Decoding the effect of body mass index on breast cancer
Clinical data reveals new link between body weight and breast cancer survival
2021-04-30
(Press-News.org) Medical researchers at Flinders University have established a new link between high body mass index (BMI) and breast cancer survival rates - with clinical data revealing worse outcomes for early breast cancer (EBC) patients and improved survival rates in advanced breast cancer (ABC).
In a new study published in a top breast cancer journal- researchers evaluated data from 5 thousand patients with EBC and 3496 with ABC to determine associations between BMI and survival rates across both stages.
Researchers say the results present an 'obesity paradox' which will impact the survival outcomes of the 19,807 women and 167 men diagnosed with breast cancer in Australia in 2020.
Natansh Modi, a NHMRC PHD Candidate at Flinders University, says understanding the biological reasons obesity impacts early and advanced breast cancer survival rates differently will be the key towards developing more effective treatments.
"Higher body mass index (BMI) is associated with an increased risk of developing many types of cancer including breast cancer as a result of elevated levels of circulating sex hormones such as estrogen, estrone, and testosterone, high serum leptin, and chronic inflammation that are associated with high BMI."
Co-author Dr Ashley Hopkins, a Senior Research Fellow at Flinders University, says the study utilises high quality contemporary medicines data to demonstrate higher BMI as independently associated with worse survival in EBC and paradoxically improved survival in advanced disease.
"This is world first evidence of an obesity paradox in breast cancer and highlights an urgent need to understand the biological basis of obesity impacts throughout breast cancer diagnosis and treatment."
INFORMATION:
The paper by Natansh D. Modi, Jin Quan Eugene Tan, Andrew Rowland, Bogda Koczwara, Ahmad Y. Abuhelwa, Ganessan Kichenadasse, Ross A. McKinnon, Michael D. Wiese, Michael J. Sorich & Ashley M. Hopkins (2021) is 'The Obesity Paradox in early and advanced HER2 positive breast cancer: pooled analysis of clinical trial data'.'
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-30
The Brazilian Amazon rainforest released more carbon than it stored over the last decade - with degradation a bigger cause than deforestation - according to new research.
More than 60% of the Amazon rainforest is in Brazil, and the new study used satellite monitoring to measure carbon storage from 2010-2019.
The study found that degradation (parts of the forest being damaged but not destroyed) accounted for three times more carbon loss than deforestation.
The research team - including INRAE, the University of Oklahoma and the University of Exeter - said large areas of rainforest were degraded or destroyed due to human activity and climate change, leading to carbon loss.
The findings, published in Nature Climate Change, also ...
2021-04-30
Mitochondria are the energy suppliers of our body cells. These tiny cell components have their own genetic material, which triggers an inflammatory response when released into the interior of the cell. The reasons for the release are not yet known, but some cardiac and neurodegenerative diseases as well as the ageing process are linked to the mitochondrial genome. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing and the CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Ageing research have investigated the reasons for the release of mitochondrial genetic material and found a direct link to cellular metabolism: when the cell's DNA building blocks are in short supply, mitochondria release their genetic material and trigger inflammation. ...
2021-04-30
Scientists at the University of Nottingham have developed an ultrasonic imaging system, which can be deployed on the tip of a hair-thin optical fibre, and will be insertable into the human body to visualise cell abnormalities in 3D.
The new technology produces microscopic and nanoscopic resolution images that will one day help clinicians to examine cells inhabiting hard-to-reach parts of the body, such as the gastrointestinal tract, and offer more effective diagnoses for diseases ranging from gastric cancer to bacterial meningitis.
The high level of performance the technology delivers is currently only possible in state-of-the-art research labs with large, scientific instruments - whereas this compact system has the potential to bring it into clinical settings to improve patient care.
The ...
