EHR usability issues linked to nurse burnout and patient outcomes
2021-04-27
(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA (April 27, 2021) - Nurses and other clinicians rely heavily upon the electronic health record (EHR) to provide patient care. This includes clinical decision-making, care planning, patient surveillance, medication ordering and administration, and communication with other health care team members. While data show that EHR technology usability can put added burden on clinicians, the relationships between EHR usability and the job outcomes of hospital staff nurses and surgical patient outcomes have not been explored.
A new study from the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing's Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research (CHOPR) has investigated associations between EHR usability and nurse job outcomes (burnout, job dissatisfaction, and intention to leave) and surgical patient outcomes (inpatient mortality and 30-day readmission). The study found that employing EHR systems with suboptimal usability was associated with higher odds of adverse nurse job outcomes and surgical patient mortality and readmission. EHR usability may be more important to nurse job and patient outcomes than comprehensive EHR adoption. The results have been published in the journal Medical Care.
"When the EHR system does not allow work to be performed efficiently and effectively, nurse burden increases, and patient outcomes are threatened," says Ann Kutney-Lee, PhD, RN, FAAN, Adjunct Associate Professor, Department of Biobehavioral Health Sciences at Penn Nursing and lead investigator of the study. "Improving EHR usability may be critical to reducing nurse burnout and to realizing the full potential of EHRs to improve the quality and safety of health care."
The study's findings have implications for nurse turnover and its associated costs. The findings can also help EHR vendors and hospital leadership teams better understand the critical importance of nurse involvement in developing, selecting, implementing, and modifying EHR systems.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Electronic Health Record Usability: Associations With Nurse and Patient Outcomes in Hospitals," is available online. Co-authors of the article include Margo Brooks Carthon, PhD, RN, FAAN; Matthew D. McHugh, PhD, JD, MPH, RN, CRNP, FAAN; Linda H. Aiken, PhD, RN, FAAN, FRCN; Kathryn Bowles, PhD, FAAN, FACMI; and Douglas M. Sloane, PhD, all of Penn Nursing.
About the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing
The University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing is one of the world's leading schools of nursing. For the sixth year in a row, it is ranked the #1 nursing school in the world by QS University and is consistently ranked highly in the U.S. News & World Report annual list of best graduate schools. Penn Nursing is ranked as one of the top schools of nursing in funding from the National Institutes of Health. Penn Nursing prepares nurse scientists and nurse leaders to meet the health needs of a global society through innovation in research, education, and practice. Follow Penn Nursing on: Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, & Instagram.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-27
A combination of remdesivir, a drug currently approved in the United States for treating COVID-19 patients, and repurposed drugs for hepatitis C virus (HCV) was 10 times more effective at inhibiting SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
The combination therapy points a way toward a treatment for unvaccinated people who become infected, as well as for vaccinated people whose immunity has waned, for example due to the emergence of virus variants that escape this immune protection.
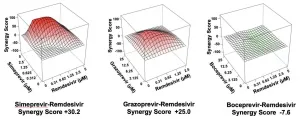
Four HCV drugs--simeprevir, vaniprevir, paritaprevir, and grazoprevir--in combination with remdesivir boosted the efficacy of remdesivir by as much as 10-fold, the researchers reported today in Cell Reports. The research team included scientists from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, the ...
2021-04-27
Nearly 80 percent of higher education faculty report dealing with student mental health issues—issues that more than 90 percent of faculty believe have worsened or significantly worsened during the pandemic, according to a new nationwide survey led by a Boston University mental health researcher.
"The vast majority of faculty members, myself included, are not trained mental health professionals, but we have a role to play in supporting student well-being," says survey principal investigator Sarah Ketchen Lipson, a BU School of Public Health assistant professor of health law, policy, and management. "These data underscore a real opportunity to better equip faculty with knowledge ...
2021-04-27
UCLA materials scientists have developed a class of optical material that controls how heat radiation is directed from an object. Similar to the way overlapping blinds direct the angle of visible light coming through a window, the breakthrough involves utilizing a special class of materials that manipulates how thermal radiation travels through such materials.
Recently published in Science, the advance could be used to improve the efficiency of energy-conversion systems and enable more effective sensing and detection technologies.
"Our goal was to show that we could effectively beam thermal radiation -- the heat all objects emanate as electromagnetic waves -- ...
2021-04-27
By translating the pattern of interconnections between nature's food chains to industrial networks, researchers at Texas A&M University have delineated guidelines for setting up successful industrial communities. The researchers said this guidance can facilitate economic growth, lower emissions and reduce waste while simultaneously ensure that partnering industries can recover from unexpected disturbances.
"Industries can often partner up to exchange byproducts and over time these industries might form bigger communities. While these networks sound quite beneficial to all industry partners within the community, they are not always successful," said Dr. Astrid Layton, assistant professor in the J. Mike Walker' ...
2021-04-27
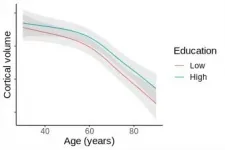
"This finding suggests that higher education does not influence brain aging" says Lars Nyberg from Umeå University in Sweden, first author of the study and also a part of the Lifebrain consortium.
Brains shrink at the same rate
All brains shrink with age, and the dominant view has been that more education slows the rate of shrinking. However, the evidence has been inconclusive because studies have not been able to track the rate of change over time. Until now.
Measured brain shrinkage over time
The researchers measured brain aging by measuring the ...
2021-04-27
EUGENE, Ore. -- April 27, 2021 -- The addition of meat alternatives such as poultry and fish is not reducing the global production and consumption of energy-gobbling land-based meats, according to new research.
That conclusion comes from an analysis of 53 years of international data by University of Oregon sociologist Richard York, who focuses on energy consumption in relationship to economic issues such as power and inequalities, and politics. His findings published April 26 in the journal Nature Sustainability.
"If you have increases in the production of poultry and fish, it doesn't tend to compete with or suppress other meat source consumption," York said. "It would be great if more ...
2021-04-27
Shopping habits and escalating consumption of many consumers are inflicting a heavy environmental toll, and while the majority of customers seem hesitant to act "green" on their own, companies are increasingly expected to implement effective eco-friendly tactics. But efforts to increase towel reuse at hotels, paperless adoption in the banking industry or "ugly" food consumption at grocery stores have been challenging.
As a result, millions of tons of cosmetically imperfect produce are wasted every year in the United States while about one billion trees worth of paper are thrown away. Electricity consumption ...
2021-04-27
An international, multidisciplinary team that includes faculty members from The University of Texas at Arlington has published a paper in the journal Philosophical Psychology that wades into the debate about whether fish feel pain.
Their conclusion: while fish lack certain regions of the brain typically associated in humans with processing the unpleasantness of pain, this does not offer definitive proof that fish don't experience painful events.
There is a divide among contemporary scientists and philosophers on the issue of animal suffering, particularly in fish. Following the discovery of pain receptors in fish in the early 21st century, scientists developed behavioral experiments that seemed to show that fish ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Deep heat creams widely used by athletes to soothe sore muscles may also boost performance when applied before exercise, according to new research presented virtually this week at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Researchers at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore studied a small group of male volunteers to determine the effects of deep heat cream on exercise endurance. Each volunteer participated in two trials--one where he applied a thin layer of a commercially available ...
2021-04-27
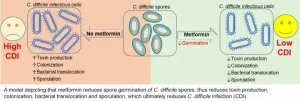
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Researchers from Wake Forest School of Medicine in North Carolina have demonstrated that a common diabetes drug inhibits the spread of Clostridioides difficile, or C. diff--a potentially life-threatening infection commonly acquired during hospital stays. The team will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
C. diff is the most common hospital-acquired infection in the U.S. It starts in the intestines, often after a course of antibiotics. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention categorizes the bacteria C. diff as a public health threat that "require[s] urgent and aggressive action." In 2017, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] EHR usability issues linked to nurse burnout and patient outcomes