UBCO engineer cautions pregnant women about speed bumps
The slower the better while driving over them, says researcher
2021-04-13
(Press-News.org) Slow down. Baby on board.
So says UBC Okanagan researcher and Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering Hadi Mohammadi. His new research, conducted in collaboration with Sharif University of Technology, determines that accelerating over speed bumps poses a danger for pregnant women and their fetuses.
"There is lots of research about the importance of movement for women during pregnancy," explains Mohammadi, who teaches in the School of Engineering. "Our latest research looked specifically at the impacts of sudden acceleration on a pregnant woman."
Using new modelling based on data from crash tests and fundamental dynamic behaviours of a pregnant woman, Mohammadi and his co-authors found that accelerating over speedbumps raises concern. If driven over quickly, they caution this can lead to minor injuries to the fetal brain, cause an abnormal fetal heart rate, abdominal pain, uterine contraction, increasing uterine activity and further complications.
Occupants in a vehicle, especially pregnant women, are subjected to relatively large forces suddenly and over a short period when a vehicle accelerates over a speedbump, he explains.
Mohammadi is particularly interested in vibrations, and in this case their impact on human organs. This recent study looked at the effect of these vibrations on a woman in her third trimester of pregnancy.
Their investigation included many factors such as the speed of the car as it goes over the speedbump, the size of the speedbump as it can cause a drag on the uterus as it goes up and then down, and the fact that all this movement puts pressure on the amniotic fluid that is protecting the fetus.
"We took all these factors into account to ensure a comprehensive differential model that mirrors real-world responses and interactions of the woman and fetus."
As a result, the researchers were very specific in their recommendations. Slow down.
In fact, they advise slowing a vehicle to less than 45 km/h when hitting a speedbump, and preferably as low as 25km/h to reduce risk to the fetus.
"Obviously, there are other variables at play when a driver approaches a speedbump, but we hope our findings provide some evidence-based guidance to keep drivers and their occupants literally and figuratively safe," says Mohammadi.
Furthermore, he hopes the findings can help researchers better understand how a pregnant woman and her fetus are subjected to risk caused by a vehicle passing bumpy terrain such as speed bumps. His end goal is for his research to make vehicular safety improvements for pregnant women.
INFORMATION:
The research is published in the latest edition of the Journal of Biomechanics.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-13
When the Webster-Kirkwood Times, a community newspaper in the greater St. Louis, Missouri area, had to endure layoffs and stop publishing its print edition -- due to a loss in revenue as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic -- its readers felt the loss and began supporting the newspaper in earnest.
"A lot of times people don't know what they've got until it's gone," said Jaime Mowers, editor-in-chief of the Webster-Kirkwood Times. "Now, there is such a newfound appreciation for the newspaper. It's amazing to have the community's support, knowing we are loved that much and appreciated enough to ...
2021-04-13
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Mindfulness is big business. Downloads of mindfulness apps generate billions of dollars annually in the U.S., and their popularity continues to rise. In addition to what individual practitioners might have on their phones, schools and prisons along with 1 in 5 employers currently offer some form of mindfulness training.
Mindfulness and meditation are associated with reducing stress and anxiety, while increasing emotional well-being. Plenty of scholarship supports these benefits. But how does mindfulness affect the range of human behaviors -- so-called prosocial behaviors -- that can potentially help or benefit other people? What happens when the research looks outwardly at social effects of mindfulness rather than inwardly at its personal effects?
It's ...
2021-04-13
Human screams signal more than fear and are more acoustically diverse than previously thought, according to a study published April 13th 2021 in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Sascha Fru?hholz of the University of Zurich, and colleagues. Remarkably, non-alarming screams are perceived and processed by the brain more efficiently than alarming screams.
In nonhuman primates and other mammalian species, scream-like calls are frequently used as an alarm signal exclusively in negative contexts, such social conflicts or the presence of predators or other environmental threats. Humans are also assumed to use screams to signal danger and to scare predators. But humans scream not only when they are ...
2021-04-13
First study to examine suicides occurring around the world during the COVID-19 pandemic finds that - in high-income and upper-middle-income countries - suicide numbers have remained largely unchanged or have declined in the early months of the pandemic, compared with expected levels.
