(Press-News.org) Young scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University as a part of the team of Arctic researchers have studied pore waters in three areas of methane release on the surface. They first managed to define in details the composition of pore waters in the cold methane seeps of the Eastern Arctic seas. The research findings are published in the Water academic journal.
The research was based on the samples obtained during the Arctic expedition aboard the research vessel "Akademik Mstislav Keldysh" in 2019. The scientists and students from 12 scientific institutions, including Tomsk Polytechnic University, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Lomonosov Moscow State University, the Research Center of Biotechnology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, the Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry and Analytical Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences, the Zhirmunsky National Scientific Center of Marine Biology of the Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences and others took part in the expedition arranged by the Shirshov Institute of Oceanology of the Russian Academy of Sciences jointly with the Ilichev Pacific Oceanological Institute of the Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
The TPU researchers completed a number of research tasks, including the study of conditions of sediments and pore waters. The pore waters are noteworthy due to their reflection of the composition of seawater and the composition of sediments. Researching the samples of pore waters from the point of view of geochemical, biochemical and hydrochemical data, it is possible to reconstruct processes occurring in the waters and sediments, as well as to forecast the development of the situation.
"During the expedition, we focused on the methane yield areas and the changes of hydrochemical properties in these areas. In total, there were six test cores and 42 samples of pore waters collected at depths of 22 to 68 m. The main focus was on the methane yield areas on the surface. Thuswise, three areas with their features were studied: the Lena River Delta, the continental margin of the Laptev Sea and the central part of the East Siberian Sea. In fact, we compared three cold methane seeps together. Moreover, the samples were collected in the sampling points in the immediate vicinity of methane release on the surface," Yulia Moiseeva, Research Fellow of the TPU Division for Geology, one of the authors of the article, says.
To collect the samples, the scientists used special filters and vacuum test tubes to exclude oxygen and obtain valid results. A part of the analyses was conducted aboard. For instance, rapidly changing indicators, i.e. biogenous elements such as nitrates, nitrites, phosphates, ammonia and total alkalinity were researched. A more detailed study of the samples was continued in the TPU laboratories.
"Having come back from the expedition, we studied the macro- and microcomponent composition of pore waters that was conducted in the accredited TPU Research Laboratory for Hydrogeochemistry using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The data on 66 elements for every sample were obtained, it allowed us to define geochemical indicators of the presence of cold methane seep: in this context, what elements can be in higher or lower concentrations in comparison with background concentrations," Darya Purgina, Research Fellow of the TPU Division for Geology, explains.
The scientists managed to define the regional features of the Eastern Arctic seas, including the features of the methane yield areas. For instance, the stations located in the East Siberian Sea are characterized by the high concentration of Mn, Al, Si, P, Fe, Cu, Ba in comparison with the stations in the Laptev Sea, where there was the high concentration of Li, B, V, Br, U and the low concentration of I, Mn.
In general, the concentration of V, Th, P, Al is increased in the methane yield areas, while the concentration of Co, Fe, Mn, U, Mo, Cu is decreased.
"Thus, we first defined a number of elements that can be used as indicators of methane yield. The research is still ongoing to confirm the results. The extended data have already been obtained on the results of the 2020 Arctic expedition. The materials are currently being processed, however, it is already possible to say that the part of the new data confirms the previously obtained results. Furthermore, the extended data will allow reconstructing processes more detailed, which occur in the methane yield areas. The uniqueness of the obtained data lies in the application of modern sampling methods, which allow minimizing failures, as well as obtaining a wide array of elements with high accuracy. The pore waters in the methane yield areas of the Eastern Arctic have not been studied so detailed and comprehensive yet," the scientists sum up.
INFORMATION:
The research was conducted with the support of the TPU Competitiveness Enhancement Program.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) largely remedies Superfund sites containing asbestos by capping them with soil to lock the buried toxin in place. But new research suggests that this may actually increase the likelihood of human exposure to the cancer-causing mineral.
"People have this idea that asbestos is all covered up and taken care of," said Jane Willenbring, who is an associate professor of geological sciences at Stanford University's School of Earth, Energy & Environmental Sciences (Stanford Earth). "But this is still a lingering legacy pollutant ...
Sugar is not just something we eat. On the contrary. Sugar is one of the most naturally occurring molecules, and all cells in the body are covered by a thick layer of sugar that protects the cells from bacteria and virus attacks. In fact, close to 80 per cent of all viruses and bacteria bind to the sugars on the outside of our cells.
