(Press-News.org) Like humans, certain plants are treated with antibiotics to ward off pathogens and protect the host. Saving millions, antibiotics are one of the 20th century's greatest scientific discoveries, but repeated use and misuse of these life-saving microbial products can disrupt the human microbiome and can have severe effects on an individual's health. Overuse has led to several microbes developing resistance to the antibiotic, rendering it useless, and created "superbugs" that overpower medication. But do we find that same phenomenon in plants and our food industry?
This was the question Dr. Anna Wallis and colleagues investigated in their recent research " END
Antibiotics protect apples from fire blight, but do they destroy the native microbiome?
2021-04-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Handwriting analysis of Dead Sea Scrolls indicates text was written by multiple scribes
2021-04-21
Handwriting analysis of one of the Dead Sea Scrolls indicates the biblical text was likely written by multiple scribes, who mirrored one another's writing styles.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Artificial intelligence based writer identification generates new evidence for the unknown scribes of the Dead Sea Scrolls exemplified by the Great Isaiah Scroll (1QIsaa)
Funding: 'Mladen Popovi? Project: The Hands that Wrote the Bible Grant Number: ERC Starting Grant 640497 European Research Council https://erc.europa.eu/ The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.'
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0249769
...
Weight gain in older age does not appear to preserve cognitive performance
2021-04-21
Weight gain in older age does not appear to preserve cognitive performance, according to study of 58,389 European adults
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Bodyweight change and cognitive performance in the older population
Funding: None of the authors of the manuscript has received specific funding for the work included in this submission. The funders mentioned below did not play any role in the study design, data analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The SHARE data collection has been primarily funded by the European Commission through FP5 (QLK6-CT-2001-00360), ...
Stress and death in female baboons
2021-04-21
DURHAM, N.C. -- Female baboons may not have bills to pay or deadlines to meet, but their lives are extremely challenging. They face food and water scarcity and must be constantly attuned to predators, illnesses and parasites, all while raising infants and maintaining their social status.
A new study appearing April 21 in Science Advances shows that female baboons with high life-long levels of glucocorticoids, the hormones involved in the 'fight or flight' response, have a greater risk of dying than those with lower levels.
Glucocorticoids are a group of hormones ...
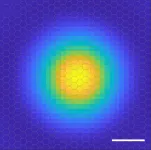
Scientists capture first ever image of an electron's orbit within an exciton
2021-04-21
In a world-first, researchers from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) have captured an image showing the internal orbits, or spatial distribution, of particles in an exciton - a goal that had eluded scientists for almost a century.
Excitons are excited states of matter found within semiconductors - a class of materials that are key to many modern technological devices, such as solar cells, LEDs, lasers and smartphones.
"Excitons are really unique and interesting particles; they are electrically neutral which means they behave very differently within materials from other particles like electrons. Their presence can ...
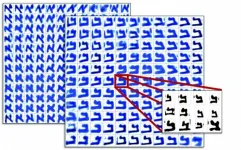
Cracking the code of the Dead Sea Scrolls
2021-04-21
The Dead Sea Scrolls, discovered some seventy years ago, are famous for containing the oldest manuscripts of the Hebrew Bible (Old Testament) and many hitherto unknown ancient Jewish texts. But the individual people behind the scrolls have eluded scientists, because the scribes are anonymous. Now, by combining the sciences and the humanities, University of Groningen researchers have cracked the code, which enables them to discover the scribes behind the scrolls. They presented their results in the journal PLOS ONE on 21 April.
The scribes who created the scrolls did not sign their work. Scholars suggested ...
Using floodwaters to weather droughts
2021-04-21
Floodwaters are not what most people consider a blessing. But they could help remedy California's increasingly parched groundwater systems, according to a new Stanford-led study. The research, published in Science Advances, develops a framework to calculate future floodwater volumes under a changing climate and identifies areas where investments in California's aging water infrastructure could amplify groundwater recharge. As the state grapples with more intense storms and droughts, stowing away floodwaters would not only reduce flood risks but also build more water reserves for ...
Chronic stress may reduce lifespan in wild baboons, according to new multi-decadal study
2021-04-21
Addressing a much-debated question about the impact of stress on survival in wild, nonhuman primates, a new multi-decadal study involving 242 wild female baboons found evidence to support chronic stress as a significant factor affecting survival. The study found that a female baboon with a stress response - as reflected in fecal glucocorticoid concentrations, a biomarker of stress response - in the top 90% for her age throughout adulthood was expected to lose 5.4 years of life compared to a female with glucocorticoid concentrations in the bottom 10% for her age group. The findings, which leveraged more than 14,000 fecal glucocorticoid measurements over a ...
'Ice cube tray' scaffold is next step in returning sight to injured retinas
2021-04-21
MADISON, Wis. -- Tens of millions of people worldwide are affected by diseases like macular degeneration or have had accidents that permanently damage the light-sensitive photoreceptors within their retinas that enable vision.
The human body is not capable of regenerating those photoreceptors, but new advances by medical researchers and engineers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison may provide hope for those suffering from vision loss. They described their work today in the journal Science Advances.
Researchers at UW-Madison have made new photoreceptors from human pluripotent stem cells. However, it remains challenging to precisely deliver those photoreceptors within the diseased or damaged eye so that ...
Scientists find CO2-rich liquid water in ancient meteorite
2021-04-21
Water is abundant in our solar system. Even outside of our own planet, scientists have detected ice on the moon, in Saturn's rings and in comets, liquid water on Mars and under the surface of Saturn's moon Enceladus, and traces of water vapor in the scorching atmosphere of Venus. Studies have shown that water played an important role in the early evolution and formation of the solar system. To learn more about this role, planetary scientists have searched for evidence of liquid water in extraterrestrial materials such as meteorites, most of which originate from asteroids that formed in the early history of the solar system.
Scientists have even found water as hydroxyls and molecules in meteorites in the context ...
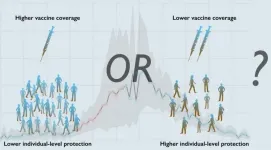
Delaying second dose of COVID-19 vaccines may be an effective public health strategy
2021-04-21
Two of the COVID-19 vaccines currently approved in the United States require two doses, administered three to four weeks apart, however, there are few data indicating how best to minimize new infections and hospitalizations with limited vaccine supply and distribution capacity. A study published on 21st April, 2021 in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Seyed Moghadas at York University in Toronto, Canada, and colleagues suggests that delaying the second dose could improve the effectiveness of vaccine programs.
The emergence of novel, more contagious SARS-CoV-2 variants has led to a public health debate on whether to vaccinate more individuals with the first ...