Intrinsic in-plane nodal chain and generalized quaternion charge protected nodal link in photonics
2021-04-22
(Press-News.org) Topological photonics has attracted a lot of attention recently. The application of topological band theory to photonics not only opens the door to novel devices, but also stimulates the exploration of new topological phases. In the photonic regime, symmetries that are unique to electromagnetic (EM) waves can intrinsically protect the band degeneracies in the momentum space. Topological systems realized using such symmetries are uniquely "photonic", having no counterparts in electronic or phononic systems.
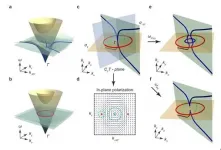
Among various topological features in momentum space, nodal chain is a special configuration of nodal line where two nodal curves touch at isolated points. It is generally perceived that the two nodal lines should reside on two separate mirror planes, each protected by their corresponding mirror symmetries. The chain points are then found to be stabilized on their intersection lines as shown in Fig. 1. However, the in-plane type of nodal chain embedded in mere one mirror symmetry is generally unstable.
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor C. T. Chan from Department of Physics, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, China, and co-workers have proposed a photonic in-plane nodal chain which is stabilized by the intrinsic symmetry of EM waves. The in-plane nodal chain is uniquely stable in photonics due to the internal symmetries of the Maxwell equations and has no counterparts in other systems. They further developed non-Abelian nodal link in the absence of Parity-Time (PT) symmetry and protected by generalized quaternion charges.
In Fig. 2, the authors present the stable in-plane nodal chain in a photonic bianisotropic metamaterials. The chain point is located at the Γ point of zero frequency and is thus stable against perturbation due to the internal symmetry of EM waves. By introduced Lorentz resonance, a dispersionless longitudinal mode appears and intersects the propagating transverse mode as nodal ring. The in-plane nodal chain(blue) thread through the nodal ring(red) and from into nodal link. The nodal link is constructed by three adjacent bands which give enough freedom to define non-Abelian charges. The non-Abelian charges represent the frame rotations of a set of real eigenfunctions, which form the elements of non-Abelian (generalized) quaternion groups.
The generalized quaternion charges can elegantly explain or predict admissible transitions of the nodal link. In order to demonstrate the transition rule of the nodal link, artificial plasmon resonances are considered to introduce cut-off frequencies and force the chain point to break. In Fig. 2c-f, the green loop (larger one) possesses nontrivial generalized quaternion charge of -1, which governs that the encircled nodal line pairs cannot disappear. When the nodal chain break along horizontal direction, a new nodal ring (blue) has to emerge so as to conserve the charge of -1. In a different configuration, the nodal chain is allowed to break along vertical direction, since the green circle is still encircling a pair of nodal lines, and the -1 non-Abelian charge remains conserved.
By designing bi-anisotropic metamaterials, the authors realized the proposed topological structures in photonics. They further characterized the in-plane nodal chain and non-Abelian nodal link with microwave experiments.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-22
Guilt and social pressure lead people to underreport COVID-19 protocol violations, according to study of experimental data across 12 countries.
Article Title: A guilt-free strategy increases self-reported non-compliance with COVID-19 preventive measures: Experimental evidence from 12 countries
Funding: J.-F. Daoust acknowledges the financial support from SSPS Open Access (University of Edinburgh). M. Foucault and S. Brouard acknowledge the financial support from ANR - REPEAT grant (Special COVID-19), CNRS, Fondation de l'innovation politique, as well as regions Nouvelle-Aquitaine and Occitanie. Richard Nadeau and Éric Bélanger acknowledge the financial support from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC/CRSH). M. Becher gratefully acknowledges ...
2021-04-22
Unconventional superconductors contain a number of exotic phases of matter that are thought to play a role, for better or worse, in their ability to conduct electricity with 100% efficiency at much higher temperatures than scientists had thought possible - although still far short of the temperatures that would allow their wide deployment in perfectly efficient power lines, maglev trains and so on.
Now scientists at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have glimpsed the signature of one of those phases, known as pair-density waves or PDW, and confirmed that it's intertwined with another phase known as charge density wave (CDW) stripes - wavelike patterns of higher and lower ...