2021-04-30
Successful navigation requires the ability to separate memories in a context-dependent manner. For example, to find lost keys, one must first remember whether the keys were left in the kitchen or the office. How does the human brain retrieve the contextual memories that drive behavior? J.B. Julian of the Princeton Neuroscience Institute at Princeton University, USA, and Christian F. Doeller of the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig, Germany, found in a recent study that modulation of map-like representations in our brain's hippocampal formation can predict contextual memory retrieval in an ambiguous environment.
The researchers developed a novel virtual reality navigation task in which human participants learned object positions in two different ...
2021-04-30
The future of particle acceleration has begun. Awake is a promising concept for a completely new method with which particles can be accelerated even over short distances. The basis for this is a plasma wave that accelerates electrons and thus brings them to high energies. A team led by the Max Planck Institute for Physics now reports a breakthrough in this context. For the first time, they were able to precisely time the production of the proton microbunches that drive the wave in the plasma. This fulfills an important prerequisite for using the Awake technology for collision experiments.
How do you create a wave for electrons? The carrier substance for this is a plasma (i.e., an ionized gas in which positive and negative charges are separated). Directing a proton beam through ...
2021-04-30
The human immune system comprises functionally specialised cellular defence mechanisms that protect the body against disease. These include the dendritic cells. Their main function is to present antigens to other immune cells, especially T cells, thereby activating a primary immune response. Dendritic cells are divided into Type 1 (DC1) and Type 2 (DC2) dendritic cells. Each type fulfils different functions: DC1 provide an immune response to bacteria and viruses, DC2 protect against fungal or parasitic infections. In a recent study conducted at MedUni Vienna's Institute of Cancer Research, researchers found that a particular group of proteins plays a major role in the development of Type 1 dendritic ...
2021-04-30
WHAT:
In a mouse study, National Institutes of Health researchers have identified and mapped a diverse spectrum of motor neurons along the spinal cord. These neurons, which send and receive messages throughout the body, include a subset that is susceptible to neurodegenerative diseases. Created with a genetic sequencing technique, the atlas reveals 21 subtypes of neurons in discrete areas throughout the spinal cord and offers insight into how these neurons control movement, how they contribute to the functioning of organ systems and why some are disproportionately affected in neurodegenerative diseases.
The study ...
2021-04-30
Researchers have developed a brain-like computing device that is capable of learning by association.
Similar to how famed physiologist Ivan Pavlov conditioned dogs to associate a bell with food, researchers at Northwestern University and the University of Hong Kong successfully conditioned their circuit to associate light with pressure.
The research will be published April 30 in the journal Nature Communications.
The device's secret lies within its novel organic, electrochemical "synaptic transistors," which simultaneously process and store information just like the human brain. The researchers demonstrated ...
2021-04-30
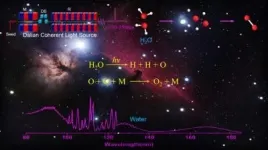
The provenance of oxygen on Earth and other solar planetary bodies is a fundamental issue. It is widely accepted that the prebiotic pathway of oxygen production in the Earth primitive atmosphere was via vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) photodissociation of CO2 and subsequent recombination of two O atoms.
In contrast, the photodissociation of H2O, one of the dominant oxygen carriers, has long been assumed to proceed mainly to produce hydroxyl (OH)- and hydrogen (H)-atom primary products, and its contribution to oxygen production is limited.
Recently, a research group ...
2021-04-30
The Worldwide Innovative Network in personalized cancer medicine consortium - WIN Consortium announces the publication of the Digital Display Precision Predictor: the prototype of a global biomarker model to guide treatments with targeted therapy and predict progression-free survival for cancer patients in NPJ Precision Oncology (10.1038/s41698-021-00171-6)
Precision oncology has led to approved, molecularly specific, biomarker-defined indications for targeted therapies. With the number of validated drug targets increasing, testing each patient's tumor for all markers related to all possible targeted therapies becomes infeasible due to limited amount of tissue usually obtained by biopsies. In addition, the current companion diagnostic approach ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Decoding the effect of body mass index on breast cancer
Clinical data reveals new link between body weight and breast cancer survival