Making waves in oceanography
New research finds upwelling defies prior theories
2021-04-15
(Press-News.org) A new scientific discovery in Australia by Flinders University has recorded for the first time how ghost currents and sediments can 'undo' the force of gravity.
The new theory, just published in the Journal of Marine Systems, helps explain obscure events in which suspended sediment particles mysteriously move upward, not downward, on the slope of submarine canyons of the deep sea.
While this activity seems to contradict the laws of gravity, Flinders University physical oceanographer Associate Professor Jochen Kaempf has found an answer, devising the first scientific explanation of the observed upslope sediment transport.
"To put it simply, the vehicle of this transport are currents that, while carrying sediments around and keeping them in suspension, leave the ambient seawater and its dissolved properties almost unchanged," he explains after studying the phenomena for two years.
"Such current, that I call ghost currents, adhere to the laws of physics and can move sediment particles over vast distances relative to the ambient seawater, also in directions opposite to the buoyancy force."
Associate Professor Kaempf believes that this astonishing new finding constitutes a breakthrough in the understanding of biogeochemical cycles at continental margins.
Suspended sediment particles in oceans are up to three times heavier than seawater of the same volume.
Hence, due to Archimedes law of buoyancy, which is an extension of Newton's law of gravity, sediment particles generally sink downward in the oceans, he says.
However, on continental margins, sediment particles can also form turbidity currents, which are rapid downslope flows of sediment-water mixtures on continental margins.
"My study may also help to better understand the feeding behaviour of suspension feeders including baleen whales and krill that often feed on particulate organic matter near the head of submarine canyons."
INFORMATION:
The article, On the upslope sediment transport at continental margins (2021) by J Kämpf, has been published in the Journal of Marine Systems, Volume 219, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2021.103546
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-15
Many long for a return to a post-pandemic "normal," which, for some, may entail concerts, travel, and large gatherings. But how to keep safe amid these potential public health risks?
One possibility, according to a new study, is dogs. A proof-of-concept investigation published today in the journal PLOS ONE suggests that specially trained detection dogs can sniff out COVID-19-positive samples with 96% accuracy.
"This is not a simple thing we're asking the dogs to do," says Cynthia Otto, senior author on the work and director of the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine Working Dog Center. "Dogs have to ...
2021-04-15
Do freshwater snails make good tennis players? One of them certainly has the name for it.
Enter Travunijana djokovici, a new species of aquatic snail named after famous Serbian tennis player Novak Djokovic.
Slovak biospeleologist Jozef Grego and Montenegrin zoologist Vladimir Pesic of the University of Montenegro discovered the new snail in a karstic spring near Podgorica, the capital of Montenegro, during a field trip in April 2019. Their scientific article, published in the open-access, peer-reviewed journal Subterranean Biology, says they named it after Djokovic "to acknowledge his inspiring enthusiasm and energy."
"To discover some of the world's rarest animals that inhabit the unique underground habitats of the Dinaric karst, to reach inaccessible cave and spring habitats ...
2021-04-15
WASHINGTON (April 15, 2021) -- Clusters of a virus known to cause stomach flu are resistant to detergent and ultraviolet disinfection, according to new research co-led by END ...
2021-04-15
Since the 1970s, the Standard Model of Physics has served as the basis from which particle physics are investigated. Both experimentalists and theoretical physicists have tested the Standard Model's accuracy, and it has remained the law of the land when it comes to understanding how the subatomic world behaves.
This week, cracks formed in that foundational set of assumptions. Researchers of the "Muon g-2" collaboration from the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL) in the United States published further experimental findings that show that muons--heavy subatomic relatives of electrons--may have a larger "magnetic moment" than earlier Standard Model estimates had predicted, indicating that an unknown particle or force might be influencing ...
2021-04-15
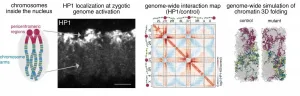
The DNA molecule is not naked in the nucleus. Instead, it is folded in a very organized way by the help of different proteins to establish a unique spatial organization of the genetic information. This 3D spatial genome organization is fundamental for the regulation of our genes and has to be established de novo by each individual during early embryogenesis. Researchers at the MPI of Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg in collaboration with colleagues from the Friedrich Mischer Institute in Basel now reveal a yet unknown and critical role of the protein HP1a in the 3D genome re-organization after fertilisation. The study published in the scientific journal Nature identifies HP1a as an epigenetic regulator that is involved in establishing ...
2021-04-15
Leesburg, VA, April 15, 2021--A Scientific E-Poster to be presented at the 2021 ARRS Virtual Annual Meeting found that as the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 transitions from a numerical score to pass or fail--as early as January 2022--radiology residency program directors will likely rely on USMLE Step 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) scores as an objective and standardized metric to screen applicants.
"However," wrote lead investigator Rebecca Zhang of the University of Maryland School of Medicine in Baltimore, "program directors remain unsure whether they will ...
2021-04-15
Leesburg, VA, April 15, 2021--A Scientific E-Poster to be presented at the 2021 ARRS Virtual Annual Meeting found that in the setting of a high pretest probability of COVID-19 infection or with a quick turnaround of the rapid real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) COVID-19 test, a chest x-ray (CXR) scoring system may be used prospectively to predict patient outcomes.
"We developed an accurate and reliable tool for classifying COVID-19 severity, which can be used both at the attending chest radiologist and junior resident level. This study identifies the laboratory, clinical and radiographic data that predict important patient outcomes such as death, intubation, and the need for chronic renal replacement ...
2021-04-15
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University has conducted research on the 35ClO2 isotope and developed a mathematical model and software, which allow predicting characteristics by 10 folds more accurate than already known results. The research work was conducted by a research team of Russian, German and Swiss scientists. The research findings are published in the Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (IF: 3,4; Q1) academic journal and listed as one of the best articles.
The ClO2 molecule is extremely important for medicine and biophysics, as well as for the Earth atmosphere. It is used in medicine for disinfection and ...
2021-04-15
A study published this week in The Lancet Public Health examines how we can use our income assistance systems to address drug use and drug-related harm.
The study, led by University of British Columbia (UBC) medical sociologist Dr. Lindsey Richardson and conducted at the British Columbia Centre on Substance Use (BCCSU), tests whether varying the timing and frequency of income assistance payments can mitigate drug-related harms linked to the existing once-monthly payment schedule that is common across North America and Europe. Monthly synchronized income assistance payments have long been linked to considerable and costly increases in drug use and resulting harm, including overdose, hospital admission, treatment interruption and emergency service calls.
The study finds that varying when ...
2021-04-15
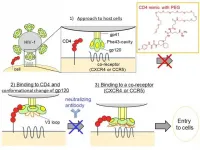
Tokyo, Japan - A team of scientists led by the Institute of Biomaterials and Bioengineering at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have created novel molecules that prevent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) particles from attacking immune cells. This is accomplished by injecting compounds mimicking the protein the virus usually uses to enter the cells. This work may lead to new treatments for HIV that may be more effective at stopping the proliferation of the virus with fewer side effects.
HIV is a very dangerous pathogen because it attacks the very immune cells, including T helper cells, that are needed for the body to fight back. An HIV particle first ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Making waves in oceanography
New research finds upwelling defies prior theories