(Press-News.org) Scientists at the University of Nottingham have developed an ultrasonic imaging system, which can be deployed on the tip of a hair-thin optical fibre, and will be insertable into the human body to visualise cell abnormalities in 3D.
The new technology produces microscopic and nanoscopic resolution images that will one day help clinicians to examine cells inhabiting hard-to-reach parts of the body, such as the gastrointestinal tract, and offer more effective diagnoses for diseases ranging from gastric cancer to bacterial meningitis.
The high level of performance the technology delivers is currently only possible in state-of-the-art research labs with large, scientific instruments - whereas this compact system has the potential to bring it into clinical settings to improve patient care.
The Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC)-funded innovation also reduces the need for conventional fluorescent labels - chemicals used to examine cell biology under a microscope - which can be harmful to human cells in large doses.
The findings are being reported in a new paper, entitled 'Phonon imaging in 3D with a fibre probe' published in the Nature journal, Light: Science & Applications.
Paper author, Salvatore La Cavera, an EPSRC Doctoral Prize Fellow from the University of Nottingham Optics and Photonics Research Group, said of the ultrasonic imaging system: "We believe its ability to measure the stiffness of a specimen, its bio-compatibility, and its endoscopic-potential, all while accessing the nanoscale, are what set it apart. These features set the technology up for future measurements inside the body; towards the ultimate goal of minimally invasive point-of-care diagnostics."
Currently at prototype stage, the non-invasive imaging tool, described by the researchers as a "phonon probe", is capable of being inserted into a standard optical endoscope, which is a thin tube with a powerful light and camera at the end that is navigated into the body to find, analyse, and operate on cancerous lesions, among many other diseases. Combining optical and phonon technologies could be advantageous; speeding up the clinical workflow process and reducing the number of invasive test procedures for patients.
3D mapping capabilities
Just as a physician might conduct a physical examination to feel for abnormal 'stiffness' in tissue under the skin that could indicate tumours, the phonon probe will take this '3D mapping' concept to a cellular level.
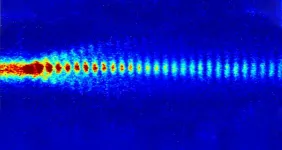
By scanning the ultrasonic probe in space, it can reproduce a three-dimensional map of stiffness and spatial features of microscopic structures at, and below, the surface of a specimen (e.g. tissue); it does this with the power to image small objects like a large-scale microscope, and the contrast to differentiate objects like an ultrasonic probe.
"Techniques capable of measuring if a tumour cell is stiff have been realised with laboratory microscopes, but these powerful tools are cumbersome, immobile, and unadaptable to patient-facing clinical settings. Nanoscale ultrasonic technology in an endoscopic capacity is poised to make that leap," adds Salvatore La Cavera.
How it works
The new ultrasonic imaging system uses two lasers that emit short pulses of energy to stimulate and detect vibrations in a specimen. One of the laser pulses is absorbed by a layer of metal - a nano-transducer (which works by converting energy from one form to another) - fabricated on the tip of the fibre; a process which results in high-frequency phonons (sound particles) getting pumped into the specimen. Then a second laser pulse collides with the sound waves, a process known as Brillouin scattering. By detecting these "collided" laser pulses, the shape of the travelling sound wave can be recreated and displayed visually.
The detected sound wave encodes information about the stiffness of a material, and even its geometry. The Nottingham team was the first to demonstrate this dual-capability using pulsed lasers and optical fibres.
The power of an imaging device is typically measured by the smallest object that can be seen by the system, i.e. the resolution. In two dimensions the phonon probe can "resolve" objects on the order of 1 micrometre, similar to a microscope; but in the third dimension (height) it provides measurements on the scale of nanometres, which is unprecedented for a fibre-optic imaging system.
Future applications
In the paper, the researchers demonstrate that the technology is compatible with both a single optical fibre and the 10-20,000 fibres of an imaging bundle (1mm in diameter), as used in conventional endoscopes.
Consequently, superior spatial resolution and wide fields of view could routinely be achieved by collecting stiffness and spatial information from multiple different points on a sample, without needing to move the device - bringing a new class of phonon endoscopes within reach.
Beyond clinical healthcare, fields such as precision manufacturing and metrology could use this high-resolution tool for surface inspections and material characterisation; a complementary or replacement measurement for existing scientific instruments. Burgeoning technologies such as 3D bio-printing and tissue engineering could also use the phonon probe as an inline inspection tool by integrating it directly to the outer diameter of the print-needle.
Next, the team will be developing a series of biological cell and tissue imaging applications in collaboration with the Nottingham Digestive Diseases Centre and the Institute of Biophysics, Imaging and Optical Science at the University of Nottingham; with the aim to create a viable clinical tool in the coming years.
INFORMATION:
More information is available from Salvatore La Cavera III on salvatore.lacaveraiii@nottingham.ac.uk or Emma Lowry, Media Relations Manager (Engineering) on 0115 84 67156 or Emma.Lowry@nottingham.ac.uk.
Notes to editors
The University of Nottingham
The University of Nottingham is a research-intensive university with a proud heritage, consistently ranked among the world's top 100. Studying at the University of Nottingham is a life-changing experience and we pride ourselves on unlocking the potential of our students. We have a pioneering spirit, expressed in the vision of our founder Sir Jesse Boot, which has seen us lead the way in establishing campuses in China and Malaysia - part of a globally connected network of education, research and industrial engagement. The University's state-of-the-art facilities and inclusive and disability sport provision is reflected in its status as The Times and Sunday Times Good University Guide 2021 Sports University of the Year. We are ranked eighth for research power in the UK according to REF 2014. We have six beacons of research excellence helping to transform lives and change the world; we are also a major employer and industry partner - locally and globally. Alongside Nottingham Trent University, we lead the Universities for Nottingham initiative, a pioneering collaboration which brings together the combined strength and civic missions of Nottingham's two world-class universities and is working with local communities and partners to aid recovery and renewal following the COVID-19 pandemic.
