous symptoms were the subject of the virtual "Workshop on Post-acute Sequelae of COVID-19" hosted on Dec. 2 and 4, 2020, by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), in collaboration with other institutes and centers of the National Institutes of Health. A paper published recently in Annals of Internal Medicine ...
2021-04-13
Researchers have identified molecular signatures of the aging process in mice, publishing their results today in the open-access eLife journal.
Their analyses provide one of the most comprehensive characterisations of the molecular signatures of aging across diverse types of cells from different tissues in a mammal, and will aid future studies on aging and related topics.
Aging leads to the decline of major organs and is the main risk factor for many diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. While previous studies have highlighted different hallmarks of the aging process, the underlying molecular and cellular mechanisms ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Giant electronic conductivity change driven by artificial switch of crystal dimensionality