(Press-News.org) Migratory waterbirds are particularly exposed to the effects of climate change at their breeding areas in the High Arctic and in Africa, according to a new study published in Bird Conservation International. The research team came to this conclusion after modelling climatic and hydrological conditions under current and future climate scenarios (in 2050) and comparing the impact on the distribution of 197 of the 255 waterbird species listed under the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds (AEWA). The international team was led by Wetlands International, BirdLife International, and the British Trust for Ornithology, involved researchers from various universities, including McGill. The results suggest that investing more in habitat conservation in the wider landscape, in addition to the conservation of managed protected areas, is urgently needed to help migratory waterbirds adapt to the impacts of climate change.
"Most of the earlier studies in the African-Eurasian flyways focused on the impact of climate change on Palearctic birds," says Frank Breiner, from Wetlands International, who developed the species distribution models. "Our results suggest that Afrotropical species will be even more exposed to the impact of climate change than most species from the temperate zone of the Palearctic. Species breeding in Southern and Eastern Africa, such as the already globally threatened Maccoa Duck and White-winged Flufftail are particularly exposed, but some still common species, such as the Cape Teal and Red-knobbed Coot are projected to suffer a net range loss exceeding 30%. Afrotropical species seem to be more sensitive to the changes in precipitation than Palearctic ones."
Major reductions in freshwater flows and wetlands
"Our models project a variety of changes in the water cycle that will affect the dynamics and extent of wetlands," explains END
Reduction in wetland areas will affect Afrotropical migratory waterbirds
Study points to need for an integrated approach to fighting impacts of climate change
2021-05-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NTU Singapore scientists invent catheter system to deliver electricity-activated glue path
2021-05-03
A team of researchers led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a device that offers a quicker and less invasive way to seal tears and holes in blood vessels, using an electrically-activated glue patch applied via a minimally invasive balloon catheter.
This device could eventually replace the need for open or keyhole surgery to patch up or stitch together internal blood vessel defects.
After inserting the catheter into an appropriate blood vessel, the glue patch - nicknamed 'Voltaglue' - can be guided through the body to where the tear is located and then activated using retractable electrodes to glue it shut in ...
Health anxiety in childhood and adolescence can become chronic
2021-05-03
Symptoms of health anxiety are common already during childhood and adolescence - and if the children do not receive the correct help, the anxiety can become a permanent problem with serious personal and socio-economic consequences. This is shown by a new research result from Aarhus University and the University of Copenhagen.
Ida is 11 years old. Six months ago, her grandmother died of cancer after a long illness and since then Ida has become more and more anxious that she too will get cancer and die. The anxiety can be triggered when she passes by a hospital or sees people who look ill. ...
How plants find their symbiotic partners
2021-05-03
What would it be like to produce fertilizer in your own basement? Leguminous plants, like peas, beans, and various species of clover, obtain the organic nitrogen they need for their growth from symbiotic soil bacteria via specialized structures in their roots. A team led by the cell biologist Prof. Dr. Thomas Ott from the University of Freiburg's Faculty of Biology has now detected a factor in the root cells that the plants need for the initial contact with these so-called root-associated bacteria, which live in the soil. They discovered a protein found only in legumes called symbiotic formin 1 (SYFO1) and demonstrated the essential role it plays in symbiosis. Together with the molecular biologist Prof. Dr. Robert Grosse University of Freiburg's Faculty of Medicine and the evolutionary ...
Strong and flexible cofactors
2021-05-03
In a number of biological processes, iron-sulfur clusters play a vital role, where they act as cofactors to enzymes. Research published in Angewandte Chemie now shows that cubic clusters can support unusual bonding states. This study shows that the cluster copes well with a multiple bond between iron and nitrogen--a structural motif that may be involved in biological nitrogen fixation.
Clusters made of iron and sulfur atoms are essential cofactors for a number of enzymes, especially in biological processes involving electron transfer. As an example, nitrogen-fixing bacteria use iron-sulfur clusters to convert ...
