AI agent helps identify material properties faster
Material research
2021-04-20
(Press-News.org) A team headed by Dr. Phillip M. Maffettone (currently at National Synchrotron Light Source II in Upton, USA) and Professor Andrew Cooper from the Department of Chemistry and Materials Innovation Factory at the University of Liverpool joined forces with the Bochum-based group headed by Lars Banko and Professor Alfred Ludwig from the Chair of Materials Discovery and Interfaces and Yury Lysogorskiy from the Interdisciplinary Centre for Advanced Materials Simulation. The international team published their report in the journal Nature Computational Science from 19 April 2021.
Previously manual, time-consuming, error-prone
Efficient analysis of X-ray diffraction data (XRD) plays a crucial role in the discovery of new materials, for example for the energy systems of the future. It is used to analyse the crystal structures of new materials in order to find out, for which applications they might be suitable. XRD measurements have already been significantly accelerated in recent years through automation and provide large amounts of data when measuring material libraries. "However, XRD analysis techniques are still largely manual, time-consuming, error-prone and not scalable," says Alfred Ludwig. "In order to discover and optimise new materials faster in the future using autonomous high-throughput experiments, new methods are required."
In their publication, the team shows how artificial intelligence can be used to make XRD data analysis faster and more accurate. The solution is an AI agent called Crystallography Companion Agent (XCA), which collaborates with the scientists. XCA can perform autonomous phase identifications from XRD data while it is measured. The agent is suitable for both organic and inorganic material systems. This is enabled by the large-scale simulation of physically correct X-ray diffraction data that is used to train the algorithm.
Expert discussion is simulated
What is more, a unique feature of the agent that the team has adapted for the current task is that it overcomes the overconfidence of traditional neuronal networks: this is because such networks make a final decision even if the data doesn't support a definite conclusion. Whereas a scientist would communicate their uncertainty and discuss results with other researchers. "This process of decision-making in the group is simulated by an ensemble of neural networks, similar to a vote among experts," explains Lars Banko. In XCA, an ensemble of neural networks forms the expert panel, so to speak, which submits a recommendation to the researchers. "This is accomplished without manual, human-labelled data and is robust to many sources of experimental complexity," says Banko.
XCA can also be expanded to other forms of characterisation such as spectroscopy. "By complementing recent advances in automation and autonomous experimentation, this development constitutes an important step in accelerating the discovery of new materials," concludes Alfred Ludwig.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-20
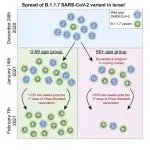
A new study at Tel Aviv University found that the British variant (termed: B.1.1.7) of Covid-19 is 45% more contagious than the original virus. The researchers relied on data from about 300,000 PCR tests for Covid-19 obtained from the COVID-19 testing lab, which was established in collaboration with the Electra Group.
The new study was conducted by Prof. Ariel Munitz and Prof. Moti Gerlitz of the Department of Clinical Microbiology and Immunology at the Sackler Faculty of Medicine, together with Dr. Dan Yamin and PhD student Matan Yechezkel from the Laboratory for Epidemic Modeling and Analysis (LEMA) at the Department of Industrial Engineering, all at Tel Aviv University. The study's results were published in the prominent scientific ...
2021-04-20
Musty, moldy, smoky or horse dung-like smelling cocoa is not suitable for chocolate production. As part of a larger research project, a team of scientists led by Martin Steinhaus from the Leibniz Institute for Food Systems Biology at the Technical University of Munich has identified the odorants responsible for such off-flavors. The food industry can now use these results to objectively assess the sensory quality of fermented cocoa based on odorant concentrations. The research team published the data in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
Who likes chocolate ...
2021-04-20
An international group of scientific experts co-directed by CNRS oceanographer Jean-Pierre Gattuso* has stated the requirements for coral reef survival in an article published in Biological Conservation. Over 500 million people rely on coral reefs for the protection they confer against submersion, the fishing resources they offer, and the tourism they help attract. Yet these ecosystems are among the most threatened by global warming: since the 1980s, there has been a rise in the number of bleaching episodes, during which corals expel the microscopic algae that keep them alive. While these events are reversible if the temperature change is only ...
2021-04-20
The largest study of its type in the UK has identified differences in the immune response to COVID-19, between people with no symptoms, compared to those suffering a more serious reaction to the virus.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Newcastle University, University College London, University of Cambridge, EMBL's European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and their collaborators within the Human Cell Atlas initiative, found raised levels of specific immune cells in asymptomatic people. They also showed people with more serious symptoms had lost these protective cell types, but gained inflammatory cells. These differences in the immune response could help explain serious lung inflammation and blood clotting symptoms, and could be used to identify potential ...
2021-04-20
Scientists have developed a new biomaterial that regrows blood vessels and bone, potentially providing a single-stage approach when repairing large bone defects.
The study, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences and SFI AMBER Centre, is published in the Journal of Controlled Release.
Previous RCSI-led research had found that activating a mechanosensitive gene, called placental growth factor (PGF), at different doses promoted bone regeneration and grew new blood vessels. Using this knowledge, the researchers developed a biomaterial that delivers PGF at different concentrations.
Inspired by the natural way in ...
2021-04-20
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A new Mayo Clinic study bolsters evidence that colorectal cancer is often imprinted in family genes and passed on from one generation to the next.
In the study, published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, researchers within the Mayo Clinic Center for Individualized Medicine found 1 in 6 patients with colorectal cancer had an inherited cancer-related gene mutation, which likely predisposed them to the disease. In addition, the researchers discovered that 60% of these cases would not have been detected if relying on a standard guideline-based approach.
"We found that 15.5% of the 361 patients with colorectal cancer had an inherited mutation in a gene associated with the development of their cancer," says Niloy Jewel Samadder, M.D., a Mayo ...
2021-04-20
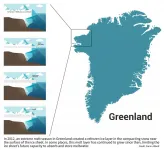
Nearly a decade ago, global news outlets reported vast ice melt in the Arctic as sapphire lakes glimmered across the previously frozen Greenland Ice Sheet, one of the most important contributors to sea-level rise. Now researchers have revealed the long-term impact of that extreme melt.
Using a new approach to ice-penetrating radar data, Stanford University scientists show that this melting left behind a contiguous layer of refrozen ice inside the snowpack, including near the middle of the ice sheet where surface melting is usually minimal. Most importantly, the formation of the melt layer changed the ice sheet's behavior by reducing its ability to store future meltwater. The research appears in Nature Communications ...
2021-04-20
PHILADELPHIA-- Researchers at Penn Medicine have identified more genetic mutations that strongly predispose younger, otherwise healthy women to peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), a rare condition characterized by weakness of the heart muscle that begins sometime during the final month of pregnancy through five months after delivery. PPCM can cause severe heart failure and often leads to lifelong heart failure and even death. The study is published today in Circulation.
PPCM affects women in one out of every 2,000 deliveries worldwide, with about a third of those women developing heart failure for life, and about five percent of them ...
2021-04-20
A myriad of genetic factors can influence the onset of diseases like high blood pressure, heart diseases, and type 2 diabetes. If we were to know how the DNA influences the risk of developing such diseases, we, we could shift from reactive to more preventive care, not only improving patients' quality of living but also saving money in the health system. However, tracing the connections between the DNA and disease onset requires solid statistical models that reliably work on very large datasets of several hundred thousand patients.
Matthew Robinson, Assistant Professor at the Institute ...
2021-04-20
Our guts may not provide long-lasting systemic immunity from COVID-19, which is where immune cells circulate through the body to provide protection to other organs, finds a new study published in Frontiers in Immunology. An analysis of blood samples from patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 revealed that immune cells circulating in the blood, which were triggered by the gut's response to infection, were limited in number when compared to immune cells that had been triggered elsewhere in the body.
"Although the gut is considered an important portal of entry for the virus, the immune response in the blood of COVID-19 patients is dominated by ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] AI agent helps identify material properties faster
Material research