KICT's solution for monitoring massive infrastructures
A trailblazer for developing a new paradigm for structural monitoring
2021-04-29
(Press-News.org) The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT) has announced the development of an effective structural monitoring technique to monitor massive infrastructures, such as long-span bridge. The method provides accurate and precise responses over whole structural system densely by fusing advantages of multi-fidelity data.
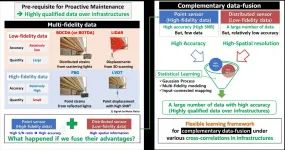
Rapid advances in sensing and information technologies have led to condition-based monitoring in civil and mechanical structural systems. The structural monitoring system plays a key role in condition-based monitoring to evaluate structural safety from responses measured by sensors. In other words, following method allows to examine the health of an existing structures, such as a long-span bridge. The structural monitoring system can enable early detection for an unsafe condition and enable proactive maintenance. As a result, it greatly reduces the inspection burden as well as maintenance costs. The prerequisite for the successful condition-based monitoring is to obtain accurate responses through the whole structural system. Especially in civil-infrastructures, high cost, and technical difficulty are some challenging issues.
In order to solve this problem, a research team in KICT, led by Dr. Seung-Seop Jin, has developed an effective as well as efficient data-fusion method for condition-based monitoring. With the following method, the complementary data-fusion for the point and distributed strain sensor is performed to combine their advantages in order to obtain the accurate strain distribution over whole infrastructures; thereby, responses can be estimated with high accuracy densely over whole infrastructures.
For structural response, the multi-fidelity data consists of point and distributed sensors, which have different fidelities. The point sensor provides high accurate and reproducible responses at discrete measurement positions (High-fidelity data, HF-data), while a distributed sensor utilizes the scattering-based or scanning sensing technique to obtain very dense responses using the quasi-continuous sensing (Low-fidelity data, LF-data). The LF data is relatively easy to acquire, so it is possible to produce large amounts of relatively inaccurate data for response trend over whole infrastructure. On the contrary, the HF data provides high accuracy; however, it is limited to acquire in terms of both time and technical limitations. Therefore, the limited amount of data is available and this can significantly impair the ability to diagnose structural conditions over whole infrastructures. Although they can be complemented each other, their complementary data-fusion has not been studied yet for the structural monitoring system. KICT firstly recognizes their potentials and developed the complementary data-fusion framework by exploiting a multi-fidelity modeling in Computational statistics and Geo-statistics. The basic concept of the developed method is to transfer knowledge of the abundant but potentially inaccurate LF-data (response trend) to enhance their accuracies by fusing the information from the HF-data (accuracy at some points).
The newly developed method was verified by a number of the numerical tests with other existing multi-fidelity data-fusion methods. In order to consider possible situations in real applications, the developed method was extensively evaluated through Monte Carlo simulations by varying the number and locations of multi-fidelity data with the noise. The results show that the prediction performance of the developed method is consistently superior to other existing methods. In both experiments, the relative percentages of accuracy (maximum absolute error) are improved up to 171.3% and 192 % to the existing methods.
The method is very versatile for structural monitoring, especially for massive infrastructures. The developed method is currently improved to make it more robust and efficient. For better generalized capability, the developed method requires flexible learning capability for extracting the information from both the HF-data and LF-data and fusing them. Such improvements include the following.
Dr. Jin said, "The rationale behind this improvement is similar to our decision-making in real life. We seek different options and combine them to make the best decision. Similar to our decision-making, we do not have high confidence on the unknown damages. In the current method, we have to utilize specific models and some parameters in these models. It should be noted that a best model and its parameters are case-dependent. Therefore, we pursue several options for flexible modeling. To deal with various conditions in infrastructures, we can adopt a flexible and self-learning framework such as optimal kernel learning for better data-fusion. This idea takes a step towards autonomous and efficient monitoring system for massive infrastructures."
INFORMATION:
The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT) is a government sponsored research institute established to contribute to the development of Korea's construction industry and national economic growth by developing source and practical technology in the fields of construction and national land management.
This research project is funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT). (No. 2020R1C1C1009236). An article explaining the results of this research was published in Volume 157 of Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, a renowned international journal in the ENGINEERING, MECHANICAL category (IF: 6.471, top 3.846% of JCR).
- Journal Paper
Jin et al. (2021), Combining point and distributed strain sensor for complementary data-fusion: A multi-fidelity approach, Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 157, 107725; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2021.107725
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-29
A ship's container lost overboard in the North Atlantic has resulted in printer cartridges washing up everywhere from the coast of Florida to northern Norway, a new study has shown.
