(Press-News.org) EUGENE, Ore. -- April 27, 2021 -- The addition of meat alternatives such as poultry and fish is not reducing the global production and consumption of energy-gobbling land-based meats, according to new research.
That conclusion comes from an analysis of 53 years of international data by University of Oregon sociologist Richard York, who focuses on energy consumption in relationship to economic issues such as power and inequalities, and politics. His findings published April 26 in the journal Nature Sustainability.
"If you have increases in the production of poultry and fish, it doesn't tend to compete with or suppress other meat source consumption," York said. "It would be great if more poultry and fish production and consumption would reduce that of beef, but that doesn't seem to be the case."
In 2012, in a study published in Nature Climate Change, York found that the same human behavior played out when new technologies offered renewable energy sources as alternatives to fossil fuel production; adding new sources doesn't substantially suppress an existing, long-used source.
"They end up not in competition," he said. "Adding more wind doesn't really result in using less coal. If we use more energy sources, we use more energy. Likewise, when additional meat choices are offered, that additional variety tends to, more simply, increase overall meat consumption."
The new study, York said, provides a baseline view of meat consumption during the years of rapid post-World War II industrialization. During this period, especially beginning in the 1960s and 1970s, poultry consumption rose fivefold per capita with a growing population, providing an alternative to beef, mutton and lamb -- land-grazing meat sources that require extensive energy to produce.
He also considered the twofold increase in the consumption and production of sea and freshwater fish, as well as aquatic non-fish foods such as crawfish, clams, mussels and shellfish. Pork also rose twofold in the 1961-2013 study period.
The failure of alternative energy and meat sources to suppress original sources, York said, is known as a displacement paradox.
"Consumer demand does not make that big of difference," York said. "Some people reduce their driving to do their part to reduce the consumption of fossil fuel. That doesn't mean that the oil industry is reducing production. If enough people drive less that makes the price of gas go down. That, in turn, means driving more becomes more desirable to others because fuel costs are lower."
From a policy perspective, he said, there needs to a concerted focus on the supply chains.
"Rather than simply increasing renewable energy production, we need to actively suppress fossil fuel production instead of just giving more options," York said. "With meats, we may need to address the level of subsidies given for meat consumption to realize a desired reduction in meat production."
INFORMATION:
Media Contact: Jim Barlow, director of science and research communications, 541-346-3481, jebarlow@uoregon.edu
Links:
About Richard York: https://sociology.uoregon.edu/profile/rfyork/
Department of Sociology: https://sociology.uoregon.edu/
2012 study: Focus on technology overlooks human behavior when addressing climate change: https://uonews.uoregon.edu/archive/news-release/2012/3/focus-technology-overlooks-human-behavior-when-addressing-climate-change
Shopping habits and escalating consumption of many consumers are inflicting a heavy environmental toll, and while the majority of customers seem hesitant to act "green" on their own, companies are increasingly expected to implement effective eco-friendly tactics. But efforts to increase towel reuse at hotels, paperless adoption in the banking industry or "ugly" food consumption at grocery stores have been challenging.
As a result, millions of tons of cosmetically imperfect produce are wasted every year in the United States while about one billion trees worth of paper are thrown away. Electricity consumption ...
An international, multidisciplinary team that includes faculty members from The University of Texas at Arlington has published a paper in the journal Philosophical Psychology that wades into the debate about whether fish feel pain.
Their conclusion: while fish lack certain regions of the brain typically associated in humans with processing the unpleasantness of pain, this does not offer definitive proof that fish don't experience painful events.
There is a divide among contemporary scientists and philosophers on the issue of animal suffering, particularly in fish. Following the discovery of pain receptors in fish in the early 21st century, scientists developed behavioral experiments that seemed to show that fish ...
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Deep heat creams widely used by athletes to soothe sore muscles may also boost performance when applied before exercise, according to new research presented virtually this week at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Researchers at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore studied a small group of male volunteers to determine the effects of deep heat cream on exercise endurance. Each volunteer participated in two trials--one where he applied a thin layer of a commercially available ...
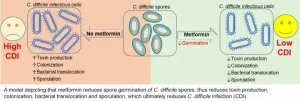
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Researchers from Wake Forest School of Medicine in North Carolina have demonstrated that a common diabetes drug inhibits the spread of Clostridioides difficile, or C. diff--a potentially life-threatening infection commonly acquired during hospital stays. The team will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
C. diff is the most common hospital-acquired infection in the U.S. It starts in the intestines, often after a course of antibiotics. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention categorizes the bacteria C. diff as a public health threat that "require[s] urgent and aggressive action." In 2017, ...
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--The popular herbicide Roundup® has been in the news because of concerns its main ingredient, glyphosate, might cause cancer. Now researchers from Florida Atlantic University (FAU) are evaluating the pesticide for potential neurological impacts. This week, the scientists will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
The roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) is a microscopic worm that lives in soil and feeds on bacteria. Scientists have studied it extensively since the 1960s to better understand fundamental physiological processes of the animal kingdom. Because roughly 38% of its genes have counterparts in humans, findings ...
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--High-intensity cycling in very short bursts can lead to performance and health benefits in just 10 minutes a day, according to a new study to be presented virtually this week at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Young adult volunteers participated in high-intensity cycling three times a week for eight weeks. They cycled at maximum effort for four seconds and rested for 15 to 30 seconds before beginning another four-second sprint. Each sprint-rest bout was repeated up to 30 times in a single workout session, for a total of 10 minutes.
By the end of the trial ...
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--A new study by researchers at the VA Portland Health Care System in Oregon found that augmenting traditional treatment for traumatic brain injury (TBI) with morning bright light therapy (MBLT) improved physical and mental symptoms for participants. The team will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
According to the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), over 185,000 veterans have been diagnosed with at least one TBI. TBI is both a common and complex injury. Because of the circumstances surrounding the brain injury, TBI frequently coincides with posttraumatic stress disorder ...
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Fatty acid supplements may protect children with high cholesterol from heart disease later in life by increasing their blood levels of healthy omega-3 fatty acids, according to a new study. Researchers from the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences in Bethesda, Maryland, will present their work virtually this week at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Previous research has shown that high blood levels of beneficial fatty acids, including omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) found in seafood, are associated with a lower risk of coronary artery disease and a higher likelihood of healthy aging. "Since coronary artery ...
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--A new study reveals that renin-angiotensin system (RAS) genes within the amygdala--the brain region important for traumatic memory processing--express differently when the brain develops fearful memories, such as when people undergo traumatic stress. Researchers have found that medication may potentially be used as a pharmacological blockade of the angiotensin type 1 receptor, thereby improving components of fear memory as assessed by freezing behavior. The research team from George Washington University in Washington, D.C., will present their findings virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a strong predictor ...
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Exposure to extreme heat (95 degrees Fahrenheit and above) and humidity for eight hours raises the core body temperature and causes dehydration, resulting in an increased risk of acute kidney injury, according to a new study. The researchers, from the Indiana University School of Public Health-Bloomington and University at Buffalo Center for Research and Education in Special Environments in New York, will present their findings virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Acute kidney injury, ...