Are our oil and gas pipelines safe during an earthquake?
The research shows that current methods used for calculating stress received by the underground pipelines during an earthquake are incorrect.
2021-04-16
(Press-News.org) Underground pipelines that transport oil and gas are very important engineering communications worldwide. Some of these underground communications are built and operated in earthquake-prone areas.
Seismic safety or seismic stability of underground pipelines began to be intensively studied since the 1950s.
Since then, a number of methodologies were proposed for calculating stress received by an underground pipeline during an earthquake. The purpose of these methodologies was to make an accurate prediction on the structural stress received by a pipeline during an earthquake, and thus it would allow to decide how resilient the pipeline must be made in the first place. It is important to find a right balance between pipeline cost and its structural resilience.
Turns out, we were wrong.
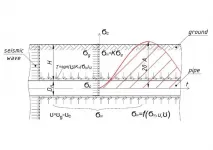
New research has been conducted by scientists from Institute of Mechanics and Seismic Stability of Structures Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan and Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU) of Russia. The research shows that current methods used for calculating stress received by the underground pipelines during an earthquake are incorrect.
"The existing methods do not consider seismic pressure, i.e., the stress normal to the pipeline's outer surface arising from the propagation of a seismic wave in the soil. This leads to an incorrect determination of the pipeline's stress; the longitudinal stress calculations lead to errors of 100% or more," said Nikolai Vatin, professor of Institute of Civil Engineering SPbPU.
Disregard of the longitudinal stress means that all oil and gas underground pipelines are more susceptible to earthquakes than was initially expected.
Researchers have developed a new theory of the seismic wave propagation process in an underground pipeline and surrounding soil to address this problem.
The related theoretical material that explains all the mathematical calculations of the new theory and its benefits in comparison to predecessor methodology can be found in the article Wave Theory of Seismic Resistance of Underground Pipelines.
"It is very admirable indeed that science moves forwards, and we get better theories and find our errors. Yet the ominous concern is that all our current pipelines are at risk will stay for some long time until they are replaced and modernized" mentioned Karim Sultanov from Institute of Mechanics and Seismic Stability of Structures Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan.
The research results in the article.
INFORMATION:
The research is funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation as part of World-class Research Center program: Advanced Digital Technologies (contract No. 075-15-2020-934 dated 17 November 2020).
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-16
A virtual human can be as good as a flesh-and-blood one when it comes to helping people practice new leadership skills. That's the conclusion from new research published in the journal Frontiers in Virtual Reality that evaluated the effectiveness of computer-generated characters in a training scenario compared to real human role-players in a conventional setting.
Practice-based training techniques, including role-playing, are sometimes used to help improve training outcomes. However, these methods can be expensive to implement, and often require specialized knowledge and even professional actors to create realistic training environments. In addition, some ...
2021-04-16
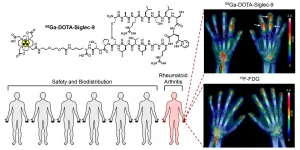
The preliminary trial results of a novel radiopharmaceutical for PET imaging of inflammation developed at the University of Turku, Finland, have been published. The compound, which targets the vascular adhesion protein 1 (VAP-1) that regulates inflammatory cell traffic, is the first radiopharmaceutical that has been developed completely in Finland and has advanced to clinical trials. In the study that started with healthy volunteers, the radiopharmaceutical was found to be well tolerated and safe.
The radiopharmaceutical is 68Ga-labelled Siglec-9 peptide.
"The dose of the radiopharmaceutical ...
2021-04-16
"It is machination, it is deception," said the Director General of the Berlin Royal Museums in his defence when criticized for buying a fake. Wilhelm Bode did not budge an inch: the sculpture he acquired in 1909 was an as yet unknown production of the great Renaissance master, Leonardo da Vinci. After one hundred years and numerous controversies, a group of scientists led by a CNRS researcher* has just proven him wrong once and for all. The Flora wax bust, conserved at the Bode Museum in Berlin, recently underwent radiocarbon (14C) dating, which provided both a precise date and an incontrovertible result: it was made in the nineteenth century, nearly 300 years after da Vinci's death. As the sculpture was made primarily from spermaceti, ...
