Ultra-high field MRI detects differences in brain's 'hippocampus'
2021-04-29
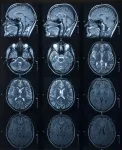
(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND--Using ultra-high field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to map the brains of people with Down syndrome (DS), researchers from Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland Clinic, University Hospitals and other institutions detected subtle differences in the structure and function of the hippocampus--a region of the brain tied to memory and learning.
Such detailed mapping, made possible by the high-powered MRI, is significant because it allowed the research team to better understand how each subregion of the hippocampus in people with DS is functionally connected to other parts of the brain.
"The ultimate goal of this approach is to have an objective technique to complement neuropsychological assessments to measure the functional skills of those with DS," said Alberto Costa, professor of pediatrics and psychiatry at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and the study's senior author.
Their study was recently published in Brain Communications.
Down syndrome is a genetic condition typically caused by having an extra copy of chromosome 21. The extra chromosome changes how a baby's body and brain develop, which can cause mental and physical challenges throughout the person's life.
The intellectual and developmental disabilities of individuals with DS are typically generalized. In other words, although abilities can range widely among people with DS, different types of cognitive skills are usually affected in a similar way in the same person. However, for a given person with DS, cognitive abilities that are heavily dependent on the hippocampus are especially affected.
"That's why we focused on this structure deep inside the brain that is responsible for functions such as forming memories of episodes in one's life and spatial memory," Costa said.
MRI scanners at ultra-high magnetic field strengths are increasingly available for human research, allowing neuroscientists to map the brain at higher resolution without losing image clarity.
Taking advantage of the increased resolution afforded by high-powered MRI, the researchers performed the first in-vivo comparison of volumes of different anatomical segments of the hippocampus between people with DS and "control" individuals of the same age and sex without DS.
"The gains in sensitivity and image resolution achievable with ultra-high field MRI provide levels of detail and accuracy that have not previously been attainable in studies of live, non-sedated individuals with Down syndrome," said Katherine Koenig, an assistant professor of radiology at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University and the study's first author.
"We also found significant relationships between the size of subregions of the hippocampus and cognitive measures," Costa said. "Although more work will be necessary to validate some of our findings, these results support the investigation of specific MRI measures as potential markers to study drug efficacy for possibly enhancing cognitive function in persons with Down syndrome."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by: the Alana USA Foundation, the Alzheimer's Association, the Cleveland Alzheimer's Disease Research Center, the National Institute on Aging, the Cleveland-based Awakening Angels Foundation and the National Institute on Aging.
The research team included: Z. Irene Wang, director of research at Cleveland Clinic Epilepsy Center; and James Leverenz, director of the Cleveland Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health - Neurological Institute and Jane and Lee Seidman Endowed Chair for Advanced Neurological Research and Education at Cleveland Clinic; Stephen Ruedrich, the L. Douglas Lenkoski Professor in the Department of Psychiatry at Case Western Reserve and University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center; Se-Hong Oh, an assistant professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at the Hankuk University of Foreign Studies; Melissa Stasko, a research assistant in Costa's lab; Elizabeth Roth, a research assistant in the Department of Pediatrics at the School of Medicine; H. Gerry Taylor, a professor of pediatrics at the Center for Biobehavioral Health, Abigail Wexner Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital and The Ohio State University.
Case Western Reserve University is one of the country's leading private research institutions. Located in Cleveland, we offer a unique combination of forward-thinking educational opportunities in an inspiring cultural setting. Our leading-edge faculty engage in teaching and research in a collaborative, hands-on environment. Our nationally recognized programs include arts and sciences, dental medicine, engineering, law, management, medicine, nursing and social work. About 5,100 undergraduate and 6,700 graduate students comprise our student body. Visit case.edu to see how Case Western Reserve thinks beyond the possible.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-29
A collaboration between experts and a Danish-based, global reaching patient organization has resulted in a groundbreaking medical publication, where guidelines are being presented on how to manage patients with unexplained low blood sugar.
Danielle Drachmann, founder of Ketotic Hypoglycemia International (KHI), spent years being dismissed by doctors due to the outdated perception that her children's dangerous low blood glucose (sugar) and high ketone levels were a normal variation.
Professor Henrik Christesen, Head of the Complex Hypoglycemia Center, Odense University Hospital, Denmark, could not identify the cause of the condition ...
2021-04-29
The SARS-CoV-2 virus is still causing a dramatic loss of human lives worldwide, constituting an unprecedented challenge for society, public health, and economy, to overcome. Currently, SARS-CoV-2 can be diagnosed in two different ways: i) antigen tests (point-of-care, POC) and ii) molecular tests (nucleic acid, RNA, or PCR-polymerase chain reaction). Antigen tests can detect parts of SARS-CoV-2 proteins, known as antigens, via a nasopharyngeal or nasal swab sampling method. The main advantages of POC-test include the high specificity, quick response (less than an hour), and portability, with no need of fixed laboratory facilities. On the other hand, in a molecular diagnostic test, a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is evolved, also known as nucleic ...
