How plants find their symbiotic partners
2021-05-03
(Press-News.org) What would it be like to produce fertilizer in your own basement? Leguminous plants, like peas, beans, and various species of clover, obtain the organic nitrogen they need for their growth from symbiotic soil bacteria via specialized structures in their roots. A team led by the cell biologist Prof. Dr. Thomas Ott from the University of Freiburg's Faculty of Biology has now detected a factor in the root cells that the plants need for the initial contact with these so-called root-associated bacteria, which live in the soil. They discovered a protein found only in legumes called symbiotic formin 1 (SYFO1) and demonstrated the essential role it plays in symbiosis. Together with the molecular biologist Prof. Dr. Robert Grosse University of Freiburg's Faculty of Medicine and the evolutionary biologist Dr. Pierre-Marc Delaux from the Laboratoire de Recherche en Sciences Végétales (LRSV) in Toulouse/France, the team published their results in the journal Current Biology.
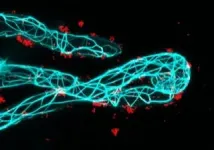
When a root nodule bacterium encounters the roots of a leguminous plant in the soil, the SYFO1 protein causes the tiny hairs of the root to change the direction of their growth. They thus wrap themselves around the potential symbiotic partner. Thanks to these bacterial helpers, legumes do not need any nitrogenous fertilizer, in contrast to other plants. "If we understood precisely how the symbiosis comes into being, we could give crop plants back this special property they have lost in the course of evolution," says Ott. Both he and Grosse are members of the Cluster of Excellence CIBSS - Centre for Integrative Biological Signalling Studies. Ott's research at CIBSS involves studying the spatial organization of the signaling paths that enable the symbiotic relationship with symbiotic bacteria in the first place. Grosse, on the other hand, focuses in his work in Freiburg on the cytoskeleton of animal cells. "In our collaboration, which was made possible by CIBSS, we were able to contribute our expertise in different areas of specialization in the best possible way," says Ott.
The team demonstrated in the legume Medicago truncatula (barrel medic) that the root hairs of plants in which the gene for SYFO1 has been switched off are practically no longer capable of wrapping themselves around the bacteria. In further studies, the researchers discovered that the protein binds to actin, a component of the cytoskeleton, and at the same time to the cell wall outside the cells, thus changing the direction of its growth: Instead of growing straight, the tiny hairs now change their direction and form a loop around the bacterium.
"SYFO1 constitutes a special innovative step in the evolution of the plants," explains Ott. "While formin proteins are present in many forms in cells and interact with actin, this special type only responds to symbiotic signals from the bacteria."
INFORMATION:
CIBSS - Centre for Integrative Biological Signalling Studies
https://www.cibss.uni-freiburg.de
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-03
In a number of biological processes, iron-sulfur clusters play a vital role, where they act as cofactors to enzymes. Research published in Angewandte Chemie now shows that cubic clusters can support unusual bonding states. This study shows that the cluster copes well with a multiple bond between iron and nitrogen--a structural motif that may be involved in biological nitrogen fixation.
Clusters made of iron and sulfur atoms are essential cofactors for a number of enzymes, especially in biological processes involving electron transfer. As an example, nitrogen-fixing bacteria use iron-sulfur clusters to convert ...
2021-05-03
An international team of scientists from 20 countries identified 47 problems that hinder the successful prevention and elimination of the consequences of the tsunami. Based on the carried out analysis, the world's leading experts on natural hazards have outlined directions for further scientific research. The research group's review is published in a special issue of the "Frontiers in Earth Science".
The main problems identified in the review are related to the large gaps and uncertainties in knowledge about tsunami, the lack of well-documented observations, and imperfect methods of processing available information. One of the reasons is the lack of coordination of the efforts of those countries for which the study and prediction of tsunamis, forecasting the corresponding risks, and preparation ...
2021-05-03
Berlin, 3 May - In a new report, ALLEA, the European Federation of Academies of Sciences and Humanities, examines the potential of technical and policy measures to tackle science disinformation and calls for improved European exchange and coordination in this field.
While disinformation strategies are intoxicating public discourses in many fields, science disinformation is particularly dangerous to democratic governance and society at large. As highlighted by the ongoing pandemic, an undermining of trust in science poses a fundamental threat to political and individual decisions based on evidence and scientific knowledge.
