Study reports links between blood types and disease risks
A scan of health data on more than five million people for links between blood type and more than 1,000 diseases reveals new connections and supports previously reported ones
2021-04-27
(Press-News.org) People with certain blood types are more likely to have blood clots or bleeding conditions, kidney stones, or pregnancy-induced hypertension, suggests a study published today in eLife.
The study confirms previously identified connections between certain blood types and the risk of blood clots and bleeding, and makes a new connection between kidney stones and having type B blood as compared to O. The discoveries may lead to new insights on how a person's blood type may predispose them to developing a certain disease.
Previous studies have found that people with blood type A or B were more likely to have cardiovascular disease or experience a blood clot than people with type O blood, and that people with type O blood were more likely to have a bleeding condition. Others have suggested that people with certain blood types may be more susceptible to some infectious diseases.
"There is still very little information available about whether people with RhD-positive or RhD-negative blood groups may be at risk of certain diseases, or how many more diseases may be affected by blood type or group," says first author Torsten Dahlén, a PhD student in the Department of Medicine, Solna, at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden. "To help fill this gap, we used an unbiased approach to investigate the link between ABO blood types and RhD groups and more than 1,000 diseases."
Dahlén and colleagues scanned Swedish health registries with information on more than five million people for links between ABO blood type or RhD-positive or RhD-negative blood groups and more than 1,000 diseases. They found 49 diseases that were linked to ABO blood types, and one that was linked to the RhD group.
Their findings confirmed that people with type A blood were more likely to experience a blood clot and that those with type O blood were more likely to experience a bleeding disorder. They also verified that women with type O blood were more likely to experience pregnancy-induced hypertension.
Additionally, they found a new connection between having type B blood and a lower risk of developing kidney stones. And women who were RhD-positive were more likely to experience pregnancy-induced hypertension.
The authors say that more studies are needed to confirm the results and to determine how different blood types or groups may increase the risk of certain diseases, or whether there are alternative explanations for these relationships.
"Our findings highlight new and interesting relationships between conditions such as kidney stones and pregnancy-induced hypertension and blood type or group," concludes senior author Gustaf Edgren, Associate Professor of Epidemiology at Karolinska Institutet, and a physician in the Department of Cardiology at Södersjukhuset Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden. "They lay the groundwork for future studies to identify the mechanisms behind disease development, or for investigating new ways to identify and treat individuals with certain conditions."
INFORMATION:
Media contact
Emily Packer, Media Relations Manager
eLife
e.packer@elifesciences.org
+44 (0)1223 855373
About eLife
eLife is a non-profit organisation created by funders and led by researchers. Our mission is to accelerate discovery by operating a platform for research communication that encourages and recognises the most responsible behaviours. We aim to publish work of the highest standards and importance in all areas of biology and medicine, including Epidemiology and Global Health, and Medicine, while exploring creative new ways to improve how research is assessed and published. eLife receives financial support and strategic guidance from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Max Planck Society and Wellcome. Learn more at https://elifesciences.org/about.
To read the latest Epidemiology and Global Health research published in eLife, visit https://elifesciences.org/subjects/epidemiology-global-health.
And for the latest in Medicine, see https://elifesciences.org/subjects/medicine.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-27
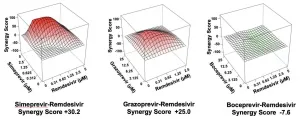
TROY, N.Y. -- When combined with drugs currently used to treat hepatitis C, the antiviral remdesivir is 10 times more effective in treating cells infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Published this week in Cell Reports, this finding -- from Gaetano Montelione, a professor of chemistry and chemical biology at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, and his collaborators at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the University of Texas at Austin -- raises the potential for repurposing available drugs as COVID-19 antivirals in cases where a vaccine isn't practical or effective.
Remdesivir, which blocks viral replication by interfering with a viral polymerase, must ...
2021-04-27
ADELPHI, Md. -- Army researchers developed a technique that allows robots to remain resilient when faced with intermittent communication losses on the battlefield.
The technique, called α-shape, provides an efficient method for resolving goal conflicts between multiple robots that may want to visit the same area during missions including unmanned search and rescue, robotic reconnaissance, perimeter surveillance and robotic detection of physical phenomena, such as radiation and underwater concentration of lifeforms.
Researchers from the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, known as DEVCOM, Army Research Laboratory and the University of Nebraska, Omaha ...
