INFORMATION:
The British variant is 45% more contagious than the original virus
Study at Tel Aviv University based on data from 300,000 tests for COVID-19
2021-04-20
(Press-News.org) A new study at Tel Aviv University found that the British variant (termed: B.1.1.7) of Covid-19 is 45% more contagious than the original virus. The researchers relied on data from about 300,000 PCR tests for Covid-19 obtained from the COVID-19 testing lab, which was established in collaboration with the Electra Group.
The new study was conducted by Prof. Ariel Munitz and Prof. Moti Gerlitz of the Department of Clinical Microbiology and Immunology at the Sackler Faculty of Medicine, together with Dr. Dan Yamin and PhD student Matan Yechezkel from the Laboratory for Epidemic Modeling and Analysis (LEMA) at the Department of Industrial Engineering, all at Tel Aviv University. The study's results were published in the prominent scientific journal Cell Reports Medicine.
The Electra-TAU laboratory was established in March 2020, right after the outbreak of the first wave of the pandemic in Israel. To date, it has analyzed hundreds of thousands of tests from all over the country - from public drive-in test facilities, as well as programs targeting specific populations - such as 'Shield for Fathers and Mothers' which routinely ran tests in at-risk hotspots like retirement homes.
Prof. Ariel Munitz explains: "We use a kit that tests for three different viral genes. In the British variant, also known as B.1.1.7, one of these genes, the S gene, has been erased by the mutation. Consequently, we were able to track the spread of the variant even without genetic sequencing."
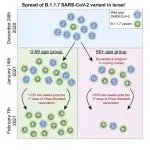
According to Prof. Munitz, the data from the lab shows that the spread of the British variant was very rapid: On December 24, 2020 only 5% of the positive results were attributed to the British variant. Just six weeks later, in January 2021, this variant was responsible for 90% of Covid-19 cases in Israel. The current figure is about 99.5%.
"To explain this dramatic increase, we compared the R number of the SARS-CoV-2 virus with the R of the British variant. In other words, we posed the question: How many people, on the average, contract the disease from every person who has either variant? We found that the British variant is 45% - almost 1.5 times - more contagious."
In the second stage of the study, the researchers segmented contagion by age groups. The results indicated that the turning point for the 60+ population compared to other age groups occurred two weeks after 50% of Israel's 60+ population received their first vaccine shot.
"Until January we saw a linear dependence of almost 100% between the different age groups in new cases per 1,000 people," says Dr. Dan Yamin. "Two weeks after 50% of the 60+ population received the first dose of the vaccine this graph broke sharply and significantly. During January a dramatic drop was observed in the number of new cases in the 60+ group, alongside a continued rise in the rest of the population. Simply put, since more than 90% of those who died from Covid-19 were over 60, we can say that the vaccine saved hundreds of lives - even in the short run."
Moreover, the new study proves that active monitoring of at-risk populations works. "There is a threshold value for determining whether a specific test is positive or negative for the virus - with a lower value indicating a higher viral load," says Prof. Munitz. "When we compared the threshold values of the different genes in 60+ residents of retirement homes with the values measured in 60+ persons in the general population, we saw significantly higher values in the retirement homes. This means that the viral load in retirement homes was lower compared to the rest of the population.
Since the residents of retirement homes are tested routinely, while other people are usually tested only when they don't feel well or have been in contact with someone who had tested positive for the virus, we conclude that constant monitoring of at-risk populations is a method that works. It is important to emphasize: the relatively low viral load was found in retirement homes despite the fact that the British variant had already begun to spread in all populations. Consequently, we show that monitoring retirement homes, together with vaccination that gives precedence to vulnerable populations, prevent illness and mortality."
Dr. Yemin concludes: "Due to crowded conditions, large households and age distribution in the Israeli population, the coronavirus had a more favorable environment for spreading in Israel compared to most Western countries. Our message to the world is that if with our problematic starting point a distinct decline was identified, other Western countries can certainly expect the curve to break - despite the high contagion of the British variant - with a dramatic drop in severe cases following the vaccination of 50% of the older population, alongside targeted testing at risk epicenters."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Reliably detecting cocoa off-flavors
2021-04-20
Musty, moldy, smoky or horse dung-like smelling cocoa is not suitable for chocolate production. As part of a larger research project, a team of scientists led by Martin Steinhaus from the Leibniz Institute for Food Systems Biology at the Technical University of Munich has identified the odorants responsible for such off-flavors. The food industry can now use these results to objectively assess the sensory quality of fermented cocoa based on odorant concentrations. The research team published the data in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
Who likes chocolate ...
Crucial action needed for coral reefs
2021-04-20
An international group of scientific experts co-directed by CNRS oceanographer Jean-Pierre Gattuso* has stated the requirements for coral reef survival in an article published in Biological Conservation. Over 500 million people rely on coral reefs for the protection they confer against submersion, the fishing resources they offer, and the tourism they help attract. Yet these ecosystems are among the most threatened by global warming: since the 1980s, there has been a rise in the number of bleaching episodes, during which corals expel the microscopic algae that keep them alive. While these events are reversible if the temperature change is only ...
