(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS - April 19, 2021 - Despite access to some of the best possible medical care in the world, Senators John McCain and Edward Kennedy both died within 18 months of their diagnosis of glioblastoma, an aggressive form of brain cancer. While this deadly outcome typifies the nature of this disease, some glioblastoma patients see exceptional benefits from chemotherapy and survive beyond expectations. Why this happens has been revealed by researchers at the University of Minnesota in a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Deciphering the molecular underpinning of these exceptional responses may hold the key to transforming the hope for miracles into the reality of an expected cure for glioblastoma patients," said Clark C. Chen, MD, PhD, Lyle French Chair in Neurosurgery and head of the Department of Neurosurgery at the University of Minnesota Medical School, who is also lead author of the study.
The study team looked at the gene expression profiles of glioblastoma specimens collected from approximately 900 glioblastoma patients from regions across the world to identify unique features associated with exceptional responders, defined as glioblastoma patients who survive more than two years after treatment.
"We utilized different state-of-the-art analytics to study these samples, including methods innovated by Dr. Aaron Sarver, a member of the University of Minnesota Institute of Health Informatics. Impressively, these analytics converged on a single observation, a paucity of microglia and macrophages," Chen said.
Microglia and macrophages are specialized, immune cells that act as scavengers to recognize and remove cells not normally present in a healthy brain, including cancer cells. These immune cells migrate to sites harboring abnormal cancer cells to defend the body against the cancer cells and can make up more than half of the cells in a glioblastoma sample.
"If microglia and macrophages normally fend off cancer cells, more of them should allow the body to better fend off the tumor. So, we expected to see more of them in the exceptional responders; however, we found the contrary," said Jun Ma, a researcher in the Department of Neurosurgery at the U of M Medical School and a co-first author of this study.
Resolving this paradox, the research team subsequently demonstrated glioblastoma cells possess the capacity to recondition the surrounding microglia and macrophages and corrupt their native anticancer functions. Instead of fending off cancer growth, these immune cells are now re-programmed by glioblastoma cells to promote tumor growth.
"It is frightening to consider the possibility that cancer cells can 'brainwash' our own immune cells and convert them from cells that fight cancer to cells that promote cancer," said Judith Varner, a co-senior author of the study and professor of pathology at the University of California, San Diego. "Fortunately, we have figured out how glioblastoma cells subvert our immune system and can now reverse this cellular version of the 'Stockholm syndrome.'"
Stockholm syndrome is a psychological response in which hostages or abuse victims develop an emotional bond with and act to help their captors.
The key to curing this cellular "Stockholm syndrome" and possibly glioblastoma lies in a protein called phosphoinositide-3-kinase gamma isoform (PI3Kγ). Activation of this protein turns microglia and macrophages from immune cells that police cancer growth into hostage cells that promote cancer growth. Varner has studied this process for many years and pioneered drugs that restore the anti-tumor activities of microglia and macrophages.
"In our animal glioblastoma models, treatment with drugs targeting PI3Kγ consistently resulted in impressively durable responses to chemotherapy," Chen said. "We are eager to translate these findings into a human trial, with the hope of transforming every glioblastoma patient into an exceptional responder."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors of this study also included: Jie Li, Jun Ma, Ming Li, Tomoyuki Koga, Aaron Sarver, Beibei Xu, Sanjay Dhawan, Jianfang Ning, Andrew Venteicher, University of Minnesota; Megan Kaned, Ryan Shephard, Kunal Patel, Frank Furnari, Jeremy Rich, Christopher Glass, Judith Varner, University of California, San Diego; Hua Zhu, Anhua Wu, Department of Neurosurgery, First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China; Gan You, Jiang Tao, Department of Neurosurgery, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Beijing China.
About the University of Minnesota Medical School
The University of Minnesota Medical School is at the forefront of learning and discovery, transforming medical care and educating the next generation of physicians. Our graduates and faculty produce high-impact biomedical research and advance the practice of medicine. Visit med.umn.edu to learn how the University of Minnesota is innovating all aspects of medicine.
In March 2020, when the pandemic hit, everything slowed, including non-essential medical procedures such as elective surgeries, to reduce the spread of the coronavirus.
Six weeks later, Mary Byrnes, Ph.D., an assistant research scientist in the Department of Surgery at Michigan Medicine, began calling University of Michigan Frankel Cardiovascular Center patients whose surgeries had been canceled or delayed. She wanted to hear about their experiences -- what undergoing surgery meant to them, how postponing their operations had affected them, whether the existence of the coronavirus complicated how they felt about their bodies and ...
Psoriasis is a common inflammatory skin condition. The underlying genetic factors have not yet been sufficiently researched. The skin inflammation is usually triggered by external factors such as infections or stress. A research team at the Institute of Cancer Research of the Medical University of Vienna has now managed to identify a new factor in signal transmission of the immune system that plays a major role in the development of a psoriatic episode. The scientists have shown that symptoms can be alleviated by inhibiting the "c-Jun" protein in signal transmission.
The common clinical manifestation of psoriasis is a pinkish-grey thickening of the epidermis in distinct foci of infection, ...
It has been known for about a year that minks can become infected with SARS-CoV-2. The virus had been transmitted from humans to farmed mink and mutated in infected animals. Mutations were acquired in the spike protein, which is crucial for the entry of the virus into host cells and represents the central point of attack for antibodies. These SARS-CoV-2 variants from mink were transmitted back to humans, raising concerns that minks could be a continuing source of infection of humans with SARS-CoV-2 variants with altered biological properties. Researchers at the German Primate Center (DPZ) - Leibniz Institute for Primate Research in Göttingen, Germany, have now shown that an antibody used for COVID-19 ...
A simple dietary supplement reduces behavioral symptoms in mice with a genetic mutation that causes schizophrenia. After additional experiments, including visualizing the fluorescently stained dancing edge of immature brain cells, researchers concluded that the supplement likely protects proteins that build neurons' cellular skeletons.
The supplement betaine was first isolated from sugar beets and is often associated with sweetness or umami flavor. Healthy levels of betaine come from both external food sources and internal synthesis in the body. Betaine ...
Up to 25 percent of global food production is lost annually due to insects, primarily beetles. For the past 500 million years, beetles have successfully spread and adapted to life around the globe and now account for one of every five animal species on Earth. Yet as far back as ancient Egypt, these tough little bugs have invaded granaries and vexed us humans by destroying our crops.
As a result, food production and an abundant use of pesticides now go hand in hand. A large share of these pesticides damage biodiversity, the environment and human health. As various pesticides are phased out, new solutions are required to target and eradicate pests without harming humans or beneficial ...
Atlantic bluefin tuna have returned to UK waters and can once again be seen during the summer and autumn months.
Their numbers appear to be increasing, following a long period of absence linked to population decline, according to research led by Cefas and the University of Exeter.
Marine scientists in the UK and Ireland have analysed multiple datasets, spanning a 16-year period, to document the increase in bluefin, which arrive into the waters of the Celtic Seas and off South West England, the Scilly Isles, and North West Ireland to feed in late summer and autumn.
The research is part of the Defra-funded "Thunnus UK" research project. ...
Stroke risk for patients with traumatic brain injuries is at its highest in the four months following injury and remains significant for up to five years post-injury, finds a new systematic review led by a team at the University of Birmingham.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a global health problem affecting over 60 million people a year worldwide. Incidences of TBI are rising due to a range of factors including increased falls in the elderly, military conflict, sports injuries and road traffic accidents. However, advances in critical care and imaging have led to a reduction in TBI-related mortality.
Previous studies have associated TBI with a long-term risk of neurological diseases including dementia, ...
There are many variants of "goblet cells" in the intestines and they seem to have different functions, according to a new study from the University of Gothenburg. The study indicates that defects in goblet cells of a particular type may be a factor contributing to ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease.
The entire inside of our intestines is covered by a thin layer of mucus that protects the fragile mucous membrane (mucosa) from bacteria and other microorganisms. If the microorganisms repeatedly come into contact with the intestinal mucosa, inflammation and even cell changes may result. These increase the risk of intestinal cancer. In a healthy colon, the mucus layer is up to a millimeter ...
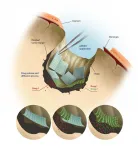
Genova (Italy), 16th April 2021 - A micro-sized polymeric net wrapping around brain tumors, just like a fishing net around a shoal of fish: this is the microMESH, a new nanomedicine device capable to conform around the surface of tumor masses and efficiently deliver drugs. It has been described by the researchers of the IIT - Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology) in Nature Nanotechnology. The new biomedical implant has been validated in preclinical studies that demonstrate its effectiveness for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme.
This work has been carried out by the group of Prof. Paolo Decuzzi, head of the IIT Laboratory of Nanotechnology ...
The prevalence of intellectual disabilities, which means difficulties with learning and understanding new things, is roughly 1-2% in the population. People with a severe intellectual disability need help from others in daily activities throughout their lives.
Such disabilities can be caused by genetic changes or external factors. According to estimates, roughly 2,500 genes underlie intellectual disability, of which approximately half remain unidentified.
In recent years, the diagnostics for intellectual disabilities have improved thanks to advancements in techniques that make it possible ...