Successful navigation requires the ability to separate memories in a context-dependent manner. For example, to find lost keys, one must first remember whether the keys were left in the kitchen or the office. How does the human brain retrieve the contextual memories that drive behavior? J.B. Julian of the Princeton Neuroscience Institute at Princeton University, USA, and Christian F. Doeller of the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig, Germany, found in a recent study that modulation of map-like representations in our brain's hippocampal formation can predict contextual memory retrieval in an ambiguous environment.
The researchers developed a novel virtual reality navigation task in which human participants learned object positions in two different ...
The future of particle acceleration has begun. Awake is a promising concept for a completely new method with which particles can be accelerated even over short distances. The basis for this is a plasma wave that accelerates electrons and thus brings them to high energies. A team led by the Max Planck Institute for Physics now reports a breakthrough in this context. For the first time, they were able to precisely time the production of the proton microbunches that drive the wave in the plasma. This fulfills an important prerequisite for using the Awake technology for collision experiments.
How do you create a wave for electrons? The carrier substance for this is a plasma (i.e., an ionized gas in which positive and negative charges are separated). Directing a proton beam through ...
The human immune system comprises functionally specialised cellular defence mechanisms that protect the body against disease. These include the dendritic cells. Their main function is to present antigens to other immune cells, especially T cells, thereby activating a primary immune response. Dendritic cells are divided into Type 1 (DC1) and Type 2 (DC2) dendritic cells. Each type fulfils different functions: DC1 provide an immune response to bacteria and viruses, DC2 protect against fungal or parasitic infections. In a recent study conducted at MedUni Vienna's Institute of Cancer Research, researchers found that a particular group of proteins plays a major role in the development of Type 1 dendritic ...
WHAT:
In a mouse study, National Institutes of Health researchers have identified and mapped a diverse spectrum of motor neurons along the spinal cord. These neurons, which send and receive messages throughout the body, include a subset that is susceptible to neurodegenerative diseases. Created with a genetic sequencing technique, the atlas reveals 21 subtypes of neurons in discrete areas throughout the spinal cord and offers insight into how these neurons control movement, how they contribute to the functioning of organ systems and why some are disproportionately affected in neurodegenerative diseases.
The study ...
Researchers have developed a brain-like computing device that is capable of learning by association.
Similar to how famed physiologist Ivan Pavlov conditioned dogs to associate a bell with food, researchers at Northwestern University and the University of Hong Kong successfully conditioned their circuit to associate light with pressure.
The research will be published April 30 in the journal Nature Communications.
The device's secret lies within its novel organic, electrochemical "synaptic transistors," which simultaneously process and store information just like the human brain. The researchers demonstrated ...
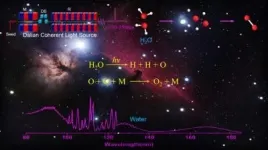
The provenance of oxygen on Earth and other solar planetary bodies is a fundamental issue. It is widely accepted that the prebiotic pathway of oxygen production in the Earth primitive atmosphere was via vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) photodissociation of CO2 and subsequent recombination of two O atoms.
In contrast, the photodissociation of H2O, one of the dominant oxygen carriers, has long been assumed to proceed mainly to produce hydroxyl (OH)- and hydrogen (H)-atom primary products, and its contribution to oxygen production is limited.
Recently, a research group ...
The Worldwide Innovative Network in personalized cancer medicine consortium - WIN Consortium announces the publication of the Digital Display Precision Predictor: the prototype of a global biomarker model to guide treatments with targeted therapy and predict progression-free survival for cancer patients in NPJ Precision Oncology (10.1038/s41698-021-00171-6)
Precision oncology has led to approved, molecularly specific, biomarker-defined indications for targeted therapies. With the number of validated drug targets increasing, testing each patient's tumor for all markers related to all possible targeted therapies becomes infeasible due to limited amount of tissue usually obtained by biopsies. In addition, the current companion diagnostic approach ...
Targeting a pathway that is essential for the survival of certain types of acute myeloid leukaemia could provide a new therapy avenue for patients, the latest research has found.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute found that a specific genetic mutation, which is linked with poor prognosis in blood cancer, is involved in the development of the disease when combined with other mutations in mice and human cell lines.
The study, published today (30th April) in Nature Communications, provides a greater understanding of how the loss-of-function mutation in the CUX1 gene leads to the development and survival of acute myeloid leukaemia. ...
A new study finds Black patients are more likely to die after their heart bypass surgery if they're at a hospital where some care teams see mostly white patients and others see mostly Black patients. On the other hand, mortality rates are comparable between Black and white patients after heart bypass surgery when the teams of health care providers at their hospitals all care for patients of all races.
Some level of care team segregation within hospitals was very common, and the findings bring up another angle to better understand racial inequities in surgical outcomes, says co-first author John Hollingsworth, M.D., M.Sc., a professor of urology at Michigan Medicine and of health management and policy at the University of Michigan School of Public Health.
Previous studies ...
Most detailed study to date including 345,000 people from 48 randomised clinical trials finds that blood pressure-lowering medication is effective in adults regardless of starting blood pressure level.
Each 5mmHg reduction in systolic blood pressure lowered the relative risk of cardiovascular events by around 10%, even in people with normal blood pressure and those who had never had a heart attack or stroke.
Authors call for global guidelines to be changed so that anyone with increased risk of cardiovascular disease is considered for blood-pressure lowering ...