Scientists warn: Humanity does not have effective tools to resist the tsunami
2021-05-03
An international team of scientists from 20 countries identified 47 problems that hinder the successful prevention and elimination of the consequences of the tsunami. Based on the carried out analysis, the world's leading experts on natural hazards have outlined directions for further scientific research. The research group's review is published in a special issue of the "Frontiers in Earth Science".
The main problems identified in the review are related to the large gaps and uncertainties in knowledge about tsunami, the lack of well-documented observations, and imperfect methods of processing available information. One of the reasons is the lack of coordination of the efforts of those countries for which the study and prediction of tsunamis, forecasting the corresponding risks, and preparation ...
European coordination needed to fight science disinformation, academies say
2021-05-03
Berlin, 3 May - In a new report, ALLEA, the European Federation of Academies of Sciences and Humanities, examines the potential of technical and policy measures to tackle science disinformation and calls for improved European exchange and coordination in this field.
While disinformation strategies are intoxicating public discourses in many fields, science disinformation is particularly dangerous to democratic governance and society at large. As highlighted by the ongoing pandemic, an undermining of trust in science poses a fundamental threat to political and individual decisions based on evidence and scientific knowledge.
Over ...
How to manage osteoporosis in hematologic stem cell transplant recipients
2021-05-03
Impaired bone health is among the most significant long-term consequences of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), a common therapy for patients with malignant and non-malignant haematological diseases.
To address this serious problem, the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) expert Working Group on Cancer and Bone Disease has published a new Executive Summary of its authoritative state-of-the-art review. The review outlined the major factors affecting bone health in HSCT patients, and provided expert guidance for the monitoring, evaluation and treatment of bone loss in these patients. ...
Tailor-made therapy of multi-resistant tuberculosis
2021-05-03
Globally, tuberculosis is the most common bacterial infectious disease leading to death. The pathogen causing tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, has a number of peculiarities. One is that it is growing very slowly. While other typical pathogens, such as pneumococcal and pseudomonads, can already be identified by their growth in the microbiological laboratory in the first 72 hours, several weeks usually pass before tuberculosis bacteria grow in the lab. Thus it often takes one to two months before the efficacy of individual medicines can be tested.
However, these efficacy tests are essential for the effective treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), which is becoming increasingly common. In these cases, the pathogen has become ...
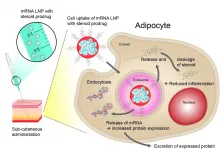
Research with neutrons for better mRNA medicines
2021-05-03
If not before, then certainly since the first messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines to combat the SARS CoV2 virus were approved in Germany, mRNA has become a recognized term even outside scientific circles. What is less well known is that mRNA can be used to produce much more than just vaccines. Around 50 different procedures for the treatment of diseases including cancer are already being studied in clinical trials. Scientists from the pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca, with the support of neutron researchers from Forschungszentrum Jülich, have now discovered how the subcutaneous administration of mRNA can be improved. The goal is for chronically ill ...
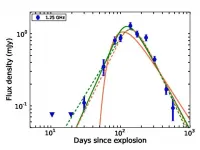
uGMRT reveals for the first time the patchy environment of a rare cosmic explosion
2021-05-03
Scientists from the National Centre for radio Astrophysics of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (NCRA-TIFR) Pune used the upgraded Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (uGMRT) to determine that AT 2018 cow, the first of a newly discovered class of cosmic explosions, has an extremely patchy environment. Sources like AT 2018cow release an enormous amount of energy, nonetheless fade extremely rapidly. This along with their extremely blue color has led to them being called FBOTs for Fast Blue Optical Transient. This is the first observational evidence of inhomogeneous emission from an FBOT. The origins of FBOTs are still under debate, but proposed models include explosion of a massive star, collision of an accreting neutron star and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Reduction in wetland areas will affect Afrotropical migratory waterbirdsStudy points to need for an integrated approach to fighting impacts of climate change