(Press-News.org) VANCOUVER, Wash. - Putting on a happy face might not be enough for entrepreneurs to win over potential investors.
Despite perceptions that entrepreneurs should always be positive about their ventures, a study led by a Washington State University researcher found that entrepreneurs whose facial expressions moved through a mix of happiness, anger and fear during funding pitches were more successful.
"Our findings show that there's a role for different emotions in pitches," said Ben Warnick, WSU assistant professor in WSU's Carson College of Business and lead author on the study published in the Journal of Business Venturing. "For example, an angry facial expression can convey how much you care about something, instead of just smiling, which on the extreme end can come off as insincere or overoptimistic. It's good to balance that out. There are different reasons for using different expressions."
While previous research--and advice for entrepreneurs--has focused on using happy or positive attitudes in pitches, Warnick and his co-authors looked at several emotions: happiness, anger, fear and sadness.
For the study, the researchers analyzed nearly 500 pitch videos from the online crowdfunding site, Kickstarter. They used facial analysis software to code the presenters' facial expressions for the four emotions as well as neutral expressions for every frame of each video. They measured the percentage of the pitch that the entrepreneurs expressed each emotion. Then, they compared the display of these emotional expressions with the ultimate success of the pitch by three measures: whether the entrepreneurs met their stated fundraising goal, total amount raised and how many people contributed.
The study showed that those who used a variety of three emotional expressions--happiness, anger and fear--had the most fundraising success. The only emotion that had a negative effect on funding was sadness.
In a qualitative analysis, the authors found that many successful entrepreneurs used different emotional expressions at different points in the pitch. For instance, many entrepreneurs would start their pitch in a happy way, introducing themselves and talking about how proud they are of their team. They would then use anger to talk about their determination or the problem they were trying to address. When the entrepreneurs talked about obstacles, the risk they were taking or need for resources, they would often use facial expressions conveying fear.
In contrast, people who expressed very little emotion on their faces did not do well in garnering funds even if the words they were saying were compelling. Entrepreneurs who stuck to just one emotion also did not do as well.
Yet there were limits to the use of emotion in pitches, even if it was varied.
"There's a Goldilocks point where you can have too little or too much," said Warnick. "Expressing happiness, anger and fear all promote funding up to a point. But if you express any one of these emotions too frequently, you're hurting your funding prospects."
This study only looked at the use of facial expressions. Warnick suggested that further research might look into other channels of expression or at the connection between what people actually feel and what they express, as the two don't always align.
"Some people might be very expressive, where what they're feeling on the inside shows quite readily to other people," said Warnick. "Others might be engaging in impression management, in other words, faking it."
INFORMATION:
New York nurses caring for COVID-19 patients during the first wave of the pandemic experienced anxiety, depression, and illness--but steps their hospitals took to protect them and support from their coworkers helped buffer against the stressful conditions, according to a study led by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing.
"A critical part of the public health response to the COVID-19 pandemic should be supporting the mental health of our frontline workers. Our study demonstrates that institutional resources--such as supportive staff relationships, professional development, providing temporary housing, ...
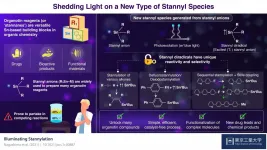
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology developed a new strategy for producing a wide range of organotin compounds, which are the building blocks of many organic synthesis methods. Their approach is based on the photoexcitation of stannyl anions, which alters their electronic state and increases their selectivity and reactivity to form useful compounds. This protocol will be helpful for the efficient synthesis of many bioactive products, novel drugs, and functional materials.
Organotin compounds, also known as stannanes, are made of tin (Sn), hydrocarbons, and sometimes other elements like nitrogen and oxygen. During the 1970s, ...
ITHACA, N.Y. - Though more than 131 million Americans have received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine to date, public confusion and uncertainty about the importance of second doses and continued public health precautions threaten to delay a U.S. return to normalcy, according to Cornell-led research published April 28 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In a nationally representative survey of more than 1,000 American adults conducted in February, less than half of respondents said they believed the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines provided strong protection against COVID-19 a week or two after a second dose, consistent with guidance from the U.S. Centers for Diseases ...
NEW YORK, NY-- Diagnosing chronic kidney disease, which is often undetected until it causes irreversible damage, may soon become automated with a new algorithm that interprets data from electronic medical records.
The algorithm, developed by researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, automatically scours a patient's electronic medical record for results of blood and urine tests and, using a mix of established equations and machine learning to process the data, can alert physicians to patients in the earliest stages of chronic kidney disease.
A study of the algorithm was published in the journal npj Digital Medicine in April.
"Identifying ...
These mysterious earthquakes originate between 400 and 700 kilometers below the surface of the Earth and have been recorded with magnitudes up to 8.3 on the Richter scale.
Xanthippi Markenscoff, a distinguished professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering, is the person who solved this mystery. Her paper " END ...
In an effort to fight the millions of tons of marine litter floating in the ocean, Florida State University researchers have developed a new virtual tool to track this debris.
Their work, which was published in Frontiers in Marine Science, will help provide answers to help monitor and deal with the problem of marine litter.
Eric Chassignet, director of the Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies and professor in the Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Science.
"Marine litter is found around the world, and we do not fully understand its ...
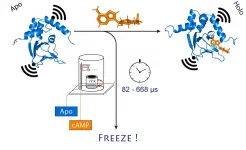
Researchers at the University of Bonn and the research center caesar have succeeded in ultra-fast freezing proteins after a precisely defined period of time. They were able to follow structural changes on the microsecond time scale and with sub-nanometer precision. Owing to its high spatial and temporal resolution, the method allows tracking rapid structural changes in enzymes and nucleic acids. The results are published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
If you want to know what the spatial structure of a biomolecule looks like, you have a formidable arsenal of tools at your disposal. The most popular ones are electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction, which can reveal even the smallest ...
Researchers have long noted that readers with dyslexia employ eye movements that are significantly different from non-dyslexics. While these movements have been studied in small sample sizes in the past, a new paper written by Concordia researchers and published in the Nature journal END ...
The ability to turn on and off a physical process with just one photon is a fundamental building block for quantum photonic technologies. Realizing this in a chip-scale architecture is important for scalability, which amplifies a breakthrough by City College of New York researchers led by physicist Vinod Menon. They've demonstrated for the first time the use of "Rydberg states" in solid state materials (previously shown in cold atom gases) to enhance nonlinear optical interactions to unprecedented levels in solid state systems. This feat is a first step towards realizing chip-scale scalable single photon switches.
In solid state systems, exciton-polaritons, half-light ...
Nearly one quarter of the land in the Northern Hemisphere, amounting to some 9 million square miles, is layered with permafrost -- soil, sediment, and rocks that are frozen solid for years at a time. Vast stretches of permafrost can be found in Alaska, Siberia, and the Canadian Arctic, where persistently freezing temperatures have kept carbon, in the form of decayed bits of plants and animals, locked in the ground.
Scientists estimate that more than 1,400 gigatons of carbon is trapped in the Earth's permafrost. As global temperatures climb, and permafrost thaws, this frozen reservoir could potentially escape into the ...