New properties of strontium titanate are significant for electronics research
A joint Russian-Czech paper appeared in Europhysics Letters.
2021-04-19
(Press-News.org) While studying strontium titanate with electron paramagnetic resonance, a team from KFU's Center for Quantum Technology has found that the shape of a specimen of strontium titanate influences its internal symmetry. The research was co-conducted by the Ioffe Institute of Physics and Technology (Russia) and the Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences.
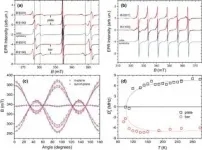
At room temperature, SrTiO3 is a crystal with high cubic symmetry, that is, the lattice of strontium titanate, like bricks, is composed of unit cells, each of which is a regular cube. However, the researchers showed the picture is a bit more nuanced. In thin plates and columns measuring microns in width, the symmetry decreases to tetragonal (uniaxial), with a structure was not previously observed in SrTiO3. That is, each elementary cell turns into a parallelepiped.
"The results are of great scientific and practical importance. In many cases, the scale of breaking is not as important as its very presence. A decrease in symmetry opens up the possibility of phenomena that are forbidden in a cubic structure," said Roman Yusupov, Lead Research Associate of the Center for Quantum Technology.
He noted that strontium titanate is actively used in thin-film technologies, where the functional properties of materials are determined by layers that sometimes have a thickness of several atoms. They are crucial for electronic devices, such as processors, monitors, mobile screens, high-capacity batteries, and storage devices.
"Thin films are based on substrates -- typically thin (less than one millimeter in thickness) slabs of materials other than the film material. The properties of thin films are largely determined by the structure of the substrate. One of the widely used substrate materials is strontium titanate," explains Yusupov.
By changing the distortion magnitude of substrates, it's possible to change the characteristics of thin films deposited on them, and thus contribute to creating new devices, sensors, and detectors.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-19
The research is conducted by Kazan University's Open Lab Gene and Cell Technologies (Center for Precision and Regenerative Medicine, Institute of Fundamental Medicine and Biology) and Republic Clinical Hospital of Kazan. Lead Research Associate Yana Mukhamedshina serves as project head.
Spinal cord injury mechanisms include primary and secondary injury factors. Primary injury is mechanical damage to the nervous tissue and vasculature with immediate cell death and hemorrhage. Secondary damage leads to significant destructive changes in the nervous tissue due to the development of excitotoxicity, death ...
2021-04-19
The project was kickstarted in 2017 when a delegation of YTC America (subsidiary of Yazaki Corporation) visited Kazan Federal University. During the talks, YTC suggested that KFU participate in developing effective methods of separating single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) into metallic and semiconducting specimens. This was to be done on Tuball tubes produced by OCSiAl, since they are the only ones currently available in industrial quantities.
Carbon nanotubes (CNT) is a family of 1D nanostructures with numerous verified applications, made possible due to their ...
2021-04-19
A recent study finds that social inequality persists, regardless of educational achievement - particularly for men.
"Education is not the equalizer that many people think it is," says Anna Manzoni, author of the study and an associate professor of sociology at North Carolina State University.
The study aimed to determine the extent to which a parent's social status gives an advantage to their children. The research used the educational achievements of parents as a proxy for social status, and looked at the earnings of adult children as a proxy for professional success.
To ...
2021-04-19
ADELPHI, Md. -- Spoken dialogue is the most natural way for people to interact with complex autonomous agents such as robots. Future Army operational environments will require technology that allows artificial intelligent agents to understand and carry out commands and interact with them as teammates.
Researchers from the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, known as DEVCOM, Army Research Laboratory and the University of Southern California's Institute for Creative Technologies, a Department of Defense-sponsored University Affiliated Research Center, created an approach to flexibly interpret and respond to Soldier intent derived from spoken dialogue with autonomous systems.
This technology is currently the primary ...
2021-04-19
The Andes Mountains of South America are the most species-rich biodiversity hotspot for plant and vertebrate species in the world. But the forest that climbs up this mountain range provides another important service to humanity.
Andean forests are helping to protect the planet by acting as a carbon sink, absorbing carbon dioxide and keeping some of this climate-altering gas out of circulation, according to new research published in Nature Communications.
The study -- which draws upon two decades of data from 119 forest-monitoring plots in Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia and Argentina -- was produced by an international team of scientists including researchers supported by the Living Earth Collaborative at Washington University in St. Louis. The lead author was Alvaro Duque from the ...
2021-04-19
A team of scientists from Russia studied the role of double-stranded fragments of the maturing RNA and showed that the interaction between distant parts of the RNA can regulate gene expression. The research was published in Nature Communications.
At school, we learn that DNA is double-stranded and RNA is single-stranded, but that is not entirely true. Scientists have encountered many cases of RNA forming a double-stranded (a.k.a. secondary) structure that plays an important role in the functioning of RNA molecules. These structures are involved in the regulation of gene expression, where the double-stranded regions typically carry specific functions and, if lost, may cause severe disorders. A double-stranded structure is created by sticky complementary ...
2021-04-19
New, detailed study of the Renland Ice Cap offers the possibility of modelling other smaller ice caps and glaciers with significantly greater accuracy than hitherto. The study combined airborne radar data to determine the thickness of the ice cap with on-site measurements of the thickness of the ice cap and satellite data. Researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute - University of Copenhagen gathered the data from the ice cap in 2015, and this work has now come to fruition in the form of more exact predictions of local climate conditions.
The accuracy ...
2021-04-19
A new study led by researchers at Johns Hopkins and the University of Pennsylvania uses computer modeling to suggest that eviction bans authorized during the COVID-19 pandemic reduced the infection rate and not only protected those who would have lost their housing but also entire communities from the spread of infections.
With widespread job loss in the U.S. during the pandemic, many state and local governments temporarily halted evictions last spring, and just as these protections were about to expire in September, the Centers for Disease Control ...
2021-04-19
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a form of progressive dementia interfering with daily living. It is caused by the decline in the number of brain cells resulting in the deterioration of our mental abilities. One of the main reasons for the worsening brain cells condition and even the brain shrinkage are molecules having a specific structure called β-amyloids (Aβ). They are peptides that tend to agglomerate around the nerve cells, becoming toxic and damage them. Recent studies, presented by scientists from the Institute of Physical Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, led by dr. Piotr Pieta, give hope for inhibition of the β-amyloids' toxicity by applying the K162 molecule. Researchers present a tremendous protective impact on the biological membranes ...
2021-04-19
UPTON, NY--Scientists have identified the primary cause of failure in a state-of-the-art lithium-metal battery, of interest for long-range electric vehicles. Using high-energy x-rays, they followed the cycling-induced changes at thousands of different points across the battery and mapped the variations in performance. At each point, they used the x-ray data to calculate the amount of cathode material and its local state of charge. These findings, combined with complementary electrochemical measurements, enabled them to determine the dominant mechanism driving the loss of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New properties of strontium titanate are significant for electronics research
A joint Russian-Czech paper appeared in Europhysics Letters.