(Press-News.org) Stroke risk for patients with traumatic brain injuries is at its highest in the four months following injury and remains significant for up to five years post-injury, finds a new systematic review led by a team at the University of Birmingham.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a global health problem affecting over 60 million people a year worldwide. Incidences of TBI are rising due to a range of factors including increased falls in the elderly, military conflict, sports injuries and road traffic accidents. However, advances in critical care and imaging have led to a reduction in TBI-related mortality.
Previous studies have associated TBI with a long-term risk of neurological diseases including dementia, Parkinson's and epilepsy, and TBI has been proposed as an independent risk factor for stroke.
This latest review, which brings together 18 studies from four countries and publishes today (April 9) in the International Journal of Stroke, is the first of its kind to investigate post-injury stroke risk.
Funded by the National Institute for Health Research's Surgical Reconstruction and Microbiology Research Centre based at University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, the review showed that TBI patients have an 86% increased risk of stroke compared to patients who have not experienced a TBI. Stroke risk may be at its highest in the first four months post-injury, but remains significant for up to five years, found the review.
Significantly, the findings suggest that TBI is a risk factor for stroke regardless of the severity or subtype of the injury. This is particularly noteworthy because 70% to 90% of TBI's are mild and suggests that TBI's should be considered a chronic condition even if it is mild and patients recover well.
Researchers also found that the use of anti-coagulants, such as VKA's and statins, could help to reduce stroke risk post-TBI, while the use of some classes of anti-depressants are associated with increased stroke risk post-TBI.
Lead author Dr Grace Turner, of the University of Birmingham's Institute of Applied Health Research, said: "Stroke is the second leading cause of death and third leading cause of disability worldwide, however, urgent treatment can prevent stroke related death and long-term disability.
"Our review found some evidence to suggest an association between reduced stroke risk post-TBI and the stroke prevention drugs VKAs and statins but, as previous studies have found, stroke prevention drugs are often stopped when an individual experiences a TBI.
She said more research is required to investigate the effectiveness of stroke prevention drugs post-TBI to help inform clinicians' prescribing and facilitate shared decision making.
Dr Turner added: "As our review has shown, TBI patients should be informed of the potential for increased stroke risk and with the risk of stroke at its highest in the first four months post-injury, this is a critical time period to educate patients and their care givers on stroke risk and symptoms.
"This initial four-month period should also be used by clinicians to administer stroke prevention medication and lifestyle advice to mitigate the excess risk of stroke associated with TBI."
INFORMATION:
For more information, please contact Emma McKinney, Communications Manager, University of Birmingham, on +44 7815607157. Alternatively, contact the Press Office out of hours on +44 (0)7789 921165.
Notes to Editors
* The University of Birmingham is ranked amongst the world's top 100 institutions, and its work brings people from across the world to Birmingham, including researchers and teachers and more than 6,500 international students from nearly 150 countries.
* Turner et al (April, 2021). Stroke risk following traumatic brain injury: systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Stroke. DOI: 10.1177/17474930211004277
* International Journal of Stroke is the official publication of the World Stroke Organization. It provides a significant contribution to the international stroke research community by concentrating on both the clinical aspects of stroke from around the world as well as basic science contributions in areas of clinical interest.
* The National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) is the nation's largest funder of health and care research. The NIHR:
- Funds, supports and delivers high quality research that benefits the NHS, public health and social care
- Engages and involves patients, carers and the public in order to improve the reach, quality and impact of research
- Attracts, trains and supports the best researchers to tackle the complex health and care challenges of the future
- Invests in world-class infrastructure and a skilled delivery workforce to translate discoveries into improved treatments and services
- Partners with other public funders, charities and industry to maximise the value of research to patients and the economy
- The NIHR was established in 2006 to improve the health and wealth of the nation through research, and is funded by the Department of Health and Social Care. In addition to its national role, the NIHR supports applied health research for the direct and primary benefit of people in low- and middle-income countries, using UK aid from the UK government.
There are many variants of "goblet cells" in the intestines and they seem to have different functions, according to a new study from the University of Gothenburg. The study indicates that defects in goblet cells of a particular type may be a factor contributing to ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease.
The entire inside of our intestines is covered by a thin layer of mucus that protects the fragile mucous membrane (mucosa) from bacteria and other microorganisms. If the microorganisms repeatedly come into contact with the intestinal mucosa, inflammation and even cell changes may result. These increase the risk of intestinal cancer. In a healthy colon, the mucus layer is up to a millimeter ...
