Microplastics affect global nutrient cycle and oxygen levels in the ocean
GEOMAR study points to possible major changes in the marine ecosystem
2021-04-21
(Press-News.org) The effects of the steadily increasing amount of plastic in the ocean are complex and not yet fully understood. Scientists at GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel have now shown for the first time that the uptake of microplastics by zooplankton can have significant effects on the marine ecosystem even at low concentrations. The study, published in the international journal Nature Communications, further indicates that the resulting changes may be responsible for a loss of oxygen in the ocean beyond that caused by global warming.
Plastic debris in the ocean is a widely known problem for large marine mammals, fish and seabirds. These animals can mistake plastic objects, such as plastic bags, for similar-looking food items, such as jellyfish. Tiny zooplankton can also mistake very small plastic particles for food and ingest them either accidentally or by chance (when the particles have combined with organic particles).
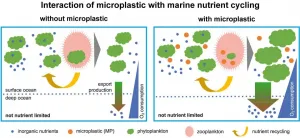
The direct effects of such microplastic ingestion on zooplankton are poorly understood, but the broader effects on ecosystems of zooplankton replacing some of their food with plastic are much less well understood. Now, for the first time, a research team has used an Earth system model to simulate how zooplankton that ingest microplastics could affect the base of the ocean food web and nutrient cycling. The results, now published in the international journal Nature Communications, suggest that even low concentrations of microplastics can have a strong impact on ecosystems. "This influence is already sufficient to affect global nutrient cycling", says Dr Karin Kvale, lead author of the study.
"These findings are significant because there has long been scepticism in the scientific community that microplastic concentrations in the ocean are high enough to have any impact on nutrient cycling", says Dr Karin Kvale "Our study shows that even at levels present in the ocean today, it may already be the case if zooplankton replace some of their natural food with microplastics. If zooplankton eat the microplastics and thus take up less food, this can have far-reaching ecological effects that can, for example, lead to increased algal blooms via a reduction in feeding pressure that affect the oxygen content of the oceans almost as much as climate change", Kvale continues. These findings point to a new potential driver of human-induced ocean change that has not been considered before. However, Kvale points out that the results are "very preliminary" because little is yet known about how the base of the food web interacts with microplastic pollution. Further work on this topic is needed, she says, but the study provides strong motivation to expand the capacity of Earth system models to include pollution effects as a new driver of ocean change.
INFORMATION:
Reference:
Kvale, K. A. E. F. Prowe, C.-T. Chien, A. Landolfi, and A. Oschlies, 2021: Zooplankton grazing of microplastic can accelerate global loss of ocean oxygen. Nature Communications, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22554-w
Contact:
Dr. Andreas Villwock (GEOMAR, Communication and Media), Tel.:+49 0431 600-2802, presse@geomar.de
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-21
The results, exceptional first time evidence of how early flocks of domesticated sheep fed and reproduced within the Iberian Peninsula, are currently the first example of the modification of sheep's seasonal reproductive rhythms with the aim of adapting them to human needs.
The project includes technical approaches based on stable isotope analysis and dental microwear of animal remains from more than 7,500 years ago found in the Neolithic Chaves cave site in Huesca, in the central Pyrennean region of Spain. The research was coordinated from the Arqueozoology Laboratory of the UAB Department of Antiquity, with the participation of researchers from the University of Zaragoza, the Museum of Natural History of Paris, and the Catalan Institute of Human Palaeocology and Social Evolution (IPHES) ...
2021-04-21
Most battery materials, novel catalysts, and storage materials for hydrogen have one thing in common: they have a structure comprised of tiny pores in the nanometer range. These pores provide space which can be occupied by guest atoms, ions, and molecules. As a consequence, the properties of the guest and the host can change dramatically. Understanding the processes inside the pores is crucial to develop innovative energy technologies.
Observing the filling process
So far, it has only been possible to characterise the pore structure of the substrate materials precisely. The exact structure of the adsorbate inside the pores has remained hidden. To probe this, a team from the HZB together with colleagues ...
2021-04-21
The natural menopause occurs when the menstrual periods cease due to the naturally decreased ovary function. There is a significant interindividual variation in the age at natural menopause but, on average, women undergo it around the age of 51 in Western countries. Furthermore, the length of the preceding menopausal transition, characterized by irregular menstrual cycles and menopausal symptoms, is also known to vary between individuals.