2021-04-27
In a uniquely deep and detailed look at how the commonly used anesthetic propofol causes unconsciousness, a collaboration of labs at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT shows that as the drug takes hold in the brain, a wide swath of regions become coordinated by very slow rhythms that maintain a commensurately languid pace of neural activity. Electrically stimulating a deeper region, the thalamus, restores synchrony of the brain's normal higher frequency rhythms and activity levels, waking the brain back up and restoring arousal.
"There's a folk psychology or tacit assumption that what anesthesia does is simply 'turn off' the brain," said ...
2021-04-27
Ecologists at the University of Cologne's Institute of Zoology have for the first time demonstrated the enormously high and also very specific species diversity of the deep sea in a comparison of 20 deep-sea basins in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Over a period of 20 years, a research team led by Professor Dr Hartmut Arndt at the Institute of Zoology has compiled a body of data that for the first time allows for a comparison of the diversity of existing eukaryotes - organisms with a cell nucleus. Sediment samples from depths of 4000 to 8350 meters, ...
2021-04-27
Tokyo, Japan - Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 (HTLV-1) is a retrovirus similar to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and has mostly been thought to be transmitted vertically (mother-to-child), or horizontally (sexually or parenterally (e.g. via blood transfusion)). The spread of this infection in metropolitan areas such as Tokyo is presumed to be due to horizontal transmission, especially sexual transmission.HTLV-1-associated diseases are thought to be caused mainly through vertical transmission. In a new study, clinicians from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) describe that horizontal transmission route ...
2021-04-27
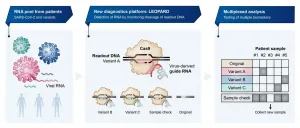
Most conventional molecular diagnostics usually detect only a single disease-related biomarker. Great examples are the PCR tests currently used to diagnose COVID-19 by detecting a specific sequence from SARS-CoV-2. Such so-called singleplex methods provide reliable results because they are "calibrated" to a single biomarker. However, determining whether a patient is infected with a new SARS-CoV-2 variant or a completely different pathogen requires probing for many different biomarkers at one time.
Scientists from the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based ...
2021-04-27
PHILADELPHIA (April 27, 2021) - Nurses and other clinicians rely heavily upon the electronic health record (EHR) to provide patient care. This includes clinical decision-making, care planning, patient surveillance, medication ordering and administration, and communication with other health care team members. While data show that EHR technology usability can put added burden on clinicians, the relationships between EHR usability and the job outcomes of hospital staff nurses and surgical patient outcomes have not been explored.
A new study from the University of ...
2021-04-27
A combination of remdesivir, a drug currently approved in the United States for treating COVID-19 patients, and repurposed drugs for hepatitis C virus (HCV) was 10 times more effective at inhibiting SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
The combination therapy points a way toward a treatment for unvaccinated people who become infected, as well as for vaccinated people whose immunity has waned, for example due to the emergence of virus variants that escape this immune protection.
Four HCV drugs--simeprevir, vaniprevir, paritaprevir, and grazoprevir--in combination with remdesivir boosted the efficacy of remdesivir by as much as 10-fold, the researchers reported today in Cell Reports. The research team included scientists from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, the ...
2021-04-27
Nearly 80 percent of higher education faculty report dealing with student mental health issues—issues that more than 90 percent of faculty believe have worsened or significantly worsened during the pandemic, according to a new nationwide survey led by a Boston University mental health researcher.
"The vast majority of faculty members, myself included, are not trained mental health professionals, but we have a role to play in supporting student well-being," says survey principal investigator Sarah Ketchen Lipson, a BU School of Public Health assistant professor of health law, policy, and management. "These data underscore a real opportunity to better equip faculty with knowledge ...
2021-04-27
UCLA materials scientists have developed a class of optical material that controls how heat radiation is directed from an object. Similar to the way overlapping blinds direct the angle of visible light coming through a window, the breakthrough involves utilizing a special class of materials that manipulates how thermal radiation travels through such materials.
Recently published in Science, the advance could be used to improve the efficiency of energy-conversion systems and enable more effective sensing and detection technologies.
"Our goal was to show that we could effectively beam thermal radiation -- the heat all objects emanate as electromagnetic waves -- ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study reports links between blood types and disease risks
A scan of health data on more than five million people for links between blood type and more than 1,000 diseases reveals new connections and supports previously reported ones