2021-04-22
Substantial proportions of pregnant and postpartum women scored high for symptoms of anxiety, depression, loneliness and post-traumatic stress in relation to COVID-19 in a survey carried out in May and June 2020, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Karestan Koenen and Archana Basu of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, US, and colleagues.
Pregnant and postpartum women face unique challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic that may put them at elevated risk of mental health problems. These include concerns about ...
2021-04-22
Time seems to pass more slowly in the UK COVID-19 lockdown - especially for people who are depressed, shielding or dissatisfied with social interactions
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Distortions to the passage of time during England's second national lockdown: A role for depression
Funding: The author received no specific funding for this work.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0250412
...
2021-04-22
Survey of 3,536 healthcare workers suggests 67 percent are suffering burnout, but people who receive frequent COVID-19 tests are less likely to be burned out.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: Determinants of burnout and other aspects of psychological well-being in healthcare workers during the Covid-19 pandemic: A multinational cross-sectional study
Funding: JK has received an educational grant from Johnson and Johnson.
Competing Interests: JK has received an educational grant from Johnson and Johnson. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE ...
2021-04-22
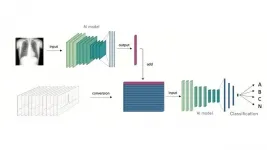
Kobe University Hospital's Dr. NISHIMORI Makoto and Project Assistant Professor KIUCHI Kunihiko et al. (of the Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine) have developed an AI that uses multiple kinds of test data to predict the location of surplus pathways in the heart called 'accessory pathways', which cause the heart to beat irregularly. In this study, the researchers were able to improve diagnosis accuracy by having the AI learn from two completely different types of test results- electrocardiography (ECG) data and X-ray images. It is hoped that this methodology can be applied to other disorders based upon the successful results of this research.
These ...
2021-04-22
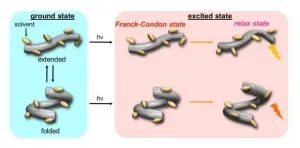
Stimulus-responsive supramolecular structures have emerged as an alternative to conventional ones, owing to their applications in sensing, drug delivery, and switchable memory systems. Now, scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology explore the hydrostatic-pressure response of "foldamers"--artificial molecules that mimic protein folding--and report a shift in their preferred conformation with changing pressure, demonstrating hydrostatic pressure-enabled dynamic control. The finding opens doors to future development of pressure-sensitive foldamers and artificial materials.
Most, if not all, biological systems are extremely complex and often rely on interactions traditional ...
2021-04-22
Animals use their sense of smell to navigate the world--to find food, sniff out mates and smell danger. But when a hungry animal smells food and a member of the opposite sex at the same time, what makes dinner the more attractive option? Exactly what is it about the odor of food that says, "Choose me?"
Research by investigators at Harvard Medical School illuminates the neurobiology that underlies food attraction and how hungry mice choose to pay attention to one object in their environment over another.
In their study, published March 3 in Nature, Stephen Liberles and co-author Nao Horio, identified the pathway that promotes attraction ...
2021-04-22
STUDY SHOWS VACCINES MAY PROTECT AGAINST NEW COVID-19 STRAINS ... AND MAYBE THE COMMON COLD
A new study by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers provides evidence that CD4+ T lymphocytes -- immune system cells also known as helper T cells -- produced by people who have received either of the two messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines for COVID-19 caused by the original SARS-CoV-2 strain also will recognize the mutant variants of the coronavirus that are rapidly becoming the dominant types worldwide.
The researchers say this suggests that T cell responses elicited or enhanced by the vaccines should be able to control the current ...
2021-04-22
Surrey, B.C. Canada and Rochester, Minn., U.S. (April 22, 2021) - Neuroscience researchers at Mayo Clinic Orthopedics and Sports Medicine in Rochester, Minnesota, U.S., the Health and Technology District and Simon Fraser University (SFU) in Surrey, British Columbia, Canada have published the latest results of their ongoing multi-year hockey concussion study examining changes in subconcussive cognitive brain function in male youth ice hockey players.
The research team monitored brain vital signs during pre- and post-season play in 23 Bantam (age 14 or under) and Junior A (age 16 to 20) male ice-hockey players in Rochester, Minnesota.
"Brain vital signs" translates complex ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Intrinsic in-plane nodal chain and generalized quaternion charge protected nodal link in photonics