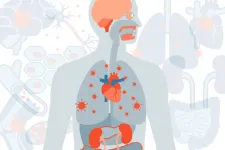
The researchers also have catalogued the numerous diseases associated with COVID-19, providing a big-picture overview of the long-term complications of COVID-19 and revealing the massive burden this disease is likely to place on the world's population in the coming years.
The study, involving more than 87,000 COVID-19 patients and nearly 5 million control patients in a federal database, appears online April 22 in the journal Nature.
"Our study demonstrates that up to six months after diagnosis, the risk of death following even a mild case of COVID-19 is not trivial and increases with disease severity," said senior author Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, an assistant professor of medicine. "It is not an exaggeration to say that long COVID-19 -- the long-term health consequences of COVID-19 -- is America's next big health crisis. Given that more than 30 million Americans have been infected with this virus, and given that the burden of long COVID-19 is substantial, the lingering effects of this disease will reverberate for many years and even decades. Physicians must be vigilant in evaluating people who have had COVID-19. These patients will need integrated, multidisciplinary care."
In the new study, the researchers were able to calculate the potential scale of the problems first glimpsed from anecdotal accounts and smaller studies that hinted at the wide-ranging side effects of surviving COVID-19, from breathing problems and irregular heart rhythms to mental health issues and hair loss.
"This study differs from others that have looked at long COVID-19 because, rather than focusing on just the neurologic or cardiovascular complications, for example, we took a broad view and used the vast databases of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) to comprehensively catalog all diseases that may be attributable to COVID-19," said Al-Aly, also director of the Clinical Epidemiology Center and chief of the Research and Education Service at the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System.
The investigators showed that, after surviving the initial infection (beyond the first 30 days of illness), COVID-19 survivors had an almost 60% increased risk of death over the following six months compared with the general population. At the six-month mark, excess deaths among all COVID-19 survivors were estimated at eight people per 1,000 patients. Among patients who were ill enough to be hospitalized with COVID-19 and who survived beyond the first 30 days of illness, there were 29 excess deaths per 1,000 patients over the following six months.
"These later deaths due to long-term complications of the infection are not necessarily recorded as deaths due to COVID-19," Al-Aly said. "As far as total pandemic death toll, these numbers suggest that the deaths we're counting due to the immediate viral infection are only the tip of the iceberg."
The researchers analyzed data from the national health-care databases of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. The dataset included 73,435 VHA patients with confirmed COVID-19 but who were not hospitalized and, for comparison, almost 5 million VHA patients who did not have a COVID-19 diagnosis and were not hospitalized during this time frame. The veterans in the study were primarily men (almost 88%), but the large sample size meant that the study still included 8,880 women with confirmed cases.
To help understand the long-term effects of more severe COVID-19, the researchers harnessed VHA data to conduct a separate analysis of 13,654 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 compared with 13,997 patients hospitalized with seasonal flu. All patients survived at least 30 days after hospital admission, and the analysis included six months of follow-up data.
The researchers confirmed that, despite being initially a respiratory virus, long COVID-19 can affect nearly every organ system in the body. Evaluating 379 diagnoses of diseases possibly related to COVID-19, 380 classes of medications prescribed and 62 laboratory tests administered, the researchers identified newly diagnosed major health issues that persisted in COVID-19 patients over at least six months and that affected nearly every organ and regulatory system in the body, including:
Respiratory system: persistent cough, shortness of breath and low oxygen levels in the blood. Nervous system: stroke, headaches, memory problems and problems with senses of taste and smell. Mental health: anxiety, depression, sleep problems and substance abuse. Metabolism: new onset of diabetes, obesity and high cholesterol. Cardiovascular system: acute coronary disease, heart failure, heart palpitations and irregular heart rhythms. Gastrointestinal system: constipation, diarrhea and acid reflux. Kidney: acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease that can, in severe cases, require dialysis. Coagulation regulation: blood clots in the legs and lungs. Skin: rash and hair loss. Musculoskeletal system: joint pain and muscle weakness. General health: malaise, fatigue and anemia.
While no survivor suffered from all of these problems, many developed a cluster of several issues that have a significant impact on health and quality of life.
Among hospitalized patients, those who had COVID-19 fared considerably worse than those who had influenza, according to the analysis. COVID-19 survivors had a 50% increased risk of death compared with flu survivors, with about 29 excess deaths per 1,000 patients at six months. Survivors of COVID-19 also had a substantially higher risk of long-term medical problems.
"Compared with flu, COVID-19 showed remarkably higher burden of disease, both in the magnitude of risk and the breadth of organ system involvement," Al-Aly said. "Long COVID-19 is more than a typical postviral syndrome. The size of the risk of disease and death and the extent of organ system involvement is far higher than what we see with other respiratory viruses, such as influenza."
In addition, the researchers found that the health risks from surviving COVID-19 increased with the severity of disease, with hospitalized patients who required intensive care being at highest risk of long COVID-19 complications and death.
"Some of these problems may improve with time -- for example, shortness of breath and cough may get better -- and some problems may get worse," Al-Aly added. "We will continue following these patients to help us understand the ongoing impacts of the virus beyond the first six months after infection. We're only a little over a year into this pandemic, so there may be consequences of long COVID-19 that are not yet visible."
In future analyses of these same datasets, Al-Aly and his colleagues also plan to look at whether patients fared differently based on age, race and gender to gain a deeper understanding of the risk of death in people with long COVID-19.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the Institute for Public Health at Washington University and two American Society of Nephrology and Kidney Cure Fellowship Awards.
Al-Aly Z, Xie Y, Bowe B. High dimensional characterization of post-acute sequalae of COVID-19. Nature. April 22, 2021. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03553-9.
Washington University School of Medicine's 1,500 faculty physicians also are the medical staff of Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals. The School of Medicine is a leader in medical research, teaching and patient care, consistently ranking among the top medical schools in the nation by U.S. News & World Report. Through its affiliations with Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals, the School of Medicine is linked to BJC HealthCare.