(Press-News.org) Research shows that a new telescope could detect a potential signature of life on other planets in as little as 60 hours.
"What really surprised me about the results is that we may realistically find signs of life on other planets in the next 5 to 10 years," said Caprice Phillips, a graduate student at The Ohio State University, who will share preliminary findings at a END
Scientists may detect signs of extraterrestrial life in the next 5 to 10 years
Telescope launching this autumn could spot biosignatures on other planets within three days
2021-04-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The fate of the planet
2021-04-16
From engineered pandemics to city-toppling cyber attacks to nuclear annihilation, life on Earth could radically change, and soon. Scientists will forecast the fate of the planet at a END ...
Tarantula's ubiquity traced back to the cretaceous
2021-04-16
Tarantulas are among the most notorious spiders, due in part to their size, vibrant colors and prevalence throughout the world. But one thing most people don't know is that tarantulas are homebodies. Females and their young rarely leave their burrows and only mature males will wander to seek out a mate. How then did such a sedentary spider come to inhabit six out of seven continents?
An international team of researchers, including Carnegie Mellon University's Saoirse Foley, set out on an ancestry.com-like investigation to find the answer to this question. They looked to the transcriptomes, ...
On the pulse of pulsars and polar light
2021-04-16
Faced with the tragic loss of the Arecibo observatory in Puerto Rico and the often prohibitive cost of satellite missions, astronomers are searching for savvy alternatives to continue answering fundamental questions in physics.
At a END ...
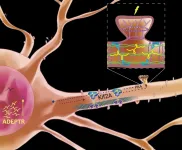
Neural plasticity depends on this long noncoding RNA's journey from nucleus to synapse
2021-04-16
JUPITER, FL--Making memories involves more than seeing friends or taking photos. The brain constantly adapts to new information and stores memories by building connections among neurons, called synapses. How neurons do this--reaching out arm-like dendrites to communicate with other neurons--requires a ballet of genes, signaling molecules, cellular scaffolding and protein-building machinery.
A new study from scientists at Scripps Research and the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience finds a central role for one signaling molecule, a long, noncoding RNA that the scientists named ADEPTR.
Using a variety of technologies, including confocal and two-photon microscopy, they track ADEPTR's moves, watching as it forms, travels, amasses at the ...
A new guide for communicating plant science
2021-04-16
AMES, Iowa - A lot is riding on the continued advancement of plant sciences.
Take the food supply, for starters. Climate change and population growth will continue to pose challenges in the future, and crop production will require innovation and progress by plant scientists in order to keep pace. It isn't an overstatement to say that populations around the world will go hungry if plant science stagnates, said Gustavo MacIntosh, a professor in the Roy J. Carver Department of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Molecular Biology at Iowa State University.
"At the end of the day, either you eat plants or you eat food that ate plants," MacIntosh said. "Plants are the basis for the food we have."
MacIntosh predicts ...
The future of particle accelerators is here
2021-04-16
When the Electron Ion Collider received the go-ahead in January 2020, it became the only new major accelerator in the works anywhere in the world.
"All the stars aligned," said Elke-Caroline Aschenauer, Brookhaven National Laboratory Staff Scientist and a leader in developing the EIC plans. "We have the technology to build this unique particle accelerator and detector to do the measurements that, together with the underlying theory, can for the first time provide answers to longstanding fundamental questions in nuclear physics."
The EIC isn't the only Brookhaven project poised to reshape nuclear and particle physics. Forthcoming data from the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider could finally detect the elusive chiral magnetic effect. Meanwhile, planned accelerators could run on sustainable ...
Simulations reveal how dominant SARS-CoV-2 strain binds to host, succumbs to antibodies
2021-04-16
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., April 16, 2021 -- Large-scale supercomputer simulations at the atomic level show that the dominant G form variant of the COVID-19-causing virus is more infectious partly because of its greater ability to readily bind to its target host receptor in the body, compared to other variants. These research results from a Los Alamos National Laboratory-led team illuminate the mechanism of both infection by the G form and antibody resistance against it, which could help in future vaccine development.
"We found that the interactions among the basic building blocks of the Spike protein become ...
New understanding of the deleterious immune response in rheumatoid arthritis
2021-04-16
Researchers within the Biomedicine Discovery Institute at Monash University have made a breakthrough in understanding the role played by high-risk immune genes associated with the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
The findings, published in Science Immunology, were the result of a seven-year collaboration led by Monash University, involving Janssen Research and Development, USA and the Karolinska Institute, Sweden.
Certain immune system genes, called Human Leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR4, cause an increased susceptibility to RA. In this study, using mice genetically ...
The Trojan-Horse mechanism: How networks reduce gender segregation
2021-04-16
The social science literature has long viewed homophily and network-based job recruitment as crucial drivers of segregation. Researchers at Linköping University and ESADE, Ramon Llull University now show that this view must be revised. In their Science Advances article, they call attention to a previously unidentified factor, the Trojan-horse mechanism, which shows that network-based recruitment can reduce rather than increase segregation levels.
The segregation of labor markets along ethnic and gender lines is an important source of socio-economic inequalities. Therefore, the understanding the mechanisms that drive segregation ...
Science Advances publishes proteomics technology from Oblique Therapeutics AB
2021-04-16
Science Advances publishes proteomics technology from Oblique Therapeutics AB with a potential to bring several novel antibody medicines to large patient populations in multiple disease areas
Gothenburg, Sweden, April 16th, 2021 - Oblique Therapeutics AB, a Sweden-based biotech company, in collaboration with Karolinska Institutet (Stockholm, Sweden), Gothenburg University (Sweden) and several local biotechs published promising research results in the highly-acclaimed scientific journal Science Advances (AAAS) entitled: Rational Antibody design for Undruggable Targets using Kinetically Controlled Biomolecular ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
[Press-News.org] Scientists may detect signs of extraterrestrial life in the next 5 to 10 yearsTelescope launching this autumn could spot biosignatures on other planets within three days