(Press-News.org) In a uniquely deep and detailed look at how the commonly used anesthetic propofol causes unconsciousness, a collaboration of labs at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT shows that as the drug takes hold in the brain, a wide swath of regions become coordinated by very slow rhythms that maintain a commensurately languid pace of neural activity. Electrically stimulating a deeper region, the thalamus, restores synchrony of the brain's normal higher frequency rhythms and activity levels, waking the brain back up and restoring arousal.
"There's a folk psychology or tacit assumption that what anesthesia does is simply 'turn off' the brain," said Earl Miller, Picower Professor of Neuroscience and co-senior author of the study in eLife. "What we show is that propofol dramatically changes and controls the dynamics of the brain's rhythms."
Conscious functions, such as perception and cognition, depend on coordinated brain communication, in particular between the thalamus and the brain's surface regions, or cortex, in a variety of frequency bands ranging from 4 to 100 Hz. Propofol, the study shows, seems to bring coordination among the thalamus and cortical regions down to frequencies around just 1 Hz.
Miller's lab, led by postdoc Andre Bastos and former graduate student Jacob Donoghue, collaborated with that of co-senior author Emery N. Brown, who is Edward Hood Taplin Professor of Medical Engineering and Computational Neuroscience and an anesthesiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital. The collaboration therefore powerfully unified the Miller lab's expertise on how neural rhythms coordinate the cortex to produce conscious brain function with the Brown lab's expertise in the neuroscience of anesthesia and statistical analysis of neural signals.
Brown said studies that show how anesthetics change brain rhythms can directly improve patient safety because these rhythms are readily visible on the EEG in the operating room. The study's main finding of a signature of very slow rhythms across the cortex offers a model for directly measuring when subjects have entered unconsciousness after propofol administration, how deeply they are being maintained in that state, and how quickly they may wake up once propofol dosing ends.
"Anesthesiologists can use this as a way to better take care of patients," Brown said.
Brown has long studied how brain rhythms are affected in humans under general anesthesia by making and analyzing measurements of rhythms using scalp EEG electrodes and to a limited extent, cortical electrodes in epilepsy patients. Because the new study was conducted in animal models of those dynamics, the team was able to implant electrodes that could directly measure the activity or "spiking" of many individual neurons and rhythms in the cortex and thalamus. Brown said the results therefore significantly deepen and extend his findings in people.
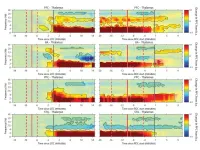
For instance, the same neurons that they measured chattering away with spikes of voltage 7-10 times a second during wakefulness routinely fired only once a second or less during propofol-induced unconsciousnesss, a notable slowing called a "down state." In all, the scientists made detailed simultaneous measurements of rhythms and spikes in five regions: two in the front of the cortex, two toward the back, and the thalamus.
"What's so compelling is we are getting data down to the level of spikes," Brown said. "The slow oscillations modulate the spiking activity across large parts of the cortex."
As much as the study explains how propofol generates unconsciousness, it also helps to explain the unified experience of consciousness, Miller said.
"All the cortex has to be on the same page to produce consciousness," Miller said. "One theory about how this works is through thalamo-cortical loops that allow the cortex to synchronize. Propofol may be breaking the normal operation of those loops by hyper synchronizing them in prolonged down states. It disrupts the ability of the cortex to communicate."
For instance, by making measurements in distinct layers of the cortex, the team found that higher frequency "gamma" rhythms, which are normally associated with new sensory information like sights and sounds, were especially reduced in superficial layers. Lower frequency "alpha" and "beta" waves, which Miller has shown tend to regulate the processing of the information carried by gamma rhythms, were especially reduced in deeper layers.
In addition to the prevailing synchrony at very slow frequencies, the team noted other signatures of unconsciousness in the data. As Brown and others have observed in humans before, alpha and beta rhythm power was notably higher in posterior regions of the cortex during wakefulness, but after loss of consciousness power at those rhythms flipped to being much higher in anterior regions.
The team further showed that stimulating the thalamus with a high frequency pulse of current (180Hz) undid propofol's effects.
"Stimulation produced an awake-like cortical state by increasing spiking rates and decreasing slow-frequency power," the authors wrote in the study. "In all areas, there was a significant increase in spiking during the stimulation interval compared to pre-stimulation baseline."
INFORMATION:
In addition to Miller, Brown, Bastos and Donoghue, the paper's other authors are Scott Brincat, Meredith Mahnke, Jorge Yanar, Josefina Correa, Ayan Waite, Mikael Lundqvist, and Jefferson Roy.
The National Institutes of Health and the JPB Foundation provided funding for the study.
Ecologists at the University of Cologne's Institute of Zoology have for the first time demonstrated the enormously high and also very specific species diversity of the deep sea in a comparison of 20 deep-sea basins in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Over a period of 20 years, a research team led by Professor Dr Hartmut Arndt at the Institute of Zoology has compiled a body of data that for the first time allows for a comparison of the diversity of existing eukaryotes - organisms with a cell nucleus. Sediment samples from depths of 4000 to 8350 meters, ...