2021-04-16
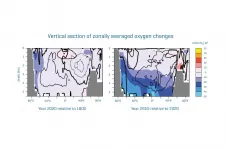
The life of almost all animals in the ocean depends on the availability of oxygen, which is dissolved as a gas in seawater. However, the ocean has been continuously losing oxygen for several decades. In the last 50 years, the loss of oxygen accumulates globally to about 2% of the total inventory (regionally sometimes significantly more). The main reason for this is global warming, which leads to a decrease in the solubility of gases and thus also of oxygen, as well as to a slowdown in the ocean circulation and vertical mixing. A new study published today in the scientific journal Nature Communications ...
2021-04-16
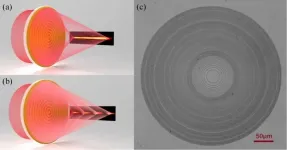
In a new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI https://doi.org/10.29026/oea.2021.200031, Researchers led by Professor Baohua Jia at Swinburne University of Technology, Victoria, Australia, Professor Cheng-Wei Qiu at National University of Singapore, Singapore and Professor Tian Lan at Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China considered the generation of super-resolved optical needle and multifocal array using graphene oxide metalenses.
Ultrathin and lightweight, metalenses are becoming increasingly significant for their use in photonic chips, biosensors and micro imaging systems such as smart phone cameras.
Compared to conventional lenses, metalenses can improve the image quality of current cameras, ...
2021-04-16
In most living animals, egg cells are vastly larger than sperm cells. In humans, for example, a single egg is 10 million times the volume of a sperm cell.
In a new study, Northwestern University researchers found that competition and natural selection drove this curious size discrepancy.
Using mathematical modeling, the researchers considered a time very early in evolution when primordial species reproduced using external fertilization. In the model, bigger reproductive cells, or gametes, presented a competitive edge because they could hold more nutrients for a potential zygote. Smaller gametes, however, required fewer resources to make, which put less stress on the parent.
"Organisms either needed to produce the biggest gametes with the most provisions ...
2021-04-16
When temperatures drop below zero degrees Celsius, water turns to ice. But does everything actually freeze if you just cool it down enough? In the classical picture, matter inherently becomes solid at low temperatures. Quantum mechanics can, however, break this rule. Therefore, helium gas, for example, can become liquid at -270 degrees, but never solid under atmospheric pressure: There is no helium ice.
The same is true for the magnetic properties of materials: at sufficiently low temperatures, the magnetic moments known as 'spins', for example, arrange themselves in such a way that they are oriented opposite/antiparallel to their respective neighbors. One can think of this as arrows pointing alternating up and down along a chain or in a checkerboard pattern. It ...
2021-04-16
Snow cover in the Alps has been melting almost three days earlier per decade since the 1960s. This trend is temperature-related and cannot be compensated by heavier snowfall. By the end of the century, snow cover at 2,500 meters could disappear a month earlier than today, as simulations by environmental scientists at the University of Basel demonstrate.
Global warming demands huge adjustments in tourism, hydropower generation and agriculture in alpine areas. But the fauna and flora also have to adapt to rising temperatures. By the end of the century, ...
2021-04-16
If you are exposed to silica (quartz) dust at work - e.g. from working with concrete and granite - you have a greater risk of certain types of rheumatic disease. This is shown by results from Aarhus University and Aarhus University Hospital, which have just been published in the International Journal of Epidemiology.
Exposure to silica dust at work, which is the case especially at workplaces within construction and industry, may lead to autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Photo: Unsplash.
Exposure to silica dust at work, which is the case especially at workplaces within construction and industry, may lead to autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Photo: Unsplash.
As the research results from Aarhus University show, exposure to ...
2021-04-16
The leading newspapers in two nuclear waste management forerunner countries, Finland and France, fulfil their "watchdog" roles in highly distinct ways. The Finnish Helsingin Sanomat (HS) tends to reproduce government and industry framings, whereas Le Monde cherishes its role as an independent critic of the powers that be. These differences reflect distinct cultural, political and media traditions in the two countries.
"The critical watchdog model works in a liberal democracy such as the French, based on mistrust towards the governing elites. But would it backfire in Finland by undermining the very institutional trust that the Nordic democracies have been built upon throughout history?" asks the first author of the article, Research Fellow Markku Lehtonen from the Department of Humanities ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Are our oil and gas pipelines safe during an earthquake?
The research shows that current methods used for calculating stress received by the underground pipelines during an earthquake are incorrect.