Low doses of radiation may improve quality of life for those with severe Alzheimer's
2021-05-03
(Press-News.org) Individuals living with severe Alzheimer's disease showed remarkable improvements in behaviour and cognition within days of receiving an innovative new treatment that delivered low doses of radiation, a recent Baycrest-Sunnybrook pilot study found.
"The primary goal of a therapy for Alzheimer's disease should be to improve the patient's quality of life. We want to optimize their well-being and restore communication with family and friends to avoid social isolation, loneliness and under-stimulation. Although the study was a small pilot and should be interpreted with caution, our results suggest that low-dose radiation therapy may successfully achieve this," says Dr. Morris Freedman, scientist at Baycrest's Rotman Research Institute, head of the division of neurology at Baycrest and senior author of the study.
The study was a clinical follow-up to a 2015 case report about a patient in hospice with Alzheimer's disease. After being treated several times with radiation to her brain, she showed such significant improvements in cognition, speech, movement and appetite that she was discharged from the hospice to a long-term care home for older adults.
High doses of radiation are known to have harmful effects on our health. However, low doses, such as those used for diagnostic CT scans, can help the body protect and repair itself.
"Numerous neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, are thought to be caused in part by oxidative stress that damages all cells, including those in the brain. We have natural protection systems to combat the damage, but they become less effective as we get older. Each dose of radiation stimulates our natural protection systems to work harder - to produce more antioxidants that prevent oxidative damage, to repair more DNA damage and to destroy more mutated cells," says Dr. Jerry Cuttler, a retired Atomic Energy of Canada scientist. He has been researching the effects of radiation on health for more than 25 years and is the lead author of the study.
In this study, published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, four individuals living with severe Alzheimer's disease were given three treatments of low-dose radiation, each spaced two weeks apart. A CT scanner at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre was employed to provide the treatments, with the supervision and support of Dr. Sandra Black, senior scientist and neurologist, and Dr. Sean Symons, radiologist-in-chief, both at Sunnybrook. The researchers used standardized tests and observation to record changes in the patients' communication and behaviour after the treatment. Most importantly, they collected information (descriptions, photos and videos) from the patients' spouse, children and caregivers.
Remarkably, three of the four individuals showed improvements within one day of the first treatment, with their relatives reporting increased alertness and responsiveness, recognition of loved ones, mobility, social engagement, mood and more.
Two days after the first treatment, the son of one of the patients reported, "When I said hello, she looked at me and said, 'Hello dear.' She hadn't said this to me in years!"
The daughter of another patient noted: "I had an amazing visit with my dad this evening. I'm speechless from last night. He was excited to see me - he spoke to me right away and gave me multiple kisses - real kisses like years ago. He was clapping his hands to the music. My mom agreed it's been years since he has done this. Everyone is amazed."
The results of this study offer hope for those with severe Alzheimer's disease and their loved ones. However, it is important to note that this was a small pilot study with some limitations, including missing a placebo group. Future research is needed to examine the effects of this novel therapy in larger clinical trials.
INFORMATION:
Dr. Freedman, senior author, was supported in part by the Saul A. Silverman Family Foundation as part of the Canada International Scientific Exchange Program (MF), and the Morris Kerzner Memorial Fund.
About Baycrest
Baycrest is a global leader in geriatric residential living, healthcare, research, innovation and education, with a special focus on brain health and aging. Baycrest is home to a robust research and innovation network, including one of the world's top research institutes in cognitive neuroscience, the Rotman Research Institute; the scientific headquarters of the Canadian Consortium on Neurodegeneration in Aging, Canada's largest national dementia research initiative; and the Baycrest-powered Centre for Aging + Brain Health Innovation, a solution accelerator focused on driving innovation in the aging and brain health sector. Fully affiliated with the University of Toronto, Baycrest provides excellent care for older adults combined with an extensive clinical training program for the next generation of healthcare professionals. Through these initiatives, Baycrest has remained at the forefront of the fight to defeat dementia as our organization works to create a world where every older adult enjoys a life of purpose, inspiration and fulfilment. Founded in 1918 as the Toronto Jewish Old Folks Home, Baycrest continues to embrace the long-standing tradition of all great Jewish healthcare institutions to improve the well-being of people in their local communities and around the globe. For more information please visit: http://www.baycrest.org
About Baycrest's Rotman Research Institute
The Rotman Research Institute at Baycrest is a premier international centre for the study of human brain function. Through generous support from private donors and funding agencies, the institute is helping to illuminate the causes of cognitive decline in seniors, identify promising approaches to treatment and lifestyle practices that will protect brain health longer in the lifespan.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-03
In the early 19th century in North America, parasitic infections were quite common in urban areas due in part to population growth and urbanization. Prior research has found that poor sanitation, unsanitary privy (outhouse) conditions, and increased contact with domestic animals, contributed to the prevalence of parasitic disease in urban areas. A new study examining fecal samples from a privy on Dartmouth's campus illustrates how rural wealthy elites in New England also had intestinal parasitic infections. The findings are published in the Journal of Archeological Science: Reports.