2021-04-29
A research group working at Uppsala University has succeeded in studying 'translation factors' - important components of a cell's protein synthesis machinery - that are several billion years old. By studying these ancient 'resurrected' factors, the researchers were able to establish that they had much broader specificities than their present-day, more specialised counterparts.
In order to survive and grow, all cells contain an in-house protein synthesis factory. This consists of ribosomes and associated translation factors that work together to ensure that the complex protein production process runs smoothly. While almost all components of the modern translational machinery are well known, until now scientists did not know how the ...
2021-04-29
Toxic pollution hits poorer populations hardest as firms experience more pollutant releases and spend less money on waste management in areas with lower average incomes.
Research from Lancaster University Management School and Texas Tech University, published in European Economic Review looked into the relationship between the location choices of potentially polluting firms and levels of local income to discover if firms made strategic decisions on site locations based on population demographics.
The team studied potentially polluting firms across Texas, and found a correlation between lower income locations and the probability of potentially polluting firms choosing to locate there. Their data, from the US Environment Agency's Toxic Release Inventory also ...
2021-04-29
Ice ages are not that easy to define. It may sound intuitive that an ice age represents a frozen planet, but the truth is often more nuanced than that.
An ice age has constant glaciations and deglaciations, with ice sheets pulsating with the rhythm of changing climate. These giants have been consistently waxing and waning, exerting, and lifting pressure from the ocean floor.
Several studies also show that the most recent deglaciation, Holocene (approximately 21ka-15ka ago) of the Barents Sea has had a huge impact on the release of methane into the water. A most recent study in Geology looks even further into the past, some 125 000 years ago, and contributes to the conclusion: Melting of the Arctic ice sheets drives the release of the potent greenhouse ...
2021-04-29
New Haven, Conn. -- The choice between two non-invasive diagnostic tests is a common dilemma in patients who present with chest pain. Yale cardiologist Rohan Khera, MD, MS, and colleagues have developed ASSIST©, a new digital decision-aiding tool.
By applying machine learning techniques to data from two large clinical trials, this new tool identifies which imaging test to pursue in patients who may have coronary artery disease or CAD, a condition caused by plaque buildup in the arterial wall.
The new tool, described in a study published April 21 in the European Heart Journal, focuses on the long-term outcome for a given patient.
"There are strengths and limitations ...
2021-04-29
Individuals who self-identify as Republicans became more skeptical of a potential COVID-19 vaccine and other inoculations, such as the flu shot, over the course of the pandemic, reveals a new study by the University of California San Diego’s Rady School of Management.
The paper, published in PLOS ONE, measured general attitudes toward vaccines and assessed whether study participants would get a potential COVID-19 vaccine as well as the seasonal flu shot. It also gauged trust in media.
“We found Republicans became increasingly vaccine hesitant and less trusting of media from March to August of 2020, while Democrats’ views on ...
2021-04-29
LONDON, ON - In a published study, a team from Lawson Health Research Institute has found that a simple device can reduce swelling after kidney transplantation. The geko™ device, manufactured by Sky Medical Technology Ltd and distributed in Canada by Trudell Healthcare Solutions Inc., is a muscle pump activator which significantly improves blood flow by stimulating the body's 'muscle pumps.' Patients using the device following kidney transplantation experienced shorter hospital stays and reduced surgical site infections by nearly 60 per cent.
Kidney and simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantations ...
2021-04-29
Scientists have recreated the reaction by which carbon isotopes made their way into different organic compounds, challenging the notion that organic compounds, such as amino acids, were formed by isotopically enriched substrates. Their discovery suggests that the building blocks of life in meteorites were derived from widely available substrates in the early solar system.
Their findings were published online in Science Advances on April 28, 2021.
Carbonaceous meteorites contain the building blocks of life, including amino acids, sugars, and nucleobases. These ...
2021-04-29
Scientists from Stony Brook University and the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior have pieced together a timeline of how brain and body size evolved in mammals over the last 150 million years. The international team of 22 scientists, including biologists, evolutionary statisticians, and anthropologists, compared the brain mass of 1400 living and extinct mammals. For the 107 fossils examined--among them ancient whales and the oldest Old World monkey skull ever found--they used endocranial volume data from skulls instead of brain mass data. The brain measurements were then analyzed along with body size ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ultra-high field MRI detects differences in brain's 'hippocampus'