Tokyo, Japan - Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 (HTLV-1) is a retrovirus similar to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and has mostly been thought to be transmitted vertically (mother-to-child), or horizontally (sexually or parenterally (e.g. via blood transfusion)). The spread of this infection in metropolitan areas such as Tokyo is presumed to be due to horizontal transmission, especially sexual transmission.HTLV-1-associated diseases are thought to be caused mainly through vertical transmission. In a new study, clinicians from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) describe that horizontal transmission route ...
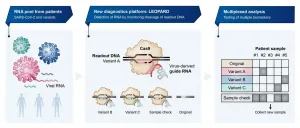
Most conventional molecular diagnostics usually detect only a single disease-related biomarker. Great examples are the PCR tests currently used to diagnose COVID-19 by detecting a specific sequence from SARS-CoV-2. Such so-called singleplex methods provide reliable results because they are "calibrated" to a single biomarker. However, determining whether a patient is infected with a new SARS-CoV-2 variant or a completely different pathogen requires probing for many different biomarkers at one time.
Scientists from the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based ...
PHILADELPHIA (April 27, 2021) - Nurses and other clinicians rely heavily upon the electronic health record (EHR) to provide patient care. This includes clinical decision-making, care planning, patient surveillance, medication ordering and administration, and communication with other health care team members. While data show that EHR technology usability can put added burden on clinicians, the relationships between EHR usability and the job outcomes of hospital staff nurses and surgical patient outcomes have not been explored.
A new study from the University of ...
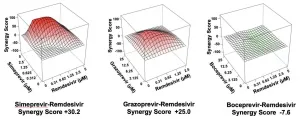
A combination of remdesivir, a drug currently approved in the United States for treating COVID-19 patients, and repurposed drugs for hepatitis C virus (HCV) was 10 times more effective at inhibiting SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
The combination therapy points a way toward a treatment for unvaccinated people who become infected, as well as for vaccinated people whose immunity has waned, for example due to the emergence of virus variants that escape this immune protection.
Four HCV drugs--simeprevir, vaniprevir, paritaprevir, and grazoprevir--in combination with remdesivir boosted the efficacy of remdesivir by as much as 10-fold, the researchers reported today in Cell Reports. The research team included scientists from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, the ...
Nearly 80 percent of higher education faculty report dealing with student mental health issues—issues that more than 90 percent of faculty believe have worsened or significantly worsened during the pandemic, according to a new nationwide survey led by a Boston University mental health researcher.
"The vast majority of faculty members, myself included, are not trained mental health professionals, but we have a role to play in supporting student well-being," says survey principal investigator Sarah Ketchen Lipson, a BU School of Public Health assistant professor of health law, policy, and management. "These data underscore a real opportunity to better equip faculty with knowledge ...
UCLA materials scientists have developed a class of optical material that controls how heat radiation is directed from an object. Similar to the way overlapping blinds direct the angle of visible light coming through a window, the breakthrough involves utilizing a special class of materials that manipulates how thermal radiation travels through such materials.
Recently published in Science, the advance could be used to improve the efficiency of energy-conversion systems and enable more effective sensing and detection technologies.
"Our goal was to show that we could effectively beam thermal radiation -- the heat all objects emanate as electromagnetic waves -- ...
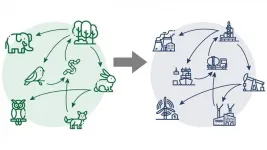
By translating the pattern of interconnections between nature's food chains to industrial networks, researchers at Texas A&M University have delineated guidelines for setting up successful industrial communities. The researchers said this guidance can facilitate economic growth, lower emissions and reduce waste while simultaneously ensure that partnering industries can recover from unexpected disturbances.
"Industries can often partner up to exchange byproducts and over time these industries might form bigger communities. While these networks sound quite beneficial to all industry partners within the community, they are not always successful," said Dr. Astrid Layton, assistant professor in the J. Mike Walker' ...
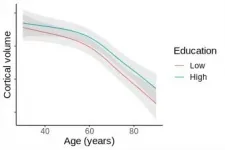
"This finding suggests that higher education does not influence brain aging" says Lars Nyberg from Umeå University in Sweden, first author of the study and also a part of the Lifebrain consortium.
Brains shrink at the same rate
All brains shrink with age, and the dominant view has been that more education slows the rate of shrinking. However, the evidence has been inconclusive because studies have not been able to track the rate of change over time. Until now.
Measured brain shrinkage over time
The researchers measured brain aging by measuring the ...
EUGENE, Ore. -- April 27, 2021 -- The addition of meat alternatives such as poultry and fish is not reducing the global production and consumption of energy-gobbling land-based meats, according to new research.
That conclusion comes from an analysis of 53 years of international data by University of Oregon sociologist Richard York, who focuses on energy consumption in relationship to economic issues such as power and inequalities, and politics. His findings published April 26 in the journal Nature Sustainability.
"If you have increases in the production of poultry and fish, it doesn't tend to compete with or suppress other meat source consumption," York said. "It would be great if more ...