"Our study is one of the first to demonstrate evidence of parasitic infection in an affluent rural household in the Northeast," says co-author Theresa Gildner, who was ...
2021-05-03
New research shows that patients who have had contact with the hospital due to serious glandular disease have a greater risk of subsequently developing depression. The study from iPSYCH is the largest yet to show a correlation between glandular fever and depression.
The vast majority of Danes have had glandular fever - also called mononucleosis - before adulthood. And for the vast majority of them, the disease can be cured at home with throat lozenges and a little extra care. But for some, the disease is so serious that they need to visit the hospital.
A new research result now shows that precisely those patients who have been in contact with the hospital in connection with their illness, have a greater risk of suffering a depression later.
"Our study ...
2021-05-03
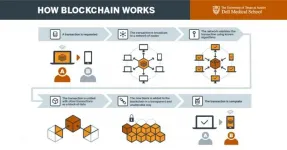
AUSTIN, Texas -- For people experiencing homelessness, missing proof of identity can be a major barrier to receiving critical services, from housing to food assistance to health care. Physical documents such as driver's licenses are highly susceptible to loss, theft or damage. However, researchers from Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin say new technology solutions such as blockchain can be used to keep important health care information secure and portable.
"Health care institutions and social services are so fragmented and siloed they're unable to accurately collect, share or verify basic identity information about a person experiencing homelessness," said Tim Mercer, M.D., MPH, director ...
2021-05-03
A study encompassing some 9,000 dogs conducted at the University of Helsinki demonstrated that fearfulness, age, breed, the company of other members of the same species and the owner's previous experience of dogs were associated with aggressive behaviour towards humans. The findings can potentially provide tools for understanding and preventing aggressive behaviour.
Aggressive behaviour in dogs can include growling, barking, snapping and biting. These gestures are part of normal canine communication, and they also occur in non-aggressive situations, such as during play. However, aggressive behaviour ...
2021-05-03
An extraordinary discovery in the Gulf of Eilat: Researchers from Tel Aviv University have discovered a species of ascidian, a marine animal commonly found in the Gulf of Eilat, capable of regenerating all of its organs - even if it is dissected into three fragments. The study was led by Prof. Noa Shenkar, Prof. Dorothee Huchon-Pupko, and Tal Gordon of Tel Aviv University's School of Zoology at the George S. Wise Faculty of Life Sciences and the Steinhardt Museum of Natural History. The findings of this surprising discovery were published in the leading journal Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.
"It is an astounding discovery, as this is an animal that belongs to the Phylum Chordata - animals with a dorsal cord - which also includes us humans," explains Prof. Noa ...
2021-05-03
Water is a scarce resource in many of the Earth's ecosystems. This scarcity is likely to increase in the course of climate change. This, in turn, might lead to a considerable decline in plant diversity. Using experimental data from all over the world, scientists from the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ), the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), and the Martin Luther University of Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) have demonstrated for the first time that plant biodiversity in drylands is particularly sensitive to changes in precipitation. In an article published in Nature Communications, the team warns that this can also have consequences for the people living in the ...
2021-05-03
The terms "co-creation" and "co-production", which denote the possibility for laypeople to participate in decision-making processes that affect their lives, have been gaining popularity. A new IIASA-led study explored options for empowering citizens as a driver for moving from awareness about the need to transform energy systems to action and participation.
The European Union's climate and energy policies for 2020-2030 require decarbonization of the energy sector. To this end, EU member countries are working on a number of key goals including greater energy efficiency, greater use of renewable energy, and increased energy security across the EU. The successful ...
2021-05-03
In recent decades, Spain has undergone rapid social changes in terms of gender equality, despite, as a result of the Franco dictatorship, starting from a more backward position than most European countries. This process is hampered by the economic downturn that began in 2008, underlining the importance of the economic context in the development of gender inequality levels. Little attention has been paid in academia to how this gender revolution is associated with factors related to individual wellbeing.
A study by Jordi Gumà, a researcher at the Department of Political and ...
2021-05-03
The human world is, increasingly, an urban one -- and that means elevators. Hong Kong, the hometown of physicist Zhijie Feng (Boston University),* adds new elevators at the rate of roughly 1500 every year...making vertical transport an alluring topic for quantitative research.
"Just in the main building of my undergraduate university, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology," Feng reflects, "there are 37 elevators, all numbered so we can use them to indicate the location of hundreds of classrooms. There is always a line outside each elevator lobby, and if they are shut down, we have to hike for 30 minutes."
Feng and Santa Fe Institute Professor ...
2021-05-03
Myotonic dystrophy is a hereditary degenerative neuromuscular disease that occurs mainly in adults, affecting about 50,000 people only in Spain. Symptoms range from difficulty walking and myotonia (great difficulty in relaxing the contracted muscles) to severe neurological problems, leading to progressive disability that unfortunately puts many of those affected in a wheelchair. This disease is very heterogeneous among patients (age of onset, progression, hereditary transmission, affected muscles), which makes the development of generic treatments especially complex.
Currently, drugs against myotonic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Low doses of radiation may improve quality of life for those with severe Alzheimer's