It has also resulted in the items weathering to form microplastics that are contaminated with a range of metals such as titanium, iron and copper.
The spillage is thought to have happened around 1,500 km east of New York, in January 2014, with the first beached cartridges reported along the coastline of the Azores in September the same year.
Since then, around 1,500 more have been reported on social media, with the greatest quantities ...
2021-04-29
VANCOUVER, Wash. - Putting on a happy face might not be enough for entrepreneurs to win over potential investors.
Despite perceptions that entrepreneurs should always be positive about their ventures, a study led by a Washington State University researcher found that entrepreneurs whose facial expressions moved through a mix of happiness, anger and fear during funding pitches were more successful.
"Our findings show that there's a role for different emotions in pitches," said Ben Warnick, WSU assistant professor in WSU's Carson College of Business and lead author on the study published in the Journal of Business Venturing. "For example, an angry facial expression can convey how much you care about something, instead of just smiling, which on the extreme end ...
2021-04-29
New York nurses caring for COVID-19 patients during the first wave of the pandemic experienced anxiety, depression, and illness--but steps their hospitals took to protect them and support from their coworkers helped buffer against the stressful conditions, according to a study led by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing.
"A critical part of the public health response to the COVID-19 pandemic should be supporting the mental health of our frontline workers. Our study demonstrates that institutional resources--such as supportive staff relationships, professional development, providing temporary housing, ...
2021-04-29
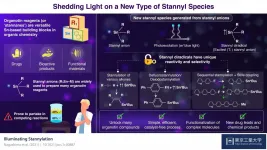
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology developed a new strategy for producing a wide range of organotin compounds, which are the building blocks of many organic synthesis methods. Their approach is based on the photoexcitation of stannyl anions, which alters their electronic state and increases their selectivity and reactivity to form useful compounds. This protocol will be helpful for the efficient synthesis of many bioactive products, novel drugs, and functional materials.
Organotin compounds, also known as stannanes, are made of tin (Sn), hydrocarbons, and sometimes other elements like nitrogen and oxygen. During the 1970s, ...
2021-04-29
ITHACA, N.Y. - Though more than 131 million Americans have received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine to date, public confusion and uncertainty about the importance of second doses and continued public health precautions threaten to delay a U.S. return to normalcy, according to Cornell-led research published April 28 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In a nationally representative survey of more than 1,000 American adults conducted in February, less than half of respondents said they believed the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines provided strong protection against COVID-19 a week or two after a second dose, consistent with guidance from the U.S. Centers for Diseases ...
2021-04-28
NEW YORK, NY-- Diagnosing chronic kidney disease, which is often undetected until it causes irreversible damage, may soon become automated with a new algorithm that interprets data from electronic medical records.
The algorithm, developed by researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, automatically scours a patient's electronic medical record for results of blood and urine tests and, using a mix of established equations and machine learning to process the data, can alert physicians to patients in the earliest stages of chronic kidney disease.
A study of the algorithm was published in the journal npj Digital Medicine in April.
"Identifying ...
2021-04-28
These mysterious earthquakes originate between 400 and 700 kilometers below the surface of the Earth and have been recorded with magnitudes up to 8.3 on the Richter scale.
Xanthippi Markenscoff, a distinguished professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering, is the person who solved this mystery. Her paper " END ...
2021-04-28
In an effort to fight the millions of tons of marine litter floating in the ocean, Florida State University researchers have developed a new virtual tool to track this debris.
Their work, which was published in Frontiers in Marine Science, will help provide answers to help monitor and deal with the problem of marine litter.
Eric Chassignet, director of the Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies and professor in the Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Science.
"Marine litter is found around the world, and we do not fully understand its ...
2021-04-28
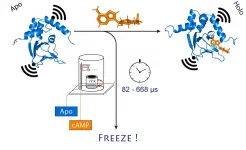
Researchers at the University of Bonn and the research center caesar have succeeded in ultra-fast freezing proteins after a precisely defined period of time. They were able to follow structural changes on the microsecond time scale and with sub-nanometer precision. Owing to its high spatial and temporal resolution, the method allows tracking rapid structural changes in enzymes and nucleic acids. The results are published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
If you want to know what the spatial structure of a biomolecule looks like, you have a formidable arsenal of tools at your disposal. The most popular ones are electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction, which can reveal even the smallest ...
2021-04-28
Researchers have long noted that readers with dyslexia employ eye movements that are significantly different from non-dyslexics. While these movements have been studied in small sample sizes in the past, a new paper written by Concordia researchers and published in the Nature journal END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] KICT's solution for monitoring massive infrastructures
A trailblazer for developing a new paradigm for structural monitoring