Sugar is such an important element that scientists refer to it as the third building block of life - after DNA and protein. And last autumn, a group of researchers found that the spike protein in corona virus needs a particular sugar to bind to our cells efficiently.
Now the same group of researchers have completed a new study that further digs into the cell receptors to which sugars and thus bacteria and virus ...
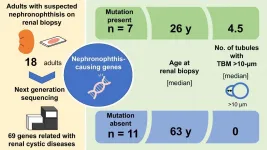
Researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) in a pioneering study identify clinical, genetic and histopathological characteristics that may help confirm the diagnosis when nephronophthisis occurs in adults
Tokyo, Japan - Nephronophthisis (NPH) is a kidney disease affecting mainly children. Now, for the first time, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have studied a number of adults with NPH and highlighted clinical, genetic and pathological characteristics that could help in confirming this challenging diagnosis.
NPH is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern and, though rare, is the commonest genetic cause of kidney failure in children. The ...
It is 2,250 kilometers long, but only 355 kilometers wide at its widest point - on a world map, the Red Sea hardly resembles an ocean. But this is deceptive. A new, albeit still narrow, ocean basin is actually forming between Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. Exactly how young it is and whether it can really be compared with other young oceans in Earth's history has been a matter of dispute in the geosciences for decades. The problem is that the newly formed oceanic crust along the narrow, north-south aligned rift is widely buried under a thick blanket of salt and sediments. This complicates direct investigations.
In the international journal Nature Communications, scientists from GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Blood vessels can be injured by the build-up of atherosclerosis and long-standing hypertension, among other conditions. As a consequence, blood vessels may undergo a process called remodeling, whereby their walls thicken and cause blockages (known as occlusion). In a new study, researchers from the University of Tsukuba discovered how cells marked by platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRa+) residing predominantly in the most outer layer of blood vessels contribute to their remodeling.
Blood vessels comprise three layers, each of which fulfills a unique role ...
Single-molecule fluorescence detection (SMFD) is able to probe, one molecule at a time, dynamical processes that are crucial for understanding functional mechanisms in biosystems. Fluorescence in the Near-infrared (NIR) offers improved Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) by reducing the scattering, absorption and autofluorescence from biological cellular or tissue samples, therefore, provides high imaging resolution with increased tissue penetration depth that are important for biomedical applications. However, most NIR-emitters suffer from low quantum yield, the weak NIR fluorescence signal makes the detection extremely difficult.
Plasmonic nanostructures are capable of converting localized electromagnetic energy into free radiation ...
Strawberry geranium (Saxifraga stolonifera) has been used in Japan as a herbal medicine to treat wounds and swelling, and continues to be an ingredient in food and cosmetics. Pharmacological studies have shown that extracts of strawberry geranium have antioxidant and antitumor activities. However, the anti-inflammatory effect of strawberry geranium on the skin had not been well characterized.
This study, first-authored by associate professor Takeshi Kawahara of the Institute of Agriculture, Shinshu University for a joint research project with Maruzen Pharmaceutical Co., ...
Dr. Sabrina Coninx from Ruhr-Universität Bochum and Dr. Peter Stilwell from McGill University, Canada, have investigated how philosophical approaches can be used to think in new ways about pain and its management. The researchers advocate not merely reducing chronic pain management to searching and treating underlying physical changes but instead adopting an approach that focuses on the person as a whole. Their work was published online in the journal "Synthese" on 15 April 2021.
It is not currently possible to treat chronic pain effectively in many cases. This has encouraged researchers from various disciplines to consider new approaches ...
A team led by Prof. GUO Guangcan and Prof. ZOU Changling from the University of Science and Technology of China of the Chinese Academy of Sciences realized efficient frequency conversion in microresonators via a degenerate sum-frequency process, and achieved cross-band frequency conversion and amplification of converted signal through observing the cascaded nonlinear optical effects inside the microresonator. The study was published in Physics Review Letters.
Coherent frequency conversion process has wide application in classical and quantum information fields such as communication, detection, ...
A new study conducted jointly by the University of Liege (Belgium) and the Ecole normale superieure - PSL (France) shows that heart brain interactions, measured using electroencephalography (EEG), provide a novel diagnostic avenue for patients with disorders of consciousness. This study is published in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Catherine Tallon-Baudry (ENS, CNRS) introduces : "The scientific community already knew that in healthy participants, the brain's response to heartbeats is related to perceptual, bodily and self-consciousness. We now show that we can obtain clinically meaningful information if we probe this interaction in ...