The study revealed that higher estradiol and follicle-stimulating hormone levels, irregular menstrual cycles, and menopausal symptoms are strong indicators of approaching menopause in middle-aged women. Additionally, information related ...
2021-04-21
DALLAS - April 21, 2021 - Food banks should be used more consistently rather than only during emergencies to better address food insecurity and related health issues, a joint study by researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center and economists at the University of Dallas shows.
"The main discovery in our research is that encouraging clients and making it easier for clients to receive food frequently improves their food security, health, and well-being," says Sandi Pruitt, Ph.D., associate professor of population and data sciences at UT Southwestern, and senior author of the ...
2021-04-21
Perhaps no other ocean creature lives in the human imagination like the great white shark. But while great white sharks might be plentiful in the minds of beachgoers across the country, there are only a handful of places in the world where white sharks can be consistently found. In those areas -- such as Central California, Guadalupe Island Mexico, South Australia and South Africa -- they tend to be found aggregated in small hotspots, often located around seal colonies.
Researchers have estimated that white shark populations are incredibly small, with only hundreds of large adults and a few thousand white sharks total in any of their global ...
2021-04-21
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- A new approach to gene editing using the CRISPR/Cas9 system bypasses disease-causing mutations in a gene, enabling treatment of genetic diseases linked to a single gene, such as cystic fibrosis, certain types of sickle cell anemia, and other rare diseases. The method, developed and tested in mice and human tissue cultures by researchers at Penn State, involves inserting a new, fully functional copy of the gene that displaces the mutated gene.
A proof-of-concept for the approach is described in a paper appearing online April 20 in the journal Molecular Therapy.
The CRISPR/Cas9 system has allowed promising new gene therapies ...
2021-04-21
The number of solar panels within shortest distance from a house is the most important factor in determining the likelihood of that house having a solar panel, when compared with a host of socio-economic and demographic variables. This is shown in a new study by scientists using satellite and census data of the city of Fresno in the US, and employing machine learning. Although it is known that peer effects are relevant for sustainable energy choices, very high-resolution data combined with artificial intelligence techniques were necessary to single out the paramount importance of proximity. The finding is relevant for policies that aim at a broad deployment of solar panels in order to replace unsustainable ...
2021-04-21
The lifestyle and eating habits of human groups that have lived for thousands of years can be examined by tooth. An international research group analyzed the prehistoric findings of the Neolithic Age. In addition to providing knowledge about the lifestyles of people who lived in prehistoric times, a novel study of tooth remains paved the way for other methods previously not used. This study applies the complementary approaches of stable isotope and dental microwear analyses to study the diets of past people living in today's Hungary. Their joint results were published in the scientific journal Scientific Reports.
The Great Hungarian Plain is considered one of the most interesting areas for archeology because ...
2021-04-21
Coronavirus researchers led by Professor Rolf Hilgenfeld of the University of Luebeck and PD Dr. Albrecht von Brunn of the Ludwig-Maximilian Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have discovered how SARS viruses enhance the production of viral proteins in infected cells, so that many new copies of the virus can be generated. Notably, coronaviruses other than SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 do not use this mechanism, which may therefore provide a possible explanation for the much higher pathogenicity of the SARS viruses. The findings appear in the EMBO Journal.
Coronaviruses that cause harmless colds in humans were discovered more than 50 years ago. When it emerged in 2002/2003, the SARS coronavirus was the first coronavirus found to cause severe pneumonia ...
2021-04-21
For more sustainability on a global level, EU legislation should be changed to allow the use of gene editing in organic farming. This is what an international research team involving the Universities of Bayreuth and Göttingen demands in a paper published in the journal "Trends in Plant Science".
In May 2020, the EU Commission presented its "Farm-to-Fork" strategy, which is part of the "European Green Deal". The aim is to make European agriculture and its food system more sustainable. In particular, the proportion of organic farming in the EU's total agricultural land is to be increased to 25 percent by 2030. However, if current EU legislation remains in place, this increase will by no means guarantee more sustainability, as the current study by scientists from Bayreuth, Göttingen, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Microplastics affect global nutrient cycle and oxygen levels in the ocean
GEOMAR study points to possible major changes in the marine ecosystem