However, the authors stress that governments must remain vigilant as the longer-term mental health and economic effects of the pandemic unfold and be poised to respond if the situation changes.
Study looked at numbers of suicides in 21 countries between 1 April and 31 July 2020 and compared these with trends in the previous one to four years.
A new observational study ...
2021-04-13
Screaming can save lives. Non-human primates and other mammalian species frequently use scream-like calls when embroiled in social conflicts or to signal the presence of predators and other threats. While humans also scream to signal danger or communicate aggression, they scream when experiencing strong emotions such as despair or joy as well. However, past studies on this topic have largely focused on alarming fear screams.
Humans respond to positive screams more quickly and with higher sensitivity
In a new study, a team at the University of Zurich Department of Psychology led by Sascha Frühholz ...
2021-04-13
Living near a hazardous waste or Superfund site could cut your life short by about a year, reports Hanadi S. Rifai, John and Rebecca Moores Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering at the University of Houston. The study, published in Nature Communications and based on evaluation of 65,226 census tracts from the 2018 Census, is the first nationwide review of all hazardous waste sites and not just the 1,300 sites on the national priority list managed by the federal government.
The analysis shows a decrease of more than two months in life expectancy for those living near a Superfund site. When coupled with high disadvantage of sociodemographic factors like age, sex, marital status and income, the decrease could be nearly 15 months, ...
2021-04-13
A group of researchers led by Brazilians has used an innovative model to map gaps in the Amazon rainforest and identify factors that contribute to tree mortality. Water stress, soil fertility, and anthropic forest degradation have the most influence on gap dynamics in the world's largest and most biodiverse tropical rainforest, according to an article on the study published in Scientific Reports.
Forest gaps are most frequent in the areas with the highest levels of soil fertility, possibly because the abundance of organic material drives faster tree growth and shorter life cycles.
The main method of data collection ...
2021-04-13
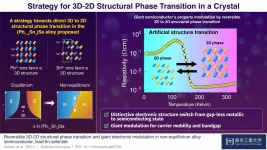
The electronic properties of solid materials are highly dependent on crystal structures and their dimensionalities (i.e., whether the crystals have predominantly 2D or 3D structures). As Professor Takayoshi Katase of Tokyo Institute of Technology notes, this fact has an important corollary: "If the crystal structure dimensionality can be switched reversibly in the same material, a drastic property change may be controllable." This insight led Prof. Katase and his research team at Tokyo Institute of Technology, in partnership with collaborators at Osaka University and National Institute for Materials Science, to embark on research into the possibility of switching the crystal structure dimensionality of a lead-tin-selenide alloy semiconductor. Their results appear in a paper published ...
2021-04-13
A study carried out by the University of Granada indicates that smoking cannabis significantly alters key visual functions, such as visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, three-dimensional vision (stereopsis), the ability to focus, and glare sensitivity
Yet, more than 90% of users believe that using cannabis has no effect on their vision, or only a slight effect
A group of researchers from the Department of Optics of the University of Granada (UGR) has studied the effects of smoking cannabis on various visual parameters compared to the effect that the users themselves perceive the drug to have on their vision.
This study, led by Carolina Ortiz Herrera and Rosario González Anera, has been published in the journal Scientific Reports. Its main author, Sonia Ortiz Peregrina, explains that ...
2021-04-13
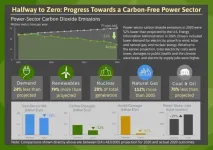
Concerns about climate change are driving a growing number of states, utilities, and corporations to set the goal of zeroing out power-sector carbon emissions. To date 17 states plus Washington, D.C. and Puerto Rico have adopted laws or executive orders to achieve 100% carbon-free electricity in the next couple of decades. Additionally, 46 U.S. utilities have pledged to go carbon free no later than 2050. Altogether, these goals cover about half of the U.S. population and economy.
These are ambitious targets, but a new look at the past 15 years in the electricity sector shows that large reductions in emissions are possible.
New research from the Department of Energy's Lawrence ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] UBCO engineer cautions pregnant women about speed bumps
The slower the better while driving over them, says researcher