Over ...
2021-05-03
Impaired bone health is among the most significant long-term consequences of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), a common therapy for patients with malignant and non-malignant haematological diseases.
To address this serious problem, the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) expert Working Group on Cancer and Bone Disease has published a new Executive Summary of its authoritative state-of-the-art review. The review outlined the major factors affecting bone health in HSCT patients, and provided expert guidance for the monitoring, evaluation and treatment of bone loss in these patients. ...
2021-05-03
Globally, tuberculosis is the most common bacterial infectious disease leading to death. The pathogen causing tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, has a number of peculiarities. One is that it is growing very slowly. While other typical pathogens, such as pneumococcal and pseudomonads, can already be identified by their growth in the microbiological laboratory in the first 72 hours, several weeks usually pass before tuberculosis bacteria grow in the lab. Thus it often takes one to two months before the efficacy of individual medicines can be tested.
However, these efficacy tests are essential for the effective treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), which is becoming increasingly common. In these cases, the pathogen has become ...
2021-05-03
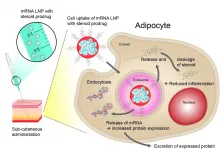
If not before, then certainly since the first messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines to combat the SARS CoV2 virus were approved in Germany, mRNA has become a recognized term even outside scientific circles. What is less well known is that mRNA can be used to produce much more than just vaccines. Around 50 different procedures for the treatment of diseases including cancer are already being studied in clinical trials. Scientists from the pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca, with the support of neutron researchers from Forschungszentrum Jülich, have now discovered how the subcutaneous administration of mRNA can be improved. The goal is for chronically ill ...
2021-05-03
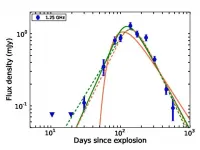
Scientists from the National Centre for radio Astrophysics of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (NCRA-TIFR) Pune used the upgraded Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (uGMRT) to determine that AT 2018 cow, the first of a newly discovered class of cosmic explosions, has an extremely patchy environment. Sources like AT 2018cow release an enormous amount of energy, nonetheless fade extremely rapidly. This along with their extremely blue color has led to them being called FBOTs for Fast Blue Optical Transient. This is the first observational evidence of inhomogeneous emission from an FBOT. The origins of FBOTs are still under debate, but proposed models include explosion of a massive star, collision of an accreting neutron star and ...
2021-05-03
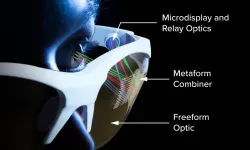
"Image" is everything in the $20 billion market for AR/VR glasses. Consumers are looking for glasses that are compact and easy to wear, delivering high-quality imagery with socially acceptable optics that don't look like "bug eyes."
University of Rochester researchers at the Institute of Optics have come up with a novel technology to deliver those attributes with maximum effect. In a paper in Science Advances, they describe imprinting freeform optics with a nanophotonic optical element called "a metasurface."
The metasurface is a veritable forest of tiny, silver, nanoscale structures on a thin metallic film that conforms, in this advance, to the freeform shape of ...
2021-05-03
According to Michael Twidale, professor in the School of Information Sciences at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, bad usability can be an irritation for everyone but "especially awful" for the underprivileged. In "Everyone Everywhere: A Distributed and Embedded Paradigm for Usability," which was recently published in the Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology (JASIST), Twidale and coauthors David M. Nichols (University of Waikato, New Zealand) and Christopher P. Lueg (Bern University of Applied Sciences, Switzerland) present a new paradigm to address the persistence of difficulties that people have ...
2021-05-03
(New York, NY) - May 3, 2021 - In advance of a wildfire season projected to be among the worst, the American Thoracic Society has released a report that calls for a unified federal response to wildfires that includes investment in research on smoke exposure and forecasting, health impacts of smoke, evaluation of interventions, and a clear and coordinated communication strategy to protect public health.
The report, Respiratory Impacts of Wildland Fire Smoke: Future Challenges and Policy Opportunities, was published online ahead of print in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society on May 3, 2021.
The report comes at a time when the U.S. is experiencing an increasing frequency of very large destructive wildfires, due to years ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How plants find their symbiotic partners