People with familial longevity show better cognitive aging
Exhibit better cognitive performance at baseline and show slower decline in processing speed
2021-05-04
(Press-News.org) (Boston)--If you come from a family where people routinely live well into old age, you will likely have better cognitive function (the ability to clearly think, learn and remember) than peers from families where people die younger. Researchers affiliated with the Long Life Family Study (LLFS) recently broadened that finding in a paper published in END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A sweet solution to hard brain implants
2021-05-04
Brain implants are used to treat neurological dysfunction, and their use for enhancing cognitive abilities is a promising field of research. Implants can be used to monitor brain activity or stimulate parts of the brain using electrical pulses. In epilepsy, for example, brain implants can determine where in the brain seizures are happening.
Over time, implants trigger a foreign body response, creating inflammation and scar tissue around the implant that reduces their effectiveness.
The problem is that traditional implants are much more rigid than brain tissue, which has a softness comparable to pudding. Stress between the implant and ...
Confirmation of an auroral phenomenon discovered by Finns
2021-05-04
A new auroral phenomenon discovered by Finnish researchers a year ago is probably caused by areas of increased oxygen atom density occurring in an atmospheric wave channel. The speculative explanation offered by the researchers gained support from a new study.
Observations made by University of Helsinki researchers increased the validity of a speculative mechanism according to which a type of aurora borealis named 'dunes' is born. In the new study, photographs of the phenomenon taken by an international group of hobbyists in Finland, Norway and Scotland were compared to concurrent satellite data.
The rare type of aurora borealis was seen in the sky on 20 January 2016 and recorded in photos taken by ...
New look at a bright stellar nursery
2021-05-04
This overlay shows radio (orange) and infrared images of a giant molecular cloud called W49A, where new stars are being formed. A team of astronomers led by Chris DePree of Agnes Scott College used the National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) to make new, high-resolution radio images of this cluster of still-forming, massive stars. W49A, 36,000 light-years from Earth, has been studied for many decades, and the new radio images revealed some tantalizing changes that have occurred since an earlier set of VLA observations in 1994 and 1995.
The ...
Scientists have developed a new "key-hole surgery" technique to extract metals from Earth
2021-05-04
Scientists have developed a new "key-hole surgery" technique to extract metals from the earth - which could revolutionise the future of metal mining
A team of international researchers, including Dr Rich Crane from the Camborne School of Mines, University of Exeter, have developed a new method to extract metals, such as copper, from their parent ore body.
The research team have provided a proof of concept for the application of an electric field to control the movement of an acid within a low permeability copper-bearing ore deposit to selectively dissolve and recover the metal in situ.
This is in contrast to the conventional approach for the mining of such deposits ...
Nanoplastics and other harmful pollutants found in disposable face masks -- Regulation and research urgently needed, say experts
2021-05-04
Swansea University scientists have uncovered potentially dangerous chemical pollutants that are released from disposable face masks when submerged in water.
The research reveals high levels of pollutants, including lead, antimony, and copper, within the silicon-based and plastic fibres of common disposable face masks.
The work is supported by the Institute for Innovative Materials, Processing and Numerical Technologies (IMPACT) and the SPECIFIC Innovation & Knowledge Centre
Project lead Dr Sarper Sarp of Swansea University College of Engineering said:
"All of us need to keep wearing masks as they are essential in ending the pandemic. But we also urgently need more research and regulation on mask production, so we can reduce any risks to the environment and ...
Pyrosomes: Enigmatic marine inhabitants with an important role in the Cabo Verde ecosystem
2021-05-04
Pyrosomes, named after the Greek words for 'fire bodies' due their bright bioluminescence, are pelagic tunicates that spend their entire lives swimming in the open ocean. They are made up of many smaller animals, known as zooids, that sit together in a tubular matrix, known as tunic (hence the name pelagic tunicates). Because they live in the open ocean, they generally go unnoticed. In spite of this, increasing research points to their importance in marine environments, as they can form dense blooms that impact food web dynamics and contribute to the movement and transformation of organic carbon.
The study conducted with GEOMAR research vessel POSEIDON in 2018 and 2019 in the vicinity of the Cabo Verde Islands, of which the results have now been published ...
Chronic exposure to low levels of blast may be associated with neurotrauma
2021-05-04
Scientists at the Walter Reed Army Institute for Research demonstrated that biomarkers associated with traumatic brain injury were elevated among law enforcement and military personnel, particularly in active duty participants with longer duration of service. Most notably, these elevated biomarker levels were observed in individuals without a diagnosed brain injury or concussion.
Some law enforcement and military personnel are regularly exposed to low levels of blast, particularly during training, due to the use of explosive charges and high caliber weapons. Understanding effects from these occupational exposures is a military health care priority to improve ...
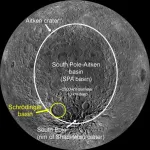
Researchers create new lunar map to help guide future exploration missions
2021-05-04
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. - A new map including rover paths of the Schrodinger basin, a geologically important area of the moon, could guide future exploration missions.The map was created by a team of interns at the Lunar and Planetary Institute, including Ellen Czaplinski, a University of Arkansas graduate student researcher at the Arkansas Center for Planetary Sciences and first author of a paper published in The Planetary Science Journal.
The researchers identified significant geologic features of the Schrödinger basin, located near the lunar south ...
Scientists at NREL report new synapse-like phototransistor
2021-05-04
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) developed a breakthrough in energy-efficient phototransistors. Such devices could eventually help computers process visual information more like the human brain and be used as sensors in things like self-driving vehicles.
The structures rely on a new type of semiconductor--metal-halide perovskites--which have proven to be highly efficient at converting sunlight into electrical energy and shown tremendous promise in a range of other technologies.
"In general, these perovskite semiconductors are a really unique ...
Cheap but desirable: Generic drugs a great alternative to the brand-names for hypertension
2021-05-04
Hypertension is a common medical condition and a primary cause of cardiovascular diseases and stroke worldwide. Unfortunately, as Professor Wei-Li Zhang of the Chinese National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases notes, "the unaffordability of drugs is a major barrier to medication adherence among patients living in low- and middle-income areas."
One of the countries where hypertension is becoming a major problem is China where, researchers estimate, between 244 million and 300 million adults are living with hypertension. But true to Prof. Zhang's words, most cases of hypertension in China are not adequately ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] People with familial longevity show better cognitive agingExhibit better cognitive performance at baseline and show slower decline in processing speed