Genova (Italy), 16th April 2021 - A micro-sized polymeric net wrapping around brain tumors, just like a fishing net around a shoal of fish: this is the microMESH, a new nanomedicine device capable to conform around the surface of tumor masses and efficiently deliver drugs. It has been described by the researchers of the IIT - Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology) in Nature Nanotechnology. The new biomedical implant has been validated in preclinical studies that demonstrate its effectiveness for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme.
This work has been carried out by the group of Prof. Paolo Decuzzi, head of the IIT Laboratory of Nanotechnology ...
The prevalence of intellectual disabilities, which means difficulties with learning and understanding new things, is roughly 1-2% in the population. People with a severe intellectual disability need help from others in daily activities throughout their lives.
Such disabilities can be caused by genetic changes or external factors. According to estimates, roughly 2,500 genes underlie intellectual disability, of which approximately half remain unidentified.
In recent years, the diagnostics for intellectual disabilities have improved thanks to advancements in techniques that make it possible ...
Language is one of the most notable abilities humans have. It allows us to express complex meanings and transmit knowledge from generation to generation. An important question in human biology is how this ability ended up being developed, and researchers from the universities of Barcelona, Cologne and Tokyo have treated this issue in a recent article.
Published in the journal Trends in Cognitive Sciences, the article counts on the participation of the experts from the Institute of Complex Systems of the UB (UBICS) Thomas O'Rourke and Pedro Tiago Martins, led by Cedric Boeckx, ICREA research professor at the Faculty of Philology ...
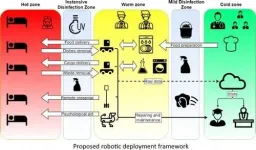
In December 2019, a new viral infection was detected in Wuhan, China. On January 30, 2020, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern, and on March 11, the COVID-19 pandemic. In light of the danger that the infection poses to human personnel, the idea to utilize automation in hospitals is one of the natural solutions in healthcare.
Among the paper's five co-authors, four are working in robotics and one is an expert in medicine. The paper presents a new concept of an infectious hospital that may become a worldwide standard in the future. The idea of this appeared while the authors ...
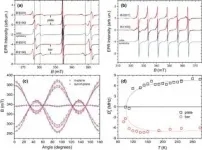
While studying strontium titanate with electron paramagnetic resonance, a team from KFU's Center for Quantum Technology has found that the shape of a specimen of strontium titanate influences its internal symmetry. The research was co-conducted by the Ioffe Institute of Physics and Technology (Russia) and the Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences.
At room temperature, SrTiO3 is a crystal with high cubic symmetry, that is, the lattice of strontium titanate, like bricks, is composed of unit cells, each of which is a regular cube. However, the researchers showed the picture is a bit more nuanced. In ...
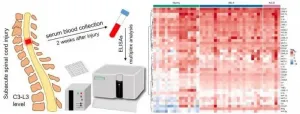
The research is conducted by Kazan University's Open Lab Gene and Cell Technologies (Center for Precision and Regenerative Medicine, Institute of Fundamental Medicine and Biology) and Republic Clinical Hospital of Kazan. Lead Research Associate Yana Mukhamedshina serves as project head.
Spinal cord injury mechanisms include primary and secondary injury factors. Primary injury is mechanical damage to the nervous tissue and vasculature with immediate cell death and hemorrhage. Secondary damage leads to significant destructive changes in the nervous tissue due to the development of excitotoxicity, death ...
The project was kickstarted in 2017 when a delegation of YTC America (subsidiary of Yazaki Corporation) visited Kazan Federal University. During the talks, YTC suggested that KFU participate in developing effective methods of separating single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) into metallic and semiconducting specimens. This was to be done on Tuball tubes produced by OCSiAl, since they are the only ones currently available in industrial quantities.
Carbon nanotubes (CNT) is a family of 1D nanostructures with numerous verified applications, made possible due to their ...
A recent study finds that social inequality persists, regardless of educational achievement - particularly for men.
"Education is not the equalizer that many people think it is," says Anna Manzoni, author of the study and an associate professor of sociology at North Carolina State University.
The study aimed to determine the extent to which a parent's social status gives an advantage to their children. The research used the educational achievements of parents as a proxy for social status, and looked at the earnings of adult children as a proxy for professional success.
To ...
ADELPHI, Md. -- Spoken dialogue is the most natural way for people to interact with complex autonomous agents such as robots. Future Army operational environments will require technology that allows artificial intelligent agents to understand and carry out commands and interact with them as teammates.
Researchers from the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, known as DEVCOM, Army Research Laboratory and the University of Southern California's Institute for Creative Technologies, a Department of Defense-sponsored University Affiliated Research Center, created an approach to flexibly interpret and respond to Soldier intent derived from spoken dialogue with autonomous systems.
This technology is currently the primary ...