Differing immune responses discovered in asymptomatic cases vs those with severe COVID-19
2021-04-20
The largest study of its type in the UK has identified differences in the immune response to COVID-19, between people with no symptoms, compared to those suffering a more serious reaction to the virus.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Newcastle University, University College London, University of Cambridge, EMBL's European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and their collaborators within the Human Cell Atlas initiative, found raised levels of specific immune cells in asymptomatic people. They also showed people with more serious symptoms had lost these protective cell types, but gained inflammatory cells. These differences in the immune response could help explain serious lung inflammation and blood clotting symptoms, and could be used to identify potential ...
New biomaterial regrows blood vessels and bone, RCSI research
2021-04-20
Scientists have developed a new biomaterial that regrows blood vessels and bone, potentially providing a single-stage approach when repairing large bone defects.
The study, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences and SFI AMBER Centre, is published in the Journal of Controlled Release.
Previous RCSI-led research had found that activating a mechanosensitive gene, called placental growth factor (PGF), at different doses promoted bone regeneration and grew new blood vessels. Using this knowledge, the researchers developed a biomaterial that delivers PGF at different concentrations.
Inspired by the natural way in ...
Mayo study finds colon cancer driven by hereditary gene mutations in 1 in 6 patients
2021-04-20
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A new Mayo Clinic study bolsters evidence that colorectal cancer is often imprinted in family genes and passed on from one generation to the next.
In the study, published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, researchers within the Mayo Clinic Center for Individualized Medicine found 1 in 6 patients with colorectal cancer had an inherited cancer-related gene mutation, which likely predisposed them to the disease. In addition, the researchers discovered that 60% of these cases would not have been detected if relying on a standard guideline-based approach.
"We found that 15.5% of the 361 patients with colorectal cancer had an inherited mutation in a gene associated with the development of their cancer," says Niloy Jewel Samadder, M.D., a Mayo ...
Can extreme melt destabilize ice sheets?
2021-04-20
Nearly a decade ago, global news outlets reported vast ice melt in the Arctic as sapphire lakes glimmered across the previously frozen Greenland Ice Sheet, one of the most important contributors to sea-level rise. Now researchers have revealed the long-term impact of that extreme melt.
Using a new approach to ice-penetrating radar data, Stanford University scientists show that this melting left behind a contiguous layer of refrozen ice inside the snowpack, including near the middle of the ice sheet where surface melting is usually minimal. Most importantly, the formation of the melt layer changed the ice sheet's behavior by reducing its ability to store future meltwater. The research appears in Nature Communications ...
Study helps unravel why pregnant women develop heart failure similar to older patients
2021-04-20
PHILADELPHIA-- Researchers at Penn Medicine have identified more genetic mutations that strongly predispose younger, otherwise healthy women to peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), a rare condition characterized by weakness of the heart muscle that begins sometime during the final month of pregnancy through five months after delivery. PPCM can cause severe heart failure and often leads to lifelong heart failure and even death. The study is published today in Circulation.
PPCM affects women in one out of every 2,000 deliveries worldwide, with about a third of those women developing heart failure for life, and about five percent of them ...
Predicting the onset of diseases
2021-04-20
A myriad of genetic factors can influence the onset of diseases like high blood pressure, heart diseases, and type 2 diabetes. If we were to know how the DNA influences the risk of developing such diseases, we, we could shift from reactive to more preventive care, not only improving patients' quality of living but also saving money in the health system. However, tracing the connections between the DNA and disease onset requires solid statistical models that reliably work on very large datasets of several hundred thousand patients.
Matthew Robinson, Assistant Professor at the Institute ...
Gut's immune response in COVID-19 may not provide efficient protection of other organs
2021-04-20
Our guts may not provide long-lasting systemic immunity from COVID-19, which is where immune cells circulate through the body to provide protection to other organs, finds a new study published in Frontiers in Immunology. An analysis of blood samples from patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 revealed that immune cells circulating in the blood, which were triggered by the gut's response to infection, were limited in number when compared to immune cells that had been triggered elsewhere in the body.
"Although the gut is considered an important portal of entry for the virus, the immune response in the blood of COVID-19 patients is dominated by ...
Understanding spoilage and quality issues may improve American artisan cheesemaking industry
2021-04-20
Philadelphia, April 20, 2021 - American artisan cheese has become increasingly popular over the past few decades. Understanding spoilage concerns and the financial consequences of defects can improve quality, profitability, and sustainability in the American artisan cheesemaking industry. In an article appearing in the END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] The British variant is 45% more contagious than the original virusStudy at Tel Aviv University based on data from 300,000 tests for COVID-19