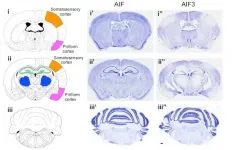
(Press-News.org) DALLAS - April 27, 2021 - Researchers with the Peter O'Donnell Jr. Brain Institute at UT Southwestern have identified a new protein implicated in cell death that provides a potential therapeutic target that could prevent or delay the progress of neurodegenerative diseases following a stroke.
Scientists from the departments of pathology, neurology, biochemistry, and pharmacology at UTSW have identified and named AIF3, an alternate form of the apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF), a protein that is critical for maintaining normal mitochondrial function. Once released from mitochondria, AIF triggers processes that induce a type of programmed cell death.
In a END
Researchers identify protein produced after stroke that triggers neurodegeneration
2021-04-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New AI tool calculates materials' stress and strain based on photos
2021-04-27
Isaac Newton may have met his match.
For centuries, engineers have relied on physical laws -- developed by Newton and others -- to understand the stresses and strains on the materials they work with. But solving those equations can be a computational slog, especially for complex materials.
MIT researchers have developed a technique to quickly determine certain properties of a material, like stress and strain, based on an image of the material showing its internal structure. The approach could one day eliminate the need for arduous physics-based calculations, instead relying on computer vision and machine learning to generate estimates in real time.
The researchers say the advance could enable faster design prototyping and material ...
Droperidol most effective sedation medication for agitation with less sides effects
2021-04-27
Des Plaines, IL - In a randomized, double-blind trial of patients with acute undifferentiated agitation in the emergency department, droperidol was more effective for sedation and was associated with fewer episodes of respiratory depression than lorazepam or either dose of ziprasidone. This is the conclusion of END ...
Lack of educational opportunities influence drug use for rural youth
2021-04-27
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Having grown up poor in a rural village in Zimbabwe, Wilson Majee saw firsthand as a child the lack of educational opportunities that were easily accessible and how that impacted the youth in his village.
Now an associate professor in the University of Missouri School of Health Professions, Majee researches the challenges facing disadvantaged, rural youth. He found in a recent study that young people who are disengaged from their communities are much more likely to participate in risky behaviors such as substance abuse, particularly in rural areas that lack educational opportunities.
For the study, Majee spoke with youth in rural South Africa about the factors contributing to drug abuse for the NEET population, which stands ...
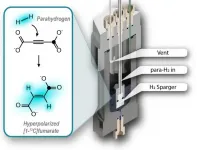
Metabolite fumarate can reveal cell damage: New method to generate fumarate for MRI
2021-04-27
A promising new concept published by an interdisciplinary research team in "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences" (PNAS) paves the way for major advances in the field of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Their new technique could significantly simplify hyperpolarized MRI, which developed around 20 years ago for observing metabolic processes in the body. The proposal involves the hyperpolarization of the metabolic product fumarate using parahydrogen and the subsequent purification of the metabolite. "This technique would not only be simpler, but also much cheaper than the previous procedure," said leader of the project Dr. James Eills, a member of the research team of Professor Dmitry Budker at Johannes Gutenberg ...
Fishing in African waters
2021-04-27
African waters have been contributing to the global supply of fish for years, with three of the four most productive marine ecosystems in the world near the continent. African countries' Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs) contributed over 6 million metric tons of fish to the world's food supply, supporting food security and livelihood in the continent, while generating $15 billion to the African gross domestic product in 2011. Every sovereign state has an EEZ, an area of ocean adjacent to their shores in which they have special rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources.
Industrial fleets from countries around the world have been increasingly fishing in African waters, but with climate change ...
Physical activity reduces cardiovascular risk in rheumatic patients
2021-04-27
The risk of developing atherosclerosis - a narrowing of the arteries as cholesterol plaque builds up, leading to obstruction of blood flow - is higher for people with autoimmune rheumatic diseases than for the general population. As a result, they are more likely to have heart attacks and other cardiovascular disorders.
The good news, according to a new study published in Rheumatology, is that regular exercise is a powerful weapon against vascular dysfunction in these patients.
In the article, researchers working in Brazil and the United Kingdom report the results of a systematic review of the scientific literature on the subject. The review, which ...
An atlas of HIV's favorite targets in the blood of infected individuals
2021-04-27
SAN FRANCISCO, CA--April 27, 2021--In the 40-some years since the beginning of the HIV/AIDS epidemic, scientists have learned a lot about the virus, the disease, and ways to treat it. But one thing they still don't completely understand is which exact cells are most susceptible to HIV infection.
Without this knowledge, it is difficult to envision targeting these cells to protect the millions of people who encounter the virus for the first time every year, or the infected people in which infection will likely rebound if they go off therapy.
Scientists have known for a long time that the virus homes in on so-called memory ...
NIST study suggests how to build a better 'nanopore' biosensor
2021-04-27
Researchers have spent more than three decades developing and studying miniature biosensors that can identify single molecules. In five to 10 years, when such devices may become a staple in doctors' offices, they could detect molecular markers for cancer and other diseases and assess the effectiveness of drug treatment to fight those illnesses.
To help make that happen and to boost the accuracy and speed of these measurements, scientists must find ways to better understand how molecules interact with these sensors. Researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU) have now developed a new approach. ...
Skoltech researchers propose a new data-driven tool to better understand startups
2021-04-27
Skoltech researchers used Google Trends' Big Data ensuing from human interactions with the Internet to develop a new methodology - a tool and a data source - for analyzing and researching the growth of startups. A paper reporting these important findings was published in technology management journal, Technological Forecasting and Social Change.
Startups and high-growth technology-based ventures they transform into are regarded as the key drivers of economic development, innovation, and job creation on the national and global level. However, despite their crucial importance for the economy and high interest from researchers and policy-makers, startups display growth patterns that are difficult to analyze. These fragile, early-stage private ...
Study suggests that silicon could be a photonics game-changer
2021-04-27
New research from the University of Surrey has shown that silicon could be one of the most powerful materials for photonic informational manipulation - opening up new possibilities for the production of lasers and displays.
While computer chips' extraordinary success has confirmed silicon as the prime material for electronic information control, silicon has a reputation as a poor choice for photonics; there are no commercially available silicon light-emitting diodes, lasers or displays.
Now, in a paper published by Light: Science and Applications journal, a Surrey-led international team of scientists has ...