(Press-News.org) There are many variants of "goblet cells" in the intestines and they seem to have different functions, according to a new study from the University of Gothenburg. The study indicates that defects in goblet cells of a particular type may be a factor contributing to ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease.
The entire inside of our intestines is covered by a thin layer of mucus that protects the fragile mucous membrane (mucosa) from bacteria and other microorganisms. If the microorganisms repeatedly come into contact with the intestinal mucosa, inflammation and even cell changes may result. These increase the risk of intestinal cancer. In a healthy colon, the mucus layer is up to a millimeter thick. This layer, which undergoes complete renewal hourly, is formed from cells of a special type, known as goblet cells.
Many different goblet cells
In the present study, now published in the journal Science, the scientists separated goblet cells from other cells and investigated which proteins each individual goblet cell expresses. There proved to be many different subtypes of these cells, and goblet cells' functions turned out to vary more than researchers have previously realized.
"We believe this is important knowledge that may enable us to influence the protective function of the gut in the future. The system that maintains the protective intestinal mucus layer seems to be able to change its functions, and we could utilize this capacity by reprogramming the layer with various signals, for example by using new drugs", says Malin Johansson, Associate Professor at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, who led the research behind the present study.
Connected with ulcerative colitis
The most impermeable part of the mucus layer is formed by glands in the gut. In particular, the research team studied one of the specific types of goblet cells, found on the outermost surface of the mucosa. These goblet cells provide another type of mucus, which contributes to the protection of the gut but allows certain nutrients to pass through.
"If the function of these specific cells is impaired, we see that unprotected cell surfaces arise. These lead to inflammation, both in studies on mice and in samples from patients with ulcerative colitis," Johansson says.
Appear to cause damage to mucosal protection
In the study, these specific goblet cells seemed to be repelled by the mucosa earlier than normal in patients with ulcerative colitis. Accordingly, the cells became fewer.
"To our surprise, we were able to observe this both in patients with active ulcerative colitis and in those who were temporarily asymptomatic. This indicates that premature rejection of the particular goblet cells we've been studying damages the mucus protection and that this is a contributing cause of inflammatory bowel disease. It could also be a partial explanation for these patients' elevated cancer risk," Johansson says.
There are some 30,000 people in Sweden with ulcerative colitis, which is a chronic but intermittent inflammatory bowel disease.
INFORMATION:
Article: An intercrypt subpopulation of goblet cells is essential for colonic mucus barrier function: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/372/6539/eabb1590
Genova (Italy), 16th April 2021 - A micro-sized polymeric net wrapping around brain tumors, just like a fishing net around a shoal of fish: this is the microMESH, a new nanomedicine device capable to conform around the surface of tumor masses and efficiently deliver drugs. It has been described by the researchers of the IIT - Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology) in Nature Nanotechnology. The new biomedical implant has been validated in preclinical studies that demonstrate its effectiveness for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme.
This work has been carried out by the group of Prof. Paolo Decuzzi, head of the IIT Laboratory of Nanotechnology ...
The prevalence of intellectual disabilities, which means difficulties with learning and understanding new things, is roughly 1-2% in the population. People with a severe intellectual disability need help from others in daily activities throughout their lives.
Such disabilities can be caused by genetic changes or external factors. According to estimates, roughly 2,500 genes underlie intellectual disability, of which approximately half remain unidentified.
In recent years, the diagnostics for intellectual disabilities have improved thanks to advancements in techniques that make it possible ...
Language is one of the most notable abilities humans have. It allows us to express complex meanings and transmit knowledge from generation to generation. An important question in human biology is how this ability ended up being developed, and researchers from the universities of Barcelona, Cologne and Tokyo have treated this issue in a recent article.
Published in the journal Trends in Cognitive Sciences, the article counts on the participation of the experts from the Institute of Complex Systems of the UB (UBICS) Thomas O'Rourke and Pedro Tiago Martins, led by Cedric Boeckx, ICREA research professor at the Faculty of Philology ...
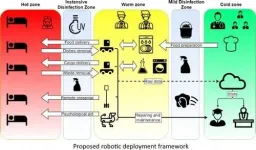
In December 2019, a new viral infection was detected in Wuhan, China. On January 30, 2020, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern, and on March 11, the COVID-19 pandemic. In light of the danger that the infection poses to human personnel, the idea to utilize automation in hospitals is one of the natural solutions in healthcare.
Among the paper's five co-authors, four are working in robotics and one is an expert in medicine. The paper presents a new concept of an infectious hospital that may become a worldwide standard in the future. The idea of this appeared while the authors ...
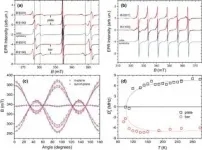
While studying strontium titanate with electron paramagnetic resonance, a team from KFU's Center for Quantum Technology has found that the shape of a specimen of strontium titanate influences its internal symmetry. The research was co-conducted by the Ioffe Institute of Physics and Technology (Russia) and the Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences.
At room temperature, SrTiO3 is a crystal with high cubic symmetry, that is, the lattice of strontium titanate, like bricks, is composed of unit cells, each of which is a regular cube. However, the researchers showed the picture is a bit more nuanced. In ...
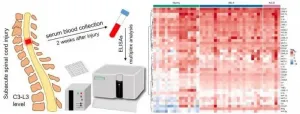
The research is conducted by Kazan University's Open Lab Gene and Cell Technologies (Center for Precision and Regenerative Medicine, Institute of Fundamental Medicine and Biology) and Republic Clinical Hospital of Kazan. Lead Research Associate Yana Mukhamedshina serves as project head.
Spinal cord injury mechanisms include primary and secondary injury factors. Primary injury is mechanical damage to the nervous tissue and vasculature with immediate cell death and hemorrhage. Secondary damage leads to significant destructive changes in the nervous tissue due to the development of excitotoxicity, death ...
The project was kickstarted in 2017 when a delegation of YTC America (subsidiary of Yazaki Corporation) visited Kazan Federal University. During the talks, YTC suggested that KFU participate in developing effective methods of separating single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) into metallic and semiconducting specimens. This was to be done on Tuball tubes produced by OCSiAl, since they are the only ones currently available in industrial quantities.
Carbon nanotubes (CNT) is a family of 1D nanostructures with numerous verified applications, made possible due to their ...
A recent study finds that social inequality persists, regardless of educational achievement - particularly for men.
"Education is not the equalizer that many people think it is," says Anna Manzoni, author of the study and an associate professor of sociology at North Carolina State University.
The study aimed to determine the extent to which a parent's social status gives an advantage to their children. The research used the educational achievements of parents as a proxy for social status, and looked at the earnings of adult children as a proxy for professional success.
To ...
ADELPHI, Md. -- Spoken dialogue is the most natural way for people to interact with complex autonomous agents such as robots. Future Army operational environments will require technology that allows artificial intelligent agents to understand and carry out commands and interact with them as teammates.
Researchers from the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, known as DEVCOM, Army Research Laboratory and the University of Southern California's Institute for Creative Technologies, a Department of Defense-sponsored University Affiliated Research Center, created an approach to flexibly interpret and respond to Soldier intent derived from spoken dialogue with autonomous systems.
This technology is currently the primary ...
The Andes Mountains of South America are the most species-rich biodiversity hotspot for plant and vertebrate species in the world. But the forest that climbs up this mountain range provides another important service to humanity.
Andean forests are helping to protect the planet by acting as a carbon sink, absorbing carbon dioxide and keeping some of this climate-altering gas out of circulation, according to new research published in Nature Communications.
The study -- which draws upon two decades of data from 119 forest-monitoring plots in Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia and Argentina -- was produced by an international team of scientists including researchers supported by the Living Earth Collaborative at Washington University in St. Louis. The lead author was